【每日】1164考試排名——中級
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-02-13
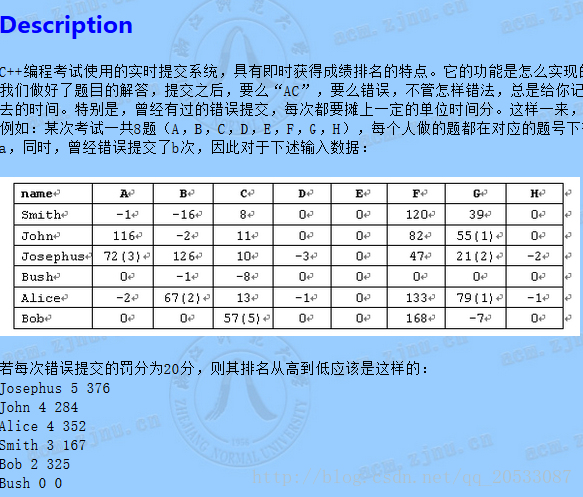
一道輸入,判斷,排序,輸出題。
學到的點:
- 結構體vector的push_back 和sort
- log要用換底公式
- 編譯的時候直接按特定if裡的當前行可以跳過其它組資料
- 輸出時的iomanip 標頭檔案
I/O流常用控制符:
使用控制符時,在程式開頭加投檔案#include <iomanip> C++有兩種方法控制格式輸出:1、用格式控制符;2、用流物件的成員函式 格式控制符:
dec 設定基數為10
hex 設定基數為16
oct 設定基數為8 程式碼如下
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<iomanip>
#include<vector>
#include<sstream>
#include<algorithm> 