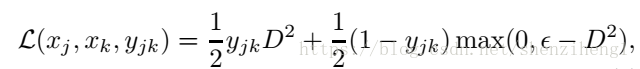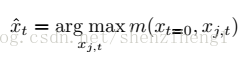Siamese Network (應用篇5) :孿生網路用於跟蹤 CVPR2016
參看論文:Tao R, Gavves E, Smeulders A W, et al. Siamese Instance Search for Tracking[J]. computer vision and pattern recognition, 2016: 1420-1429.
會議水平:CVPR2016
comment:利用孿生網路的匹配能力進行跟蹤,這種思想不難想到。跟蹤的很大的一個分支就是基於目標檢測(匹配)的跟蹤。在以後相當長的一段時間裡,基於孿生網路的跟蹤方案並解決長時間(long-term)問題一定是跟蹤領域的熱點。但相比於DCF及其衍生的CNN-DCF優秀的跟蹤效能,Siamese還有相當長的路要走。一方面,基於匹配的跟蹤何如引入時間場效應(temporal smooth)?如何引入attention機制將是難點。此外,如果想成為一種普適性的方法,很顯然網路不能太複雜太深,否則時效性不好,平衡精度與速度始終是跟蹤領域兩座大山。
1. 摘要 及 目的
作者提出一個和之前頂級跟蹤器都不一樣的新型跟蹤器,沒有模型更新,沒有遮擋檢測,沒有跟蹤器級聯和重檢測,也沒有幾何匹配(就是啥也沒有,完全依賴深度卷積強大的特徵表達能力)。方法就是用學習到的匹配函式進行最佳塊匹配策略。
以DCF為核心的方法征服整個跟蹤領域的途中,偶然出現一篇最佳匹配實現跟蹤確實讓人眼前一亮,但是這也只是停留在最初步階段,更多的是給研究者更多的選擇。本文另外一個亮點應該在重識別上,在一個完整是視訊中,如何解決目標確實後的重識別問題一直是研究的熱點。
作者原文是這樣說的:We focus on learning the matching function suited for application in trackers. Hence, our aim is not to build a fully fledged tracker which might need explicit occlusion detection, model updating, tracker combination, forget mechanisms and other. We rather focus on the matching function alone, similar to the simplicity of the normalized cross-correlation (NCC) tracker .In each frame, the tracker simply finds the candidate patch that matches best to the initial patch of the target in the first frame by the learned matching function.
2. 方法 及 細節
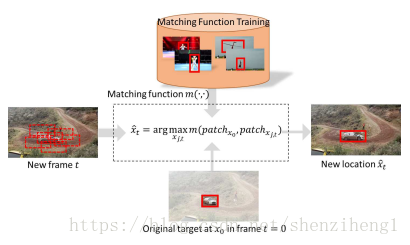
圖1:預訓練好的匹配函式,用於跟蹤例項中的最佳快匹配跟蹤
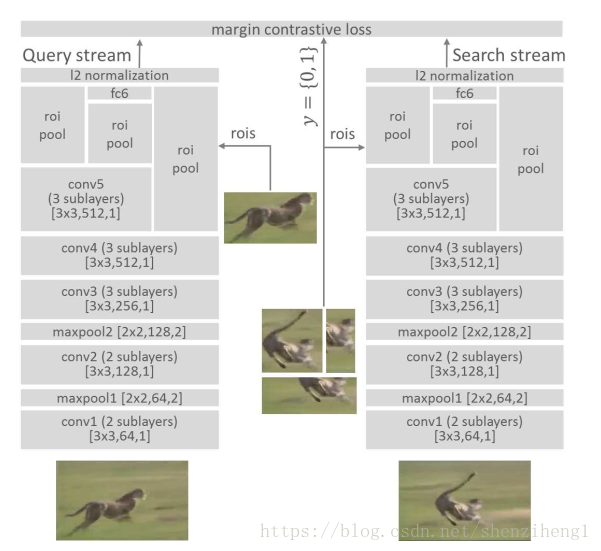
圖2 The proposed Siamese invariance network to learn the generic matching function for tracking. ‘conv’, ‘maxpool’, ‘roipool’ and ‘fc’ stand for convolution, max pooling, region-of-interest pooling and fully connected layers respectively. Numbers in square brackets are kernel size, number of outputs and stride. The fully connected layer has 4096 units. All conv layers are followed by rectified linear units (ReLU)。(這裡沒有翻譯,主要在於作者提到的兩個點。其一,ROI池化;其二,全連線層採用了大量的神經元)
損失函式用的還是hinge loss:
D是指兩個特徵表達的歐氏距離。 訓練採用的還是老方法,一對影象以及他們的標籤。
跟蹤過程:
