Two-Pass演算法——影象連通域分析
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-02-17
在處理二值影象,提取感興趣目標時經常需要通過連通域的大小對候選目標進行初步篩選。OpenCV中findContour 方法可以返回輪廓並能夠計算輪廓面積。可其侷限性在對於非凸多邊形的面積計算是不準確的。 此時,利用連通域計算面積的方法更可靠,然而 findContour方法並不返回連通域結果。
其中,Two-Pass法步驟簡單,易於理解。但是該博文的實現演算法存在Bug, 會將連通的區域分割成不同標籤。測試圖如下:
使用其連通區域的結果如下:
不難發現,第二、四字元的連通區域計算出現了錯誤。 出錯的原因是在於連通域的等價表上面。(equivalences )
其方法利用一維列表結構儲存等價關係。例如存在一個具有等價性的標籤組:{ 1,3,5,7};
則可以用一維陣列表示: a[7] = 5, a[5] = 3, a[3] = 1,a[1] = 1, 或者更高效地是 a[7] = 1, a[5] = 1, a[3] = 1, a[1] = 1。 而前者的方式可以更準確地傳遞等價性,因為大多數時候 7 與 1 , 5 與1 的關係並不明確,或者很難獲知。相對地, 3 與 1, 5 與 3 , 7 與 5的關係 更容易獲得。 原因在於其標籤值相近,代表空間相近,繼而可通過鄰域判斷連通性。這裡理解有困難可看這裡 Wiki: Connected-component labeling。
具體上面提到的參考演算法的bug不細表,給出我的實現方法。
- 主演算法
bool twoPass(cv::Mat pBinary, int background,int foreground, int border, cv::Mat& pLabel)
{
// connected component analysis (4- component)
// use two-pass algorithm
// 1. first pass: label each foreground pixel with a label 結果:
2、 有條件選擇連通域標籤
void thresholdLabel(const cv::Mat& _labelImg, vector<int>& _labelList)
{
if (_labelImg.empty() || _labelImg.type() != CV_32SC1)
return;
std::map<int,int> labelCount;
int rows = _labelImg.rows;
int cols = _labelImg.cols;
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++)
{
const int* data_src = (int*)_labelImg.ptr<int>(i);
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++)
{
int pixelValue = data_src[j];
if (0 == pixelValue) continue;
if (labelCount.count(pixelValue) <= 0)
labelCount[pixelValue] = 1;
else
labelCount[pixelValue]++;
}
}
std::map<int, int>::iterator st = labelCount.begin();
std::map<int, int>::iterator et = labelCount.end();
for (; st != et; ++st)
{
if (st->second < 100 ) continue; // 連通域小於100,忽略
_labelList.push_back(st->first);
cout << "label " << st->first << ": " << st->second<<endl;
}
}
3、 隨機著色
cv::Scalar randColor()
{
uchar r = 255 * (rand() / (1.0 + RAND_MAX));
uchar g = 255 * (rand() / (1.0 + RAND_MAX));
uchar b = 255 * (rand() / (1.0 + RAND_MAX));
return cv::Scalar(b, g, r);
}
void getLabelColor(const cv::Mat& _labelImg, vector<int>_labelList, cv::Mat& _colorLabelImg)
{
if (_labelImg.empty() || _labelImg.type() != CV_32SC1 || _labelList.empty())
return;
std::map<int, cv::Scalar> colors;
int rows = _labelImg.rows;
int cols = _labelImg.cols;
_colorLabelImg.release();
_colorLabelImg.create(rows, cols, CV_8UC3);
_colorLabelImg = cv::Scalar::all(0);
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++)
{
const int* data_src = (int*)_labelImg.ptr<int>(i);
uchar* data_dst = _colorLabelImg.ptr<uchar>(i);
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++)
{
int pixelValue = data_src[j];
vector<int>::iterator it = find(_labelList.begin(), _labelList.end(), pixelValue);
if (it == _labelList.end())
{
data_dst++;
data_dst++;
data_dst++;
continue;
}
if (pixelValue > 1)
{
if (colors.count(pixelValue) <= 0)
{
colors[pixelValue] = randColor();
}
cv::Scalar color = colors[pixelValue];
*data_dst++ = color[0];
*data_dst++ = color[1];
*data_dst++ = color[2];
}
else
{
data_dst++;
data_dst++;
data_dst++;
}
}
}
}
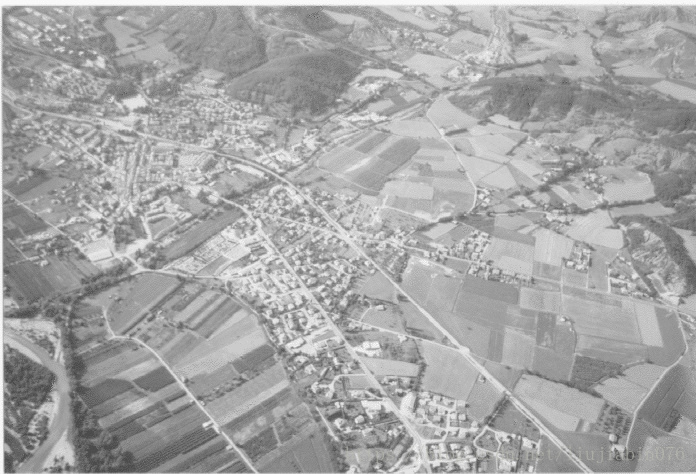
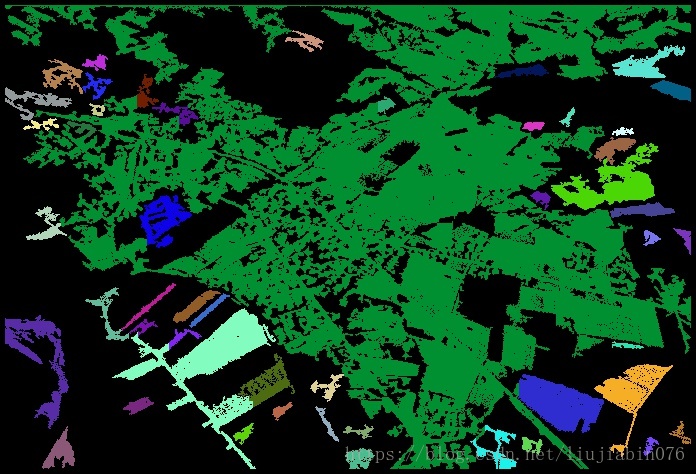
更多結果:
原圖
結果:
此文僅討論Two-Pass 實現問題。Two-Pass 方法相較於SeedFill ,運算效率比較低。
完。
Lewis, 2018-06-24