leetcode--二叉樹和圖
基礎知識
二叉樹的資料結構
struct TreeNode{
int val; //資料域
TreeNode *left //左右指標
TreeNode *right
TreeNode(int x):val(x),left(NULL),right(NULL){}
//建構函式
}構造二叉樹
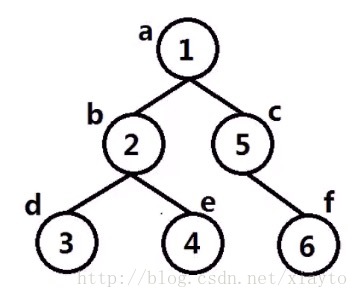
構造如下的一棵二叉樹:
int main(){
TreeNode a(1);
TreeNode b(2);
TreeNode c(3);
TreeNode d(4);
TreeNode e(5);
TreeNode f(6 二叉樹的深度遍歷
前序遍歷訪問
traversal(node->left)
中序遍歷訪問
traversal(node->right)
後序遍歷訪問
前中後指的是訪問根節點的順序,前序:先根再左再右
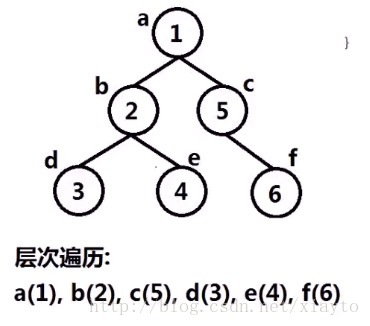
二叉樹的層次遍歷
也就是廣度優先搜尋,用佇列一層一層的訪問節點,訪問一個節點壓入該節點的孩子節點,佇列不空,持續該過程。
void BFS_print(TreeNode* root){
queue leetcode題目
113 Path Sum
題意:
給定一個二叉樹與整數sum,找出所有從根節點到葉節點的路徑,要求這些路徑上節點值的和等於sum。
解題思路:
用深度優先搜尋路徑。
1 先序遍歷時將節點值儲存到path棧中,path_value累加節點值
2 當遍歷到葉節點時判斷path_value是不是等於sum,if等於push進result中。
3 在後序遍歷時,將節點從path棧中彈出,path_value減去節點值
程式碼:
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int sum) {
vector<vector<int>> result;
vector<int> path;
int path_value=0;
preorder(root,path_value,sum,path,result);
return result;
}
private:
void preorder(TreeNode *node,int &path_value,int sum,vector<int> &path,vector<vector<int>> &result){
//先序遍歷內容:
if(!node){
return;
}
path_value=path_value+node->val;
path.push_back(node->val);
if(!node->left&&!node->right&&path_value==sum){
result.push_back(path);
}
preorder(node->left,path_value,sum,path,result);
preorder(node->right,path_value,sum,path,result);
//後序遍歷內容:
path.pop_back();
path_value=path_value-node->val;
}
};236 Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree
題意:
給出兩個節點,求出他們最近的公共祖先。
解題思路:
1 用深度優先搜尋找點,找到點後儲存路徑。
2 同時遍歷兩個路徑,找最後一個相同點。
程式碼:
void preorder(TreeNode* node,
TreeNode *search,
std::vector<TreeNode*> &path,
std::vector<TreeNode*> &result,
int &finish){
if (!node || finish){
return; //結束技巧,finish用於標記已找到節點
}
path.push_back(node);
if (node == search){
finish = 1;
result = path;
}
preorder(node->left, search, path, result, finish);
preorder(node->right, search, path, result, finish);
path.pop_back();//後序遍歷時根節點要做退出操作,就是左右節點都不是要找的點,根節點彈出
}
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
std::vector<TreeNode*> path;
std::vector<TreeNode*> node_p_path;
std::vector<TreeNode*> node_q_path;
int finish = 0;
preorder(root, p, path, node_p_path, finish);//找p點的路徑並保存於node_p_path
path.clear();
finish = 0;
preorder(root, q, path, node_q_path, finish);//找q點的路徑並保存於node_q_path
int path_len = 0;
if (node_p_path.size() < node_q_path.size()){
path_len = node_p_path.size();
}
else{
path_len = node_q_path.size();
}
TreeNode *result = 0;
//找兩個路徑中最後一個相同點
for (int i = 0; i < path_len; i++){
if (node_p_path[i] == node_q_path[i]){
result = node_p_path[i];//少寫一點程式碼
}
}
return result;
}
};114. Flatten Binary Tree to Linked List
題意:
不用大的額外空間,將二叉樹轉換為連結串列,left為null,right為連結串列的next指標。連結串列的順序是樹的先序遍歷。
解題思路:
如果不考慮大的額外空間,最簡單的做法是用一個vector存先序遍歷的結果,然後遍歷這個vector。
程式碼:
class Solution {
public:
void flatten(TreeNode *root) {
std::vector<TreeNode *> node_vec;
preorder(root, node_vec);
for (int i = 1; i < node_vec.size(); i++){
node_vec[i-1]->left = NULL;
node_vec[i-1]->right = node_vec[i];
}
}
private:
void preorder(TreeNode *node,vector<TreeNode *> &node_vec){
if (!node){
return;
}
node_vec.push_back(node);
preorder(node->left, node_vec);
preorder(node->right, node_vec);
}
};解題思路2:
思考過程是:獨立開樹的一部分,思考前中後遍歷時候應該做什麼。考慮輸入和輸出:
* 先序遍歷:第一次訪問根節點時,我們要保留左右節點,讓right指標指向左節點。右指標指向NULL。
