Softmax迴歸C++實現
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-02-04
前言
Softmax迴歸模型的理論知識上一篇博文已經介紹。C++程式碼來源於一個開源專案,連結地址我忘了 ,哪天找到了再附上。對原始碼改動不大,只是進行了一些擴充。
,哪天找到了再附上。對原始碼改動不大,只是進行了一些擴充。
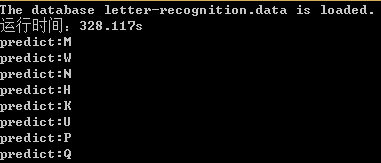 程式中用了前1w個樣本來訓練分類器,整個訓練過程花了328.117s。為了加快程式的執行速度,決定使用OpenMP來加速for迴圈。
在Visual Studio裡面使用OpenMP很簡單。
點選專案-->屬性,進入屬性頁。在c/c++下面的Language中開啟Open MP Support即可。
程式中用了前1w個樣本來訓練分類器,整個訓練過程花了328.117s。為了加快程式的執行速度,決定使用OpenMP來加速for迴圈。
在Visual Studio裡面使用OpenMP很簡單。
點選專案-->屬性,進入屬性頁。在c/c++下面的Language中開啟Open MP Support即可。
 修改過後的train函式:
修改過後的train函式:
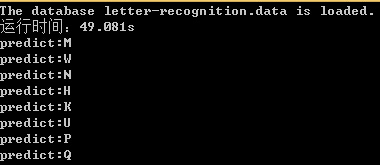 訓練時間從之前的328.117s較少到49.081s,提升了6.68倍。
訓練時間從之前的328.117s較少到49.081s,提升了6.68倍。
從測試結果來看,分類器把R預測成了K,把X預測成了U。本文沒有對分類器的準確率進行嚴格的測試,有興趣的同學可以自己去測一下。
 ,哪天找到了再附上。對原始碼改動不大,只是進行了一些擴充。
,哪天找到了再附上。對原始碼改動不大,只是進行了一些擴充。
實驗環境
Visual Studio 2013
資料
裡面共有20000個樣本,每個樣本16維。
實驗目的
完成對資料集中字元樣本的分類。
實驗程式碼
1.定義一個LogisticRegression的類:
標頭檔案 LogisticRegression.h
#include <iostream> #include <math.h> #include<algorithm> #include <functional> #include <string> #include <cassert> #include <vector> using namespace std; class LogisticRegression { public: LogisticRegression(int inputSize, int k, int dataSize, int num_iters,double learningRate); ~LogisticRegression(); bool loadData(const string& filename);//載入資料 void train();//訓練函式 void softmax(double* thetaX);//得到樣本對應的屬於某個類別的概率 double predict(double* x);//預測函式 double** getX(); double** getY(); void printX(); void printY(); void printTheta(); private: int inputSize;//輸入特徵數,不包括bias項 int k;//類別數 int dataSize;//樣本數 int num_iters;//迭代次數 double **theta;//學習得到的權值引數 double alpha;//學習速率 double** x;//訓練資料集 double** y;//訓練資料集對應的標號 };
實現檔案 LogisticRegression.cpp
2.程式碼測試:#include "LogisticRegression.h" LogisticRegression::LogisticRegression(int in, int out,int size, int num_iters,double learningRate) { inputSize = in; k = out; alpha = learningRate; dataSize = size; this->num_iters = num_iters; // initialize theta theta = new double*[k]; for (int i = 0; i<k; i++) theta[i] = new double[inputSize]; for (int i = 0; i<k; i++) { for (int j = 0; j<inputSize; j++) { theta[i][j] = 0; } } //initialize x x = new double*[dataSize]; for (int i = 0; i<dataSize; i++) x[i] = new double[inputSize]; for (int i = 0; i<dataSize; i++) { for (int j = 0; j<inputSize; j++) { x[i][j] = 0; } } //initialize y y = new double*[dataSize]; for (int i = 0; i<dataSize; i++) y[i] = new double[k]; for (int i = 0; i<dataSize; i++) { for (int j = 0; j<k; j++) { y[i][j] = 0; } } } LogisticRegression::~LogisticRegression() { for (int i = 0; i<k; i++) delete[] theta[i]; delete[] theta; for (int i = 0; i < dataSize; i++) { delete[] x[i]; delete[] y[i]; } delete[] x; delete[] y; } void LogisticRegression::train() { for (int n = 0; n < num_iters; n++) { for (int s = 0; s < dataSize; s++) { double *py_x = new double[k]; double *dy = new double[k]; //1.求出theta*x for (int i = 0; i<k; i++) { py_x[i] = 0; for (int j = 0; j<inputSize; j++) { py_x[i] += theta[i][j] * x[s][j]; } } //2.求出概率 softmax(py_x); for (int i = 0; i<k; i++) { dy[i] = y[s][i] - py_x[i];//真實值與預測值的差異 for (int j = 0; j<inputSize; j++) { theta[i][j] += alpha * dy[i] * x[s][j] / dataSize; } } delete[] py_x; delete[] dy; } } } void LogisticRegression::softmax(double *x) { double max = 0.0; double sum = 0.0; for (int i = 0; i<k; i++) if (max < x[i]) max = x[i]; for (int i = 0; i<k; i++) { x[i] = exp(x[i] - max); sum += x[i]; } for (int i = 0; i<k; i++) x[i] /= sum; } double LogisticRegression::predict(double *x) { double clsLabel; double* predictY = new double[k]; for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) { predictY[i] = 0; for (int j = 0; j < inputSize; j++) { predictY[i] += theta[i][j] * x[j]; } } softmax(predictY); double max = 0; for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) { if (predictY[i]>max) { clsLabel = i; max = predictY[i]; } } return clsLabel; } double** LogisticRegression::getX() { return x; } double** LogisticRegression::getY() { return y; } bool LogisticRegression::loadData (const string& filename) { const int M = 1024; char buf[M + 2]; int i; vector<int> responses; FILE* f = fopen(filename.c_str(), "rt"); if (!f) { cout << "Could not read the database " << filename << endl; return false; } int rowIndex = 0; for (;;) { char* ptr; if (!fgets(buf, M, f) || !strchr(buf, ','))// char *strchr(const char *s,char c):查詢字串s中首次出現字元c的位置 break; y[rowIndex][buf[0] - 'A'] = 1; ptr = buf + 2; for (i = 0; i < inputSize; i++) { int n = 0;//存放sscanf當前已讀取了的總字元數 int m = 0; sscanf(ptr, "%d%n", &m, &n);//sscanf() - 從一個字串中讀進與指定格式相符的資料 x[rowIndex][i] = m; ptr += n + 1; } rowIndex++; if (rowIndex >= dataSize) break; if (i < inputSize) break; } fclose(f); cout << "The database " << filename << " is loaded.\n"; return true; } void LogisticRegression::printX() { for (int i = 0; i<dataSize; i++) { for (int j = 0; j<inputSize; j++) { cout << x[i][j] << " "; } cout << endl; } } void LogisticRegression::printY() { for (int i = 0; i<dataSize; i++) { for (int j = 0; j<k; j++) { cout << y[i][j] << " "; } cout << endl; } } void LogisticRegression::printTheta() { for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < inputSize; j++) { cout << theta[i][j] << " "; } cout << endl; } }
#include "LogisticRegression.h" void letter_recog() { double learning_rate = 0.1; int num_iters = 500;//迭代次數 int train_N =10000;//訓練樣本個數 int test_N = 8;//測試樣本個數 int n_in = 16;//輸入特徵維數 int n_out = 26;//類別數 LogisticRegression classifier(n_in, n_out, train_N, num_iters, learning_rate); classifier.loadData("letter-recognition.data"); //訓練 classifier.train(); // test data double test_X[8][16] = { { 5, 10, 6, 8, 4, 7, 7, 12, 2, 7, 9, 8, 9, 6, 0, 8 },//M { 6, 12, 7, 6, 5, 8, 8, 3, 3, 6, 9, 7, 10, 10, 3, 6 },//W { 3, 8, 4, 6, 4, 7, 7, 12, 1, 6, 6, 8, 5, 8, 0, 8 },//N { 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 7, 8, 10, 1, 7, 5, 8, 2, 8, 0, 8 },//H { 3, 6, 5, 5, 6, 6, 8, 3, 3, 6, 5, 9, 6, 7, 5, 9 },//R { 7, 11, 11, 8, 7, 4, 8, 2, 9, 10, 11, 9, 5, 8, 5, 4 }, //X { 6, 9, 6, 4, 4, 8, 9, 5, 3, 10, 5, 5, 5, 10, 5, 6 },//P { 4, 7, 6, 5, 5, 8, 5, 7, 4, 6, 7, 9, 3, 7, 6, 9 }//Q }; // test for (int i = 0; i<test_N; i++) { double predict = classifier.predict(test_X[i]); char char_predict = 'A' + predict; cout << "predict:" << char_predict << endl; } } int main() { letter_recog(); getchar(); return 0;
輸出結果:
 程式中用了前1w個樣本來訓練分類器,整個訓練過程花了328.117s。為了加快程式的執行速度,決定使用OpenMP來加速for迴圈。
在Visual Studio裡面使用OpenMP很簡單。
點選專案-->屬性,進入屬性頁。在c/c++下面的Language中開啟Open MP Support即可。
程式中用了前1w個樣本來訓練分類器,整個訓練過程花了328.117s。為了加快程式的執行速度,決定使用OpenMP來加速for迴圈。
在Visual Studio裡面使用OpenMP很簡單。
點選專案-->屬性,進入屬性頁。在c/c++下面的Language中開啟Open MP Support即可。
 修改過後的train函式:
修改過後的train函式:
void LogisticRegression::train() {
for (int n = 0; n < num_iters; n++)
{
#pragma omp parallel for
for (int s = 0; s < dataSize; s++)
{
double *py_x = new double[k];
double *dy = new double[k];
//1.求出theta*x
for (int i = 0; i<k; i++) {
py_x[i] = 0;
for (int j = 0; j<inputSize; j++) {
py_x[i] += theta[i][j] * x[s][j];
}
}
//2.求出概率
softmax(py_x);
#pragma omp parallel for
for (int i = 0; i<k; i++) {
dy[i] = y[s][i] - py_x[i];//真實值與預測值的差異
for (int j = 0; j<inputSize; j++) {
theta[i][j] += alpha * dy[i] * x[s][j] / dataSize; //- lambda*theta[i][j];
}
}
delete[] py_x;
delete[] dy;
}
}
}void LogisticRegression::softmax(double *x) {
double max = 0.0;
double sum = 0.0;
for (int i = 0; i<k; i++) if (max < x[i]) max = x[i];
#pragma omp parallel for
for (int i = 0; i<k; i++) {
x[i] = exp(x[i] - max);//防止資料溢位
sum += x[i];
}
#pragma omp parallel for
for (int i = 0; i<k; i++) x[i] /= sum;
} 訓練時間從之前的328.117s較少到49.081s,提升了6.68倍。
訓練時間從之前的328.117s較少到49.081s,提升了6.68倍。從測試結果來看,分類器把R預測成了K,把X預測成了U。本文沒有對分類器的準確率進行嚴格的測試,有興趣的同學可以自己去測一下。
