k-近鄰演算法用於實際應用
摘要:
本章所有內容資料均來自《機器學習實戰》的資料,是對K近鄰演算法的應用以及熟練
例項1改進約會網站的配對效果
題目描述:海倫喜歡在線上約會網站尋找適合自己的物件,但是她不是喜歡每一個人。她發現交往過三種類型的人:
1.不喜歡的人
2.魅力一般的人
3.極具魅力的人
所以需要對網站的物件歸入恰當的分類。她週一到週五喜歡魅力一般的人,而週末則更喜歡極具魅力的人。所以需要根據資料來分類
準備資料:
資料在文字datingTestSet.txt中,每個樣本佔據一行,總共1000行,每個樣本有3個特徵:
每年獲得的飛行常客里程數
玩視訊遊戲所消耗的時間
每週消費的冰淇淋的公升
那麼這些資料從文字讀取後需要改寫成分類器可以接受的格式。輸出為樣本矩陣和類標籤向量
def file2matrix(filename): fr = open(filename) arrayOlines = fr.readlines() numberOfLines = len(arrayOlines) returnMat = zeros((numberOfLines,3)) classLabelVector=[] index = 0 for line in arrayOLines: line = line.strip() #去回車 listFromLine = line.split('\t') #以\t分割 returnMat[index,:] = listFromLine[0:3] classLabelVector.append(int(listFromLine[-1])) index+=1 return returnMat,classLabelVector
其實python處理文字檔案很容易。
reload(kNN)
datingDataMat,datingLabels = kNN.file2matrix('datingTestSet2.txt')
>>> datingDataMat
array([[ 4.09200000e+04, 8.32697600e+00, 9.53952000e-01],
[ 1.44880000e+04, 7.15346900e+00, 1.67390400e+00],
[ 2.60520000e+04, 1.44187100e+00, 8.05124000e-01],
...,
[ 2.65750000e+04, 1.06501020e+01, 8.66627000e-01],
[ 4.81110000e+04, 9.13452800e+00, 7.28045000e-01],
[ 4.37570000e+04, 7.88260100e+00, 1.33244600e+00]])
接下來需要分析資料,使用Matplotlib建立散點圖
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
>>> fig = plt.figure()
>>> ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
>>> ax.scatter(datingDataMat[:,1],datingDataMat[:,2]) #顏色以及尺寸標識了資料點屬性類別
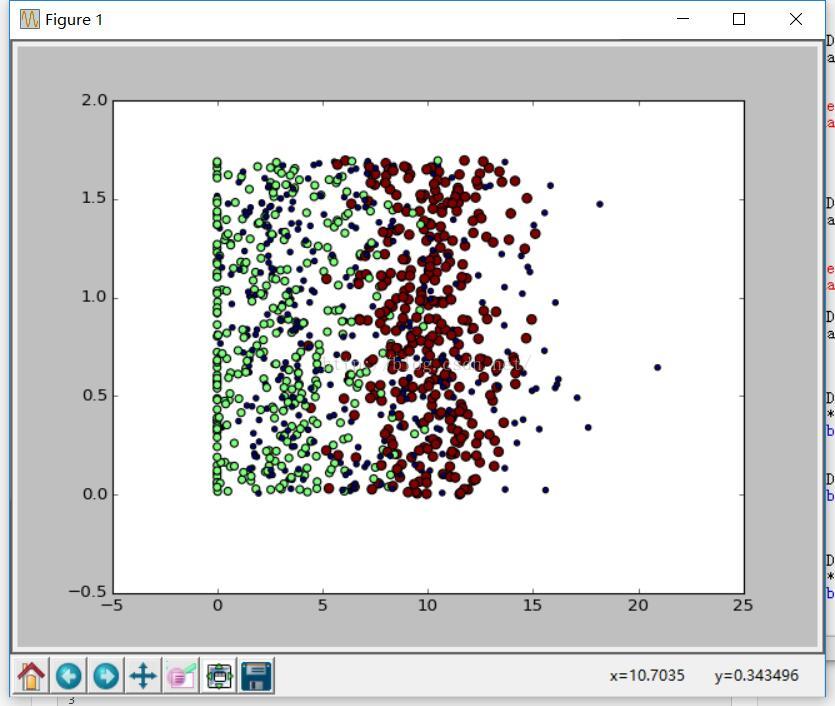
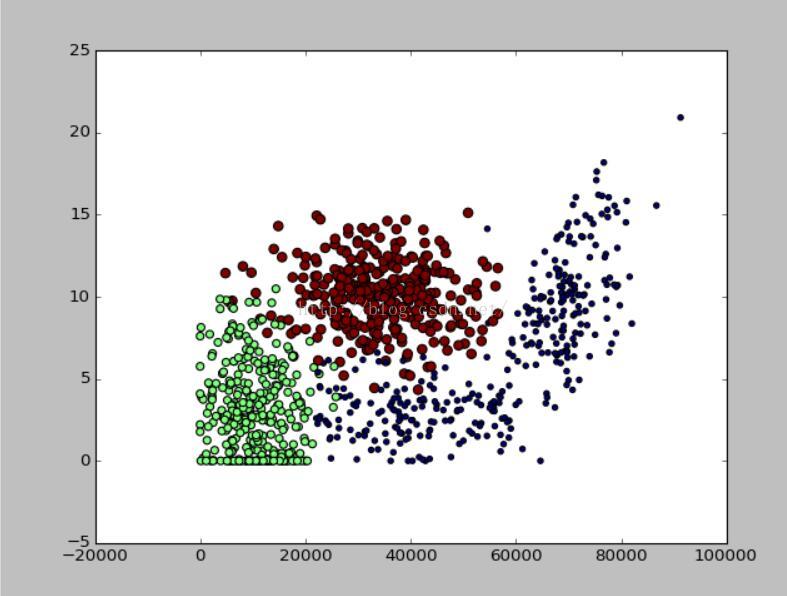
散點圖使用datingDataMat矩陣的第二,第三列資料代表玩視訊遊戲所耗時間百分比,每週所消耗的冰淇凌公升數
由於沒有樣本分類的特徵值。很難看到任何有用的資料模型資訊。一般用採用色彩或其他記號標記不同分類
而展現的資料圖如下:
但是如果標識了三個不同的樣本分類區域,採用第1.2列效果會更直觀
對資料進行歸一化處理:
如果我們對資料樣本直接進行計算距離。(0-67)^2 + (20000-32000)^2 + (1.1-0.1)^2數字最大屬性對結果影響很大。
也就是說飛行常客對於結果的影響遠遠大於其他特徵。但是我們應該認為這3個屬性同等重要。所i有需要數值歸一化我們可以將任意值轉化到
0到1之間 newValue = (oldValue-min)/(max-min)
def autoNorm(dataSet):
minVals = dataSet.min(0)
maxVals = dataSet.max(0)
ranges = maxVals - minVals
normDataSet = zeros(shape(dataSet))
m = dataSet.shape[0]
normDataSet = dataSet - tile(minVals,(m,1))
normDataSet = normDataSet/tile(ranges,(m,1))
return normDataSet,ranges,minVals原來的資料為