* 中序遍歷:第二次訪問根節點,這時左子樹完成了連結串列變形,要將左子樹的最後節點指向,右子樹的開始節點。所以要輸出一個末尾節點,可以用&引用去維護。
* 後續遍歷:維護最末的節點。
程式碼:
class Solution {
public:
void flatten(TreeNode* root) {
TreeNode *last=NULL;
preorder(root,last);
}
private:
void preorder(TreeNode* node,TreeNode* &last){
//*& TreeNode*的意思是傳入TreeNode的指標變數,&是可以在函式中改變這個變數
if(!node){
return;
}
if(!node->left&&!node->right){
last=node;
return;
}
TreeNode* left=node->left; //保留左右節點
TreeNode* right=node->right;
TreeNode* left_last=NULL;//初始化要維護的末尾節點。
TreeNode* right_last=NULL;
if(left){
preorder(left,left_last);//遞迴,維護左子樹的末尾節點
node->left=NULL; //放在中序遍歷執行時因為可以省去判斷是否有左子樹的語句。
node->right=left;
last=left_last;
}
if(right){
preorder(right,right_last);
if(left_last){
left_last->right=right;//讓左子樹的末尾節點指向右子樹的開始節點。放在後序遍歷執行可以省去判斷是否有右子樹的語句。
}
last=right_last;//維護右子樹的末尾節點
}
}
};199.Binary Tree Right Side View
題意:
從右邊觀察二叉樹,輸出每一層最右邊的節點。
解題思路:
層次遍歷二叉樹,將節點和層數繫結微pair,壓入佇列時,將節點和層數同時壓入,記錄每一層的最後一個節點。
程式碼:
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> rightSideView(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> view; //儲存每層最後的節點。
queue<pair<TreeNode*,int>> Q;
//廣度優先搜尋,用一個pair儲存節點和它對應的層數。
if(root){
Q.push(make_pair(root,0));
}
while(!Q.empty()){
TreeNode* node=Q.front().first;
int depth=Q.front().second;
Q.pop();
if(view.size()==depth){
view.push_back(node->val); //當出現新的層時壓入一個節點。
}
else{
view[depth]=node->val;
}
if(node->left){
Q.push(make_pair(node->left,depth+1)); //壓入左節點,標記為下一層
}
if(node->right){
Q.push(make_pair(node->right,depth+1)); //壓入右節點,標記為下一層
}
}
return view;
}
};圖
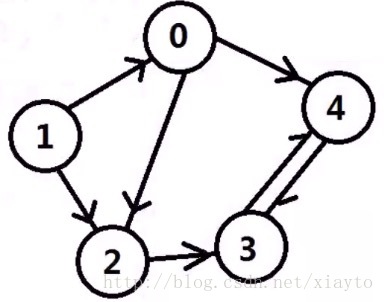
圖的表示(鄰接矩陣):
程式碼:
int main(){
const int MAX_N = 5;
int Graph[MAX_N][MAX_N] = {0};
Graph[0][2] = 1;
Graph[0][4] = 1;
Graph[1][0] = 1;
Graph[1][2] = 1;
Graph[2][3] = 1;
Graph[3][4] = 1;
Graph[4][3] = 1;
printf("Graph:\n");
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_N; i++){
for (int j = 0; j < MAX_N; j++){
printf("%d ", Graph[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}表示稠密圖作用比較大,但是表示稀疏圖一般用鄰接表。
圖的表示(鄰接表):
程式碼:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <vector>
struct GraphNode{
int label;
std::vector<GraphNode *> neighbors;
GraphNode(int x) : label(x) {};
};
int main(){
const int MAX_N = 5;
GraphNode *Graph[MAX_N];
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_N; i++){
Graph[i] = new GraphNode(i);
}
Graph[0]->neighbors.push_back(Graph[2]);
Graph[0]->neighbors.push_back(Graph[4]);
Graph[1]->neighbors.push_back(Graph[0]);
Graph[1]->neighbors.push_back(Graph[2]);
Graph[2]->neighbors.push_back(Graph[3]);
Graph[3]->neighbors.push_back(Graph[4]);
Graph[4]->neighbors.push_back(Graph[3]);
printf("Graph:\n");
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_N; i++){
printf("Label(%d) : ", i);
for (int j = 0; j < Graph[i]->neighbors.size(); j++){
printf("%d ", Graph[i]->neighbors[j]->label);
}
printf("\n");
}
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_N; i++){
delete Graph[i];
}
return 0;
}深度優先搜尋
struct GraphNode{
int label;
std::vector<GraphNode *> neighbors;
GraphNode(int x) : label(x) {};
};
void DFS_graph(GraphNode *node, int visit[]){
visit[node->label] = 1;
printf("%d ", node->label);
for (int i = 0; i < node->neighbors.size(); i++){
if (visit[node->neighbors[i]->label] == 0){
