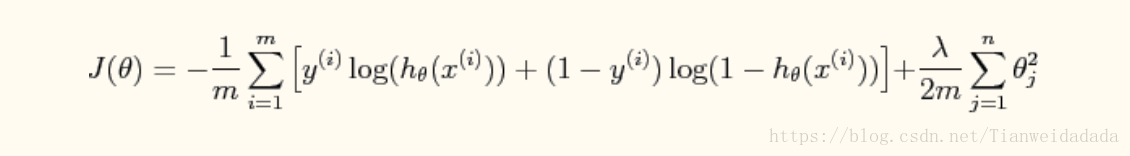機器學習 LogsticRegression 正則化(matlab實現)
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-02-01
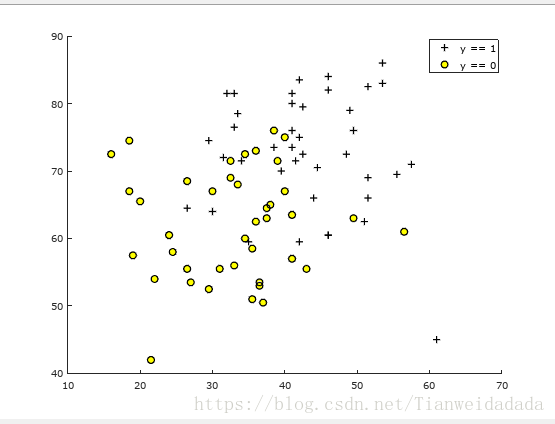
仍然使用之前的根據學生兩學期分數,預測錄取情況
主程式:
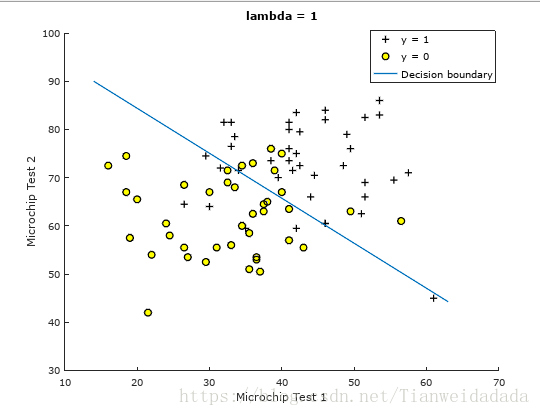
X = load('ex4x.dat'); y = load('ex4y.dat'); plotData(X,y); [m,n] = size(X); X = [ones(m,1),X]; lambda = 1; %[cost,grad] = costFunction(theta,X,y,lambda); %fprintf('Cost at initial theta (zeros): %f\n', cost); init_theta = zeros(n+1,1); options = optimset('GradObj', 'on', 'MaxIter', 400); f = @(t)(costFunction(t, X, y, lambda)); [theta, J, exit_flag] = fminunc(f, init_theta, options); % Plot Boundary plotDecisionBoundary(theta, X, y); hold on; title(sprintf('lambda = %g', lambda)) % Labels and Legend xlabel('Microchip Test 1') ylabel('Microchip Test 2') legend('y = 1', 'y = 0', 'Decision boundary') hold off; % Compute accuracy on our training set p = predict(theta, X); fprintf('Train Accuracy: %f\n', mean(double(p == y)) * 100);
畫原始的兩學期分數分佈圖:
function plotData(X, y) figure; hold on; pos = find(y == 1); neg = find(y == 0); plot(X(pos, 1), X(pos, 2), 'k+', 'LineWidth', 2, 'MarkerSize', 7); plot(X(neg, 1), X(neg, 2), 'ko', 'MarkerFaceColor', 'y', 'MarkerSize', 7); legend('y == 1','y == 0'); hold off; end
代價函式:
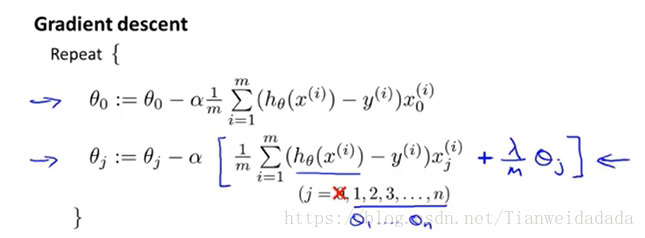
梯度(正則化,theta0不參與正則化):
function [J, grad] = costFunction(theta,X,y,lambda) m = length(y); %grad = zeros(m,1); sig = inline('1./(1+exp(-z))'); grad = zeros(size(theta)); J = 1/m*(sum(-y.*log(sig(X*theta))-(1-y).*log(1-sig(X*theta)))) +lambda/(2*m)*sum(theta(2:size(theta)).^2);%計算代價 for j = 1:size(theta) if j == 1 grad(j) = 1/m*sum((sig(X*theta)-y)'*X(:,j)); else grad(j) = 1/m*sum((sig(X*theta)-y)'*X(:,j)) + lambda/m*theta(j); end end end
畫圖裡麵包含了各種情況(這裡只是用了最簡單的那種):
function plotDecisionBoundary(theta, X, y)
%PLOTDECISIONBOUNDARY Plots the data points X and y into a new figure with
%the decision boundary defined by theta
% PLOTDECISIONBOUNDARY(theta, X,y) plots the data points with + for the
% positive examples and o for the negative examples. X is assumed to be
% a either
% 1) Mx3 matrix, where the first column is an all-ones column for the
% intercept.
% 2) MxN, N>3 matrix, where the first column is all-ones
% Plot Data
plotData(X(:,2:3), y);
hold on
if size(X, 2) <= 3
% Only need 2 points to define a line, so choose two endpoints
plot_x = [min(X(:,2))-2, max(X(:,2))+2];
% Calculate the decision boundary line
plot_y = (-1./theta(3)).*(theta(2).*plot_x + theta(1));
% Plot, and adjust axes for better viewing
plot(plot_x, plot_y)
% Legend, specific for the exercise
legend('Admitted', 'Not admitted', 'Decision Boundary')
axis([10, 70, 30, 100])
else
% Here is the grid range
u = linspace(-1, 1.5, 50);
v = linspace(-1, 1.5, 50);
z = zeros(length(u), length(v));
% Evaluate z = theta*x over the grid
for i = 1:length(u)
for j = 1:length(v)
z(i,j) = mapFeature(u(i), v(j))*theta;
end
end
z = z'; % important to transpose z before calling contour
% Plot z = 0
% Notice you need to specify the range [0, 0]
contour(u, v, z, [0, 0], 'LineWidth', 2)
end
hold off
end預測:
function p = predict(theta, X)
sig = inline('1./(1+exp(-z))');
p = sig(X * theta) >= 0.5;
end