array([[ 4.09200000e+04, 8.32697600e+00, 9.53952000e-01],
[ 1.44880000e+04, 7.15346900e+00, 1.67390400e+00],
[ 2.60520000e+04, 1.44187100e+00, 8.05124000e-01],
...,
[ 2.65750000e+04, 1.06501020e+01, 8.66627000e-01],
[ 4.81110000e+04, 9.13452800e+00, 7.28045000e-01],
[ 4.37570000e+04, 7.88260100e+00, 1.33244600e+00]])
進過處理後的資料為
array([[ 0.44832535, 0.39805139, 0.56233353],
[ 0.15873259, 0.34195467, 0.98724416],
[ 0.28542943, 0.06892523, 0.47449629],
...,
[ 0.29115949, 0.50910294, 0.51079493],
[ 0.52711097, 0.43665451, 0.4290048 ],
[ 0.47940793, 0.3768091 , 0.78571804]])
測試演算法:使用完成程式測試分類
機器學習的重要工作就是評估演算法的正確率,通常按照上述的演算法如果正確分類,那麼可以使用這個軟體來處理約會網站提供的約會名單了。
但是還需要測試當前分類器的效能,我們以測試錯誤率為主對這個程式測試程式如下:
def datingClassTest():
hoRation = 0.10
datingDataMat,datingLabels = file2matrix('E:\pythonProject\ML\datingTestSet2.txt')
normMat,ranges,minVals = autoNorm(datingDataMat)
m = normMat.shape[0]
numTestVecs = int(m*hoRation)
errorCount = 0.0
for i in range(numTestVecs):
classifierResult = classify0(normMat[i,:],normMat[numTestVecs:m,:],datingLabels[numTestVecs:m],3)
print ("the classifier came back with %d,the real answer is %d"
%(classifierResult,datingLabels[i]))
if(classifierResult!=datingLabels[i]):errorCount+=1.0
print "the total error rate is %f" % (errorCount/float(numTestVecs))
其實就是計算錯誤個數佔據總數的百分比,而最先給定的比率是測試集的個數
最後:進行泛化預測構造完整系統
上面已經對資料處理測試以及處理了,那麼下面就是隊資料進行預測
def classifyPerson():
resultList = ['not at all','in small doses','in large doses']
percentTats = float(raw_input("percentage of time spent playing?"))
ffMiles = float(raw_input("frequent flier miles earned per year?"))
iceCream = float(raw_input("liters of ice cream consume?"))
datingDataMat,datingLabels = file2matrix('E:\pythonProject\ML\datingTestSet2.txt')
normMat,ranges,minVals = autoNorm(datingDataMat)
inArr = array([ffMiles,percentTats,iceCream])
classifierResult = classify0((inArr-minVals)/ranges,normMat,datingLabels,3)
print "You will probably like this person:",resultList[classifierResult-1]根據型別輸出喜好的程度
>>> kNN.classifyPerson()
percentage of time spent playing?10
frequent flier miles earned per year?10000
liters of ice cream consume?0.
You will probably like this person: in small doses