DFS_graph(node->neighbors[i], visit);
}
}
} 廣度優先搜尋
struct GraphNode{
int label;
std::vector<GraphNode *> neighbors;
GraphNode(int x) : label(x) {};
};
void BFS_graph(GraphNode *node, int visit[]){
std::queue<GraphNode *> Q;
Q.push(node);
visit[node->label] = 1;
while(!Q.empty()){
GraphNode *node = Q.front();
Q.pop();
printf("%d ", node->label);
for (int i = 0; i < node->neighbors.size(); i++){
if (visit[node->neighbors[i]->label] == 0){
Q.push(node->neighbors[i]);
visit[node->neighbors[i]->label] = 1;
}
}
}
}leetcode題目
207. Course Schedule
題意:給出課程之間的依賴關係,求是否可以將所有的課程全部完成。其實就是求有向圖是否有環。
解題思路一:
- 用深度優先搜尋,如果遞迴搜尋某一條路徑時發現路徑中有重複的節點,則有環,不能完成。
- 這裡的visit的陣列要設計三種狀態:-1是未被搜尋,0是正在被搜尋的路徑上,1是已經完成搜尋的節點。
- 像遞迴二叉樹思考方式一樣,思考先序中序後序遍歷要進行什麼操作:
- 先序遍歷:將該節點標記狀態visit為0
- 中序遍歷:如果訪問過程中出現訪問到visit為0的點則返回false
- 後續遍歷:訪問完成將該節點標記狀態visit為-1
程式碼:
struct GraphNode{
int label;
std::vector<GraphNode *> neighbors;
GraphNode(int x) : label(x) {};
};
bool DFS_graph(GraphNode *node, std::vector<int> &visit){
visit[node->label] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < node->neighbors.size(); i++){
if (visit[node->neighbors[i]->label] == -1){
if (DFS_graph(node->neighbors[i], visit) == 0){
return false;
}
}
else if (visit[node->neighbors[i]->label] == 0){
return false;
}
}
visit[node->label] = 1;
return true;
}
class Solution {
public:
bool canFinish(int numCourses,
std::vector<std::pair<int, int> >& prerequisites) {
std::vector<GraphNode*> graph;
std::vector<int> visit;
for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++){
graph.push_back(new GraphNode(i));
visit.push_back(-1);
}
for (int i = 0; i < prerequisites.size(); i++){
GraphNode *begin = graph[prerequisites[i].second];
GraphNode *end = graph[prerequisites[i].first];
begin->neighbors.push_back(end);
}
for (int i = 0; i < graph.size(); i++){
if (visit[i] == -1 && !DFS_graph(graph[i], visit)){
return false;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++){
delete graph[i];
}
return true;
}
};解題思路二:
用廣度優先搜尋,用入度的概念,每次只將入度為0的點壓入佇列,它指向的所有節點的入度都-1,-1後入度為0的點可以壓入佇列,如果能遍歷整個圖,則可以完成,不能遍歷則不能完成。
程式碼:
struct GraphNode{
int label;
std::vector<GraphNode *> neighbors;
GraphNode(int x) : label(x) {};
};
class Solution {
public:
bool canFinish(int numCourses,
std::vector<std::pair<int, int> >& prerequisites) {
std::vector<GraphNode*> graph;
std::vector<int> degree;
for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++){
degree.push_back(0);
graph.push_back(new GraphNode(i));
}
for (int i = 0; i < prerequisites.size(); i++){
GraphNode *begin = graph[prerequisites[i].second];
GraphNode *end = graph[prerequisites[i].first];
begin->neighbors.push_back(end);
degree[prerequisites[i].first]++;
}
std::queue<GraphNode *> Q;
for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++){
if (degree[i] == 0){
Q.push(graph[i]);
}
}
while(!Q.empty()){
GraphNode *node = Q.front();
Q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < node->neighbors.size(); i++){
degree[node->neighbors[i]->label]--;
if (degree[node->neighbors[i]->label] == 0){
Q.push(node->neighbors[i]);
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < graph.size(); i++){
delete graph[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < degree.size(); i++){
if (degree[i]){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
};