opencv從零開始——4. 離散傅立葉變換的體驗
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-02-05
opencv的強大之處,從這裡開始,越來越能和訊號處理接軌了,贊一個。
程式碼:
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp> #include <opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp> #include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp> #include <iostream> using namespace std; using namespace cv; // "/mnt/hgfs/code_for_Linux/code_opencv/test1/pic/" int main() { Mat srcImage = imread("/mnt/hgfs/code_for_Linux/code_opencv/test1/pic/3.jpg", 0); if (!srcImage.data) { return -1; } imshow("[灰度圖]", srcImage); int m = getOptimalDFTSize(srcImage.rows); int n = getOptimalDFTSize(srcImage.cols); Mat padded; copyMakeBorder(srcImage, padded, 0, m - srcImage.rows, 0, n - srcImage.cols, BORDER_CONSTANT, Scalar::all(0)); Mat planes[] = {Mat_<float>(padded), Mat::zeros(padded.size(), CV_32F)}; Mat complexI; merge(planes, 2, complexI); dft(complexI, complexI); split(complexI, planes); magnitude(planes[0], planes[1], planes[0]); Mat magnitudeImage = planes[0]; magnitudeImage += Scalar::all(1); log(magnitudeImage, magnitudeImage); magnitudeImage = magnitudeImage(Rect(0, 0, magnitudeImage.cols & - 2, magnitudeImage.rows & - 2)); int cx = magnitudeImage.cols/2; int cy = magnitudeImage.rows/2; Mat q0(magnitudeImage, Rect(0, 0, cx, cy)); Mat q1(magnitudeImage, Rect(cx, 0, cx, cy)); Mat q2(magnitudeImage, Rect(0, cy, cx, cy)); Mat q3(magnitudeImage, Rect(cx, cy, cx, cy)); Mat tmp; q0.copyTo(tmp); q3.copyTo(q0); tmp.copyTo(q3); q1.copyTo(tmp); q2.copyTo(q1); tmp.copyTo(q2); normalize(magnitudeImage, magnitudeImage, 0, 1, NORM_MINMAX); imshow("頻譜幅值", magnitudeImage); waitKey(0); return 0; }
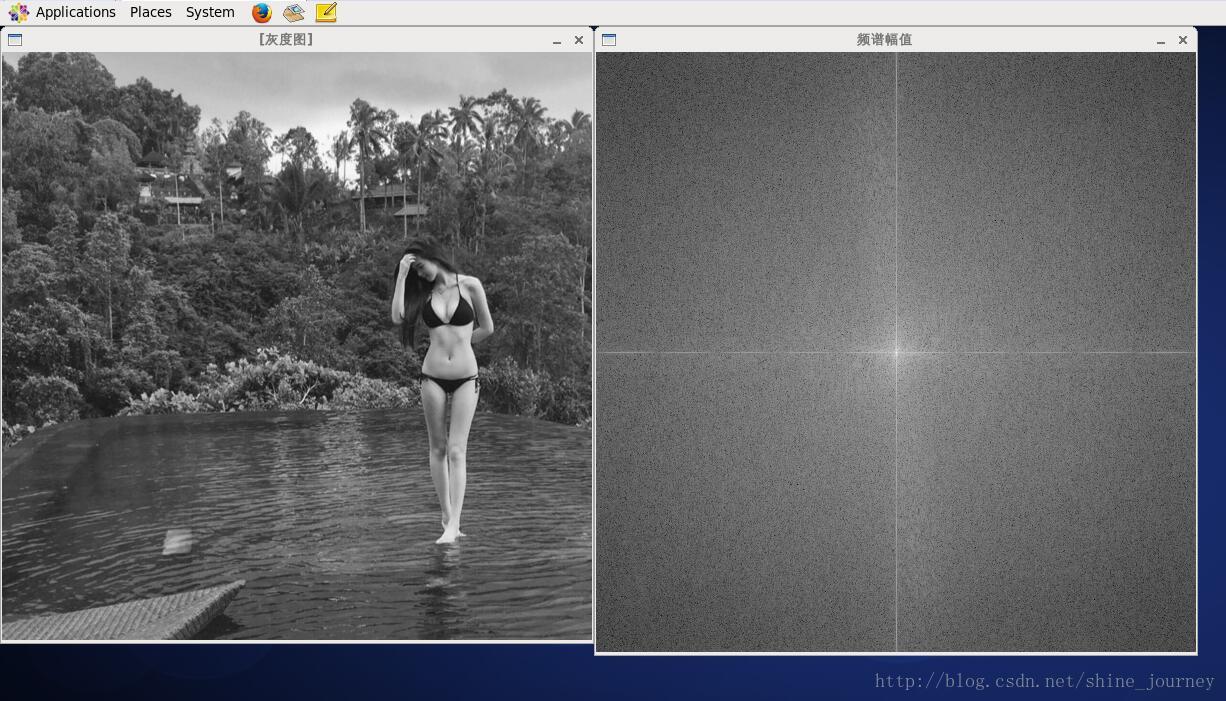
效果如下:
------