We propose a simple tracking strategy. As the only reliable data we have for the target object is its location at the first frame, at each frame we compare the sampled candidate boxes with the target object at the first frame. We pass all the candidate boxes from the search stream of our network and pick the candidate box that matches best to the original target:
HighLight候選樣本的採集策略:
We employ the radius sampling strategy. More specifically, around the predicted location of the previous frame we sample locations evenly on circles of different radii。
為了避免候選樣本的窮盡搜尋問題,作者提議採用半徑取樣策略。更確切地說,以前一幀預測中心為基準利用不同半徑進行候選樣本取樣。We use 10 radial and 10 angular divisions
和文獻中不同的是,作者將候選樣本進行多尺度/多解析度處理
Box Refinement 策略:作者訓練四個嶺迴歸分類器,針對矩形框的圓心座標、高度、寬度進行優化。這主要參考了前人的工作,通過迴歸進行矩形窗精修可以大大提高目標定位的準確度。
很奇怪.....作者採用權重衰減為0.001;然而作為對別人孿生網路的精修,作者竟然採用了0.001的初始學習率。
3. 結論 及 反思
comment:這篇文章有毒...作者竟然直接剔除了遮擋的視訊,而且文章中大量的小tricks 和 處理只是給了別人的效果,卻沒有解釋自己實驗中的效益!
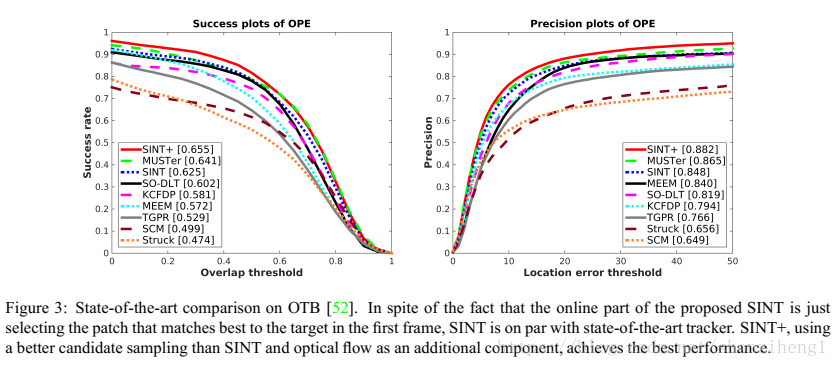
通過後續作者補充提交的失敗案例來看,果不其然,跟蹤效能是真的差啊...
圖4. 兩例跟蹤失敗的情況。左邊:基於最佳匹配原理很難處理空間相似性目標的干擾。因為搜尋空間的等權重的,這裡應該利用餘弦窗函式加以約束,施加位移懲罰。 右邊:最佳匹配跟蹤無法解決遮擋問題,這主要還是因為模型更新沒有做好。在作者的文章中壓根沒有做模型更新。所以該方法應用非常有限。
4.補充材料
4.1 雙流孿生網路鼻祖文章:
J. Bromley, J. W. Bentz, L. Bottou, I. Guyon, Y. LeCun, C. Moore, E. S¨ackinger, and R. Shah. Signature verification using a siamese time delay neural network. International Journal of Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, 7(04):669–688, 1993
4.2 Instance Searching:可以簡單理解為影象檢索與目標定位
R. Tao, A. W. M. Smeulders, and S.-F. Chang. Attributes and categories for generic instance search from one example. In CVPR, 2015. 2, 3
4.3 半徑取樣避免窮盡搜尋
S. Hare, A. Saffari, and P. H. Torr. Struck: Structured output tracking with kernels. In ICCV, 2011
4.4 Box Refinement
P. F. Felzenszwalb, R. B. Girshick, D. McAllester, and D. Ramanan. Object detection with discriminatively trained partbased models. TPAMI, 32(9):1627–1645, 2010.
R. Girshick, J. Donahue, T. Darrell, and J. Malik. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic
segmentation. In CVPR, 2014.