Flyweight(享元)設計模式
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-02-15
宣告:本博文篇幅短,適合review。
一、概念
運用共享技術,有效地支援大量細粒度的物件。減少記憶體消耗。它有兩個狀態:
內部狀態:儲存在享元物件內部,並且不會隨環境改變而改變的物件,可以共享。
外部狀態:隨環境改變而改變的物件,不可共享。
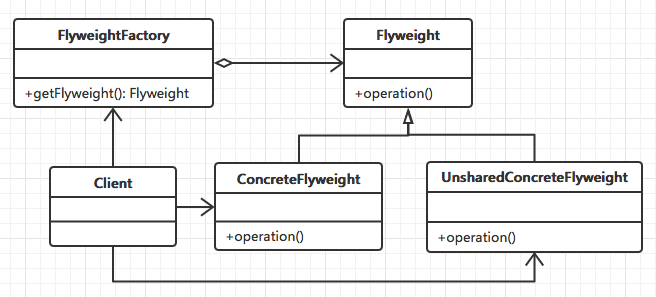
二、結構模式圖
class Flyweight { public: virtual ~Flyweight(); virtual void Operation(const std::string & _others){} std::string getState(){ return this->m_state; } protected: Flyweight(std::string _state){ this->m_state = _state; } private: std::string m_state; }; class ConcreteFlyweight : public Flyweight { public: ConcreteFlyweight(std::string _state) : Flyweight(_state) {} ~ConcreteFlyweight(); void Operation(const std::string & _others) { cout<<"ConcreteFlyweight Operation : "<<m_state<<endl; }; }; class FlyweightFactory { public: FlyweightFactory(); ~FlyweightFactory(); Flyweight * getFlyweight(const std::string & key){ std::vector<Flyweight *>::iterator it = m_Vec.begin(); for (; it != m_Vec.end() ; it++){ if ( (*it)->getState() == key ) { cout<<"has created"<<endl; return *it; } } Flyweight * fw = new ConcreteFlyweight(key); m_Vec.push_back(fw); return fw; } private: std::vector<Flyweight *> m_Vec; }; void main(){ FlyweightFactory * fc = new FlyweightFactory(); Flyweight * fw1 = fc->getFlyweight("xxx"); Flyweight * fw2 = fc->getFlyweight("yyy"); Flyweight * fw3 = fc->getFlyweight("xxx"); }
三、例子
class Chess { public: virtual ~Chess(); virtual void draw(const std::string & _color){} std::string getState(){ return this->m_state; } protected: Chess(std::string _state){ this->m_state = _state; } private: std::string m_state; }; class FiveChess : public Chess { public: FiveChess(std::string _state) : Chess(_state) {} ~FiveChess(); void draw(const std::string & _color) { cout<<"FiveChess draw : "<<m_state<<" "<<_color<<endl; }; }; class ChessFactory { public: ChessFactory(); ~ChessFactory(); Chess * getChess(const std::string & key){ std::vector<Chess *>::iterator it = m_Vec.begin(); for (; it != m_Vec.end() ; it++){ if ( (*it)->getState() == key ) { cout<<"has created"<<endl; return *it; } } Chess * c = new FiveChess(key); m_Vec.push_back(c); return c; } private: std::vector<Chess *> m_Vec; }; void main(){ ChessFactory * cf = new ChessFactory(); Chess * c1 = cf->getChess("white"); c1.draw("白色"); Chess * c2 = cf->getChess("black"); c2.draw("黑色"); Chess * c3 = cf->getChess("white"); c3.draw("白色"); }
四、優缺點
1、優點
a、極大的減少系統中物件的個數。
b、享元模式使得享元物件能夠在不同的環境被共享。
2、缺點
a、使得系統更加複雜。為了使物件可以共享,需要將一些狀態外部化,這使得程式的邏輯複雜化。
b、享元模式將享元物件的狀態外部化,而讀取外部狀態使得執行時間稍微變長。