最短路徑(弗洛伊德演算法)
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-02-11
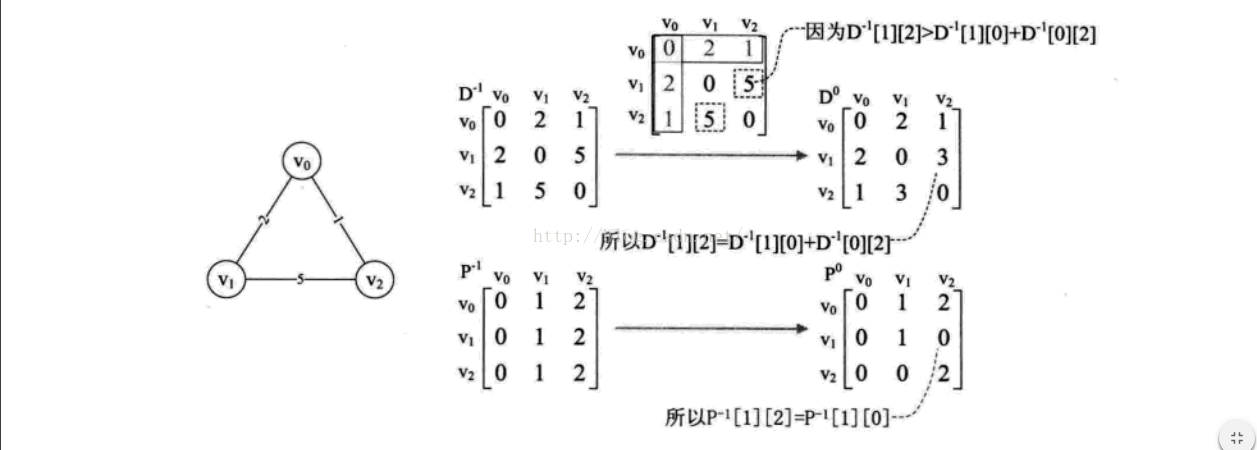
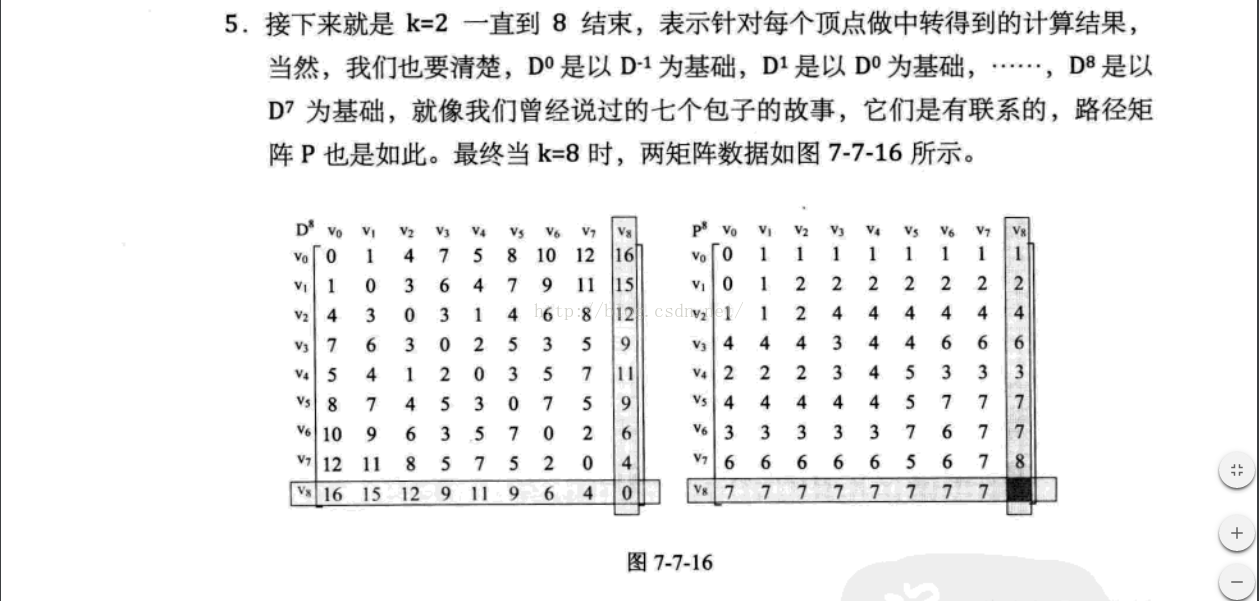
1 原理 ,假設存在一個最簡單的連通圖
2 程式碼
package leaning.graph; /* * * 弗洛伊德演算法求最短路徑 * * */ public class Floyd { // 表示V0頂點到v8頂點的最短路徑的值 private int[][] D = new int[9][9]; // 最短路徑節點走法 private int[][] P = new int[9][9]; //定義無窮大的數 private int MAX = Integer.MAX_VALUE/2; //定義地圖變數 private int[][] map = new int[9][9]; //定義頂點變數 private String[] points = {"v0","v1","v2","v3","v4","v5","v6","v7","v8"}; //初始化地圖 public void createMap(){ this.map[0] = new int[]{ 0, 1, 5,MAX,MAX,MAX,MAX,MAX,MAX}; this.map[1] = new int[]{ 1, 0, 3, 7, 5,MAX,MAX,MAX,MAX}; this.map[2] = new int[]{ 5, 3, 0,MAX, 1, 7,MAX,MAX,MAX}; this.map[3] = new int[]{MAX, 7,MAX, 0, 2,MAX, 3,MAX,MAX}; this.map[4] = new int[]{MAX, 5, 1, 2, 0, 3, 6, 9,MAX}; this.map[5] = new int[]{MAX,MAX, 7,MAX, 3, 0,MAX, 5,MAX}; this.map[6] = new int[]{MAX,MAX,MAX, 3, 6,MAX, 0, 2, 7}; this.map[7] = new int[]{MAX,MAX,MAX,MAX, 9, 5, 2, 0, 4}; this.map[8] = new int[]{MAX,MAX,MAX,MAX,MAX,MAX, 7, 4, 0}; } //初始化變數 public void iniVar(){ for(int v = 0 ; v < this.points.length ; v++){ for(int w = 0 ; w < this.points.length ; w++){ this.D[v][w] = this.map[v][w]; this.P[v][w] = w; } } } /* * 弗洛伊德演算法核心 * 引數 startPoint 為起始點 * 引數 endPoint 為終點 * */ public void floydCore(String startPoint,String endPoint){ // 1 初始化變數 this.createMap(); this.iniVar(); // 2 迴圈 for(int k = 0 ; k < this.points.length ; k++){ for( int v = 0 ; v < this.points.length ;v++){ for(int w = 0 ; w < this.points.length ;w++){ if(this.D[v][w] > this.D[v][k] + this.D[k][w]){ this.D[v][w] = this.D[v][k] + this.D[k][w]; this.P[v][w] = this.P[v][k]; } } } } // 3 輸出結果 this.show(startPoint,endPoint); } //根據名稱得到它的位置 public int getNumber(String pointName){ int position = -1; for(int i = 0 ; i < this.points.length ;i++ ){ if(this.points[i].endsWith(pointName.replace(" ", ""))){ position = i; break; } } return position; } // 得到v0頂點到pointName頂點的路徑 public String getPath(String startPointName,String endPointName){ //初始化變數 StringBuffer path = new StringBuffer(); int startPosition = this.getNumber(startPointName); int endPosition = this.getNumber(endPointName); // 得到path值 path.append(startPointName); int cenPosition = this.P[startPosition][endPosition]; while(cenPosition!=endPosition){ path.append("->"+this.points[cenPosition]); cenPosition = this.P[cenPosition][endPosition]; } path.append("->"+endPointName); return path.toString(); } //輸出結果 public void show(String startPointName,String endPointName){ // 1 輸出權值大小 int startPosition = this.getNumber(startPointName); int endPosition = this.getNumber(endPointName); System.out.println("節點"+startPointName+"到節點"+endPointName+":"); System.out.println("最小權值為 : " + this.D[startPosition][endPosition]); // 2 輸出路徑 System.out.println("路徑為 : " + this.getPath(startPointName, endPointName)); } public static void main(String[] args) { Floyd floyd = new Floyd(); floyd.floydCore("v0","v8"); } }
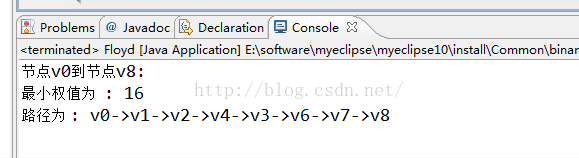
3 輸出結果