最小生成樹及其基本實現
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-02-05
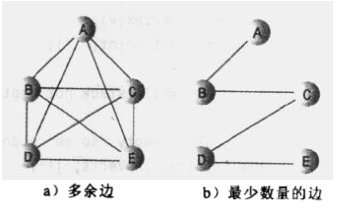
最小生成樹(MST Minimum Spanning Tree):用最少的邊連線了所有的頂點。
最小生成樹邊的數量總比頂點V的數量小1.
即 E = V -1;
建立最小生成樹的演算法與搜尋演算法幾乎是相同的。它同樣可以基於廣度優先搜尋或者深度優先搜尋,本例使用深度優先搜尋。
在執行深度優先搜尋的過程中,記錄走過的邊,就可以建立一棵最小生成樹。最下生成樹演算法與前面的深度優先搜尋之間唯一的區別是mst()方法必須記錄走過的邊。
——————————
最小生成樹完整程式碼:
class StackX
{
private final int SIZE = 20