常用資料結構——Map
環境:JDK1.8
HashMap
1、底層為陣列+連結串列(當容量達到8時變為紅黑樹)
2、非執行緒安全;
3、key和value均可為null;
4、初始容量為16;
5、最大容量為MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30=2^30
6、負載因子為0.75,意思是比如我初始容量為16,那麼當鍵值對超過16*0.75=12時就會進行擴容,新容量=舊容量*2;
7、擴容條件:1️⃣元素數量達到閾值;2️⃣HashMap準備樹形化時發現數組長度太短(長度小於MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY=64)
/**
* Replaces all linked nodes in bin at index for given hash unless
* table is too small, in which case resizes instead.
*/ 8、初始容量儘量設定為2的冪次,便於底層進行位移運算,具體解釋點這裡;
9、HashMap容量=initailCapacity*loadFactor;
10、put方法:先根據key的hash值得到這個元素在陣列中的位置(即下標),然後就可以把這個元素放到對應的位置中了。如果這個元素所在的位子上已經存放有其他元素了,那麼在同一個位子上的元素將以連結串列的形式存放,新加入的放在鏈頭,最先加入的放在鏈尾。
11、get方法:首先計算key的hashcode,找到陣列中對應位置的某一元素,然後通過key的equals方法在對應位置的連結串列中找到正確的節點,即能找到需要的元素。
12、獲取value:Object value=map.get(key);
13、獲取key:
// key的集合
Set set=map.keySet() ;
// key value的集合
Set<Map.Entry<String, Object>> entries = map.entrySet();遍歷方式
Iterator<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> entryIterator = map.entrySet().iterator();
while (entryIterator.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<String, Integer> next = entryIterator.next();
System.out.println("key=" + next.getKey() + " value=" + next.getValue());
}Iterator<String> iterator = map.keySet().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
String key = iterator.next();
System.out.println("key=" + key + " value=" + map.get(key));
}map.forEach((key,value)->{
System.out.println("key=" + key + " value=" + value);
});建議使用第一種EntrySet遍歷方式
第一種可以把key和value同時取出來;
第二種要先取出key,再去取value,效率較低;
第三種是JDK1.8及以上,通過外層遍歷table,內層遍歷連結串列或紅黑樹
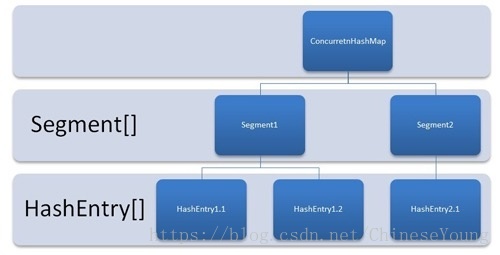
ConcurrentHashMap
1、ConcurrentHashMap採用了分段鎖技術,其中Segment繼承於 ReentrantLock;
原始碼如下:
/**
* Stripped-down version of helper class used in previous version,
* declared for the sake of serialization compatibility
*/
static class Segment<K,V> extends ReentrantLock implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 2249069246763182397L;
final float loadFactor;
Segment(float lf) { this.loadFactor = lf; }
}2、get方法,ConcurrentHashMap 的 get 方法是非常高效的,因為整個過程都不需要加鎖。
只需要將 Key 通過 Hash 之後定位到具體的 Segment ,再通過一次 Hash 定位到具體的元素上。由於 Node中的 value 屬性是用 volatile 關鍵詞修飾的,保證了記憶體可見性,所以每次獲取時都是最新值
/**
* Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped,
* or {@code null} if this map contains no mapping for the key.
*
* <p>More formally, if this map contains a mapping from a key
* {@code k} to a value {@code v} such that {@code key.equals(k)},
* then this method returns {@code v}; otherwise it returns
* {@code null}. (There can be at most one such mapping.)
*
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified key is null
*/
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> e, p; int n, eh; K ek;
int h = spread(key.hashCode());
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(e = tabAt(tab, (n - 1) & h)) != null) {
if ((eh = e.hash) == h) {
if ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))
return e.val;
}
else if (eh < 0)
return (p = e.find(h, key)) != null ? p.val : null;
while ((e = e.next) != null) {
if (e.hash == h &&
((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek))))
return e.val;
}
}
return null;
}3、put方法:
雖然 Node中的 value 是用 volatile 關鍵詞修飾的,但是並不能保證併發的原子性,所以 put 操作時仍然需要加鎖處理。
首先也是通過 Key 的 Hash 定位到具體的 Segment,在 put 之前會進行一次擴容校驗。這裡比 HashMap 要好的一點是:HashMap 是插入元素之後再看是否需要擴容,有可能擴容之後後續就沒有插入就浪費了本次擴容(擴容非常消耗效能)。
而 ConcurrentHashMap 不一樣,它是先將資料插入之後再檢查是否需要擴容,之後再做插入。
/**
* Key-value entry. This class is never exported out as a
* user-mutable Map.Entry (i.e., one supporting setValue; see
* MapEntry below), but can be used for read-only traversals used
* in bulk tasks. Subclasses of Node with a negative hash field
* are special, and contain null keys and values (but are never
* exported). Otherwise, keys and vals are never null.
*/
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final int hash;
final K key;
volatile V val;
volatile Node<K,V> next;
Node(int hash, K key, V val, Node<K,V> next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(key, value, false);
}
/** Implementation for put and putIfAbsent */
final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException();
int hash = spread(key.hashCode());
int binCount = 0;
for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) {
Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh;
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
tab = initTable();
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) {
if (casTabAt(tab, i, null,
new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null)))
break; // no lock when adding to empty bin
}
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
tab = helpTransfer(tab, f);
else {
V oldVal = null;
synchronized (f) { //此處加鎖
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
if (fh >= 0) {
binCount = 1;
for (Node<K,V> e = f;; ++binCount) {
K ek;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((ek = e.key) == key ||
(ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {
oldVal = e.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
e.val = value;
break;
}
Node<K,V> pred = e;
if ((e = e.next) == null) {
pred.next = new Node<K,V>(hash, key,
value, null);
break;
}
}
}
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
Node<K,V> p;
binCount = 2;
if ((p = ((TreeBin<K,V>)f).putTreeVal(hash, key,
value)) != null) {
oldVal = p.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
p.val = value;
}
}
}
}
if (binCount != 0) {
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
treeifyBin(tab, i);
if (oldVal != null)
return oldVal;
break;
}
}
}
addCount(1L, binCount);
return null;
}