【演算法導論】B樹
一棵B樹T是具有如下性質的有根樹(設根為root):
一棵B樹可以表示如下:1.每個節點x有一下域:
(a)num,當前儲存在節點x的關鍵字個數,關鍵字以非降序存放,因此key[i]<=key[i+1]<=……key[n];
(b)isleaf,是一個bool值,如果x為葉子節點,則isleaf=true.
(c)每個節點包括num+1個指向其子女的指標p[0],p[1],……p[num]。如果x為葉子,則p=NULL
(d)每個節點包括num個關鍵字key[0],key[1],……key[num-1]。各關鍵字key[i]對儲存在各子樹中的關鍵字範圍加以分隔: k1<=key[1]<=k2<=key[2]……
2.每個葉節點具有相同的深度。
3.每一個節點包含的關鍵字有上下界。這些界可以用一個稱為B樹的最小度數的固定整數M>=2來表示。每個非根節點的個數n必須滿足M-1<=n<=2M-1。根節點至少包括 一個關鍵字。如果一個節點是滿的,則它恰好有2M-1個關鍵字。
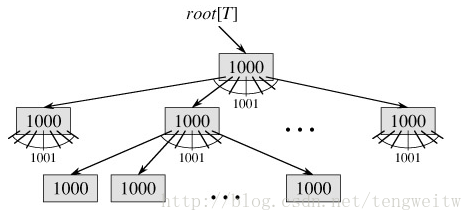
B樹與紅黑樹的相似之處在於,每棵有n個節點的B樹高度為O(lgn),但可能要比一棵紅黑樹的高度小很多,因為它的分支比較多!因為在磁碟儲存中,需要經常讀取資料,所以選擇一個大的分支因子,可以大大地降低樹的高度,以及磁碟存取次數。這樣說可能比較抽象,下面舉例說明:下圖為一棵分支因子為1001、高度為2的B樹,可以看出它可以儲存超過10億個關鍵字;但是,因為根節點可以持久的保留在主存中,因此需找某個關鍵字至多隻需要兩次磁碟存取。如果用二叉樹儲存的話,樹的深度將會很大,那麼尋找位於葉子節點處的關鍵字將需要很多次磁碟讀取!假設有n個節點,那麼二叉樹的高度為h<=lg(n+1),而B樹為h<=log((n+1)/2)/log(M),其中M為最小度數。
B樹的各種操作:
1.查詢
查詢b樹和查詢二叉樹類似,就是在分支處進行判斷選擇正確的子樹,然後遞迴呼叫。查詢過程的時間複雜讀為Mlgn/lgM具體程式實現如下:
/**********************************************************\ 函式功能:查詢關鍵字所在的節點 輸入: 樹的根,關鍵字 輸出: 關鍵字所在的節點 \**********************************************************/ BtreeNode *BtreeSearch(BtreeNode *TestNode,int keyword) { int i=0; while(i<TestNode->num&&keyword>TestNode->key[i]) i=i+1; if(i<=TestNode->num&&keyword==TestNode->key[i]) return TestNode; if(TestNode->isleaf) { printf("Not founded!\n"); return NULL; } else { return BtreeSearch(TestNode->p[i],keyword); } }
2.建立空的B樹
/**********************************************************\
函式功能:建立節點
輸入:無
輸出:新節點
\**********************************************************/
BtreeNode * BtreeCreate()
{
BtreeNode *node=(BtreeNode *)malloc(sizeof(BtreeNode));
if(NULL==node)
return NULL;
node->isleaf=true;
node->num=0;
for(int i=0;i<2*M;i++)
node->p[i]=NULL;
for(int i=0;i<2*M-1;i++)
node->key[i]=0;
return node;
}3.插入
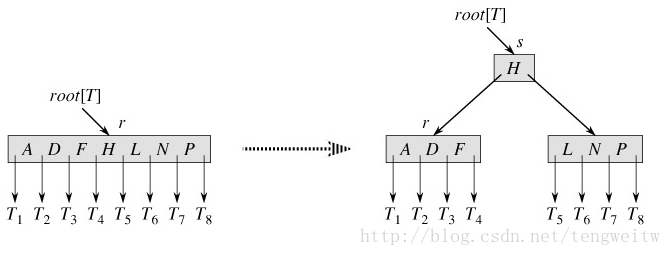
B樹的插入比二叉樹的插入要複雜的多,因為二叉樹的插入是插入新的節點,而B樹的插入是將關鍵字插入到已存在的節點,而節點可能已經是滿節點(前面提到過),就會破壞B樹的性質。因此不能將關鍵字插入到滿節點上。根據B樹的規則,每個節點的關鍵字個數在[M-1, 2M-1]之間,故當keyword(要插入的關鍵字)要加入到某個葉子時,如果該葉子節點已經有2M-1個關鍵字,則再加入keyword就違反了B樹的定義,這時就需要對該葉子節點進行分裂,將葉子以中間節點為界,分成兩個包含M-1個關鍵字的子節點,同時把中間節點提升到該葉子的父節點中,如果這樣使得父節點的關鍵字個數超過2M-1,則要繼續向上分裂,直到根節點,根節點的分裂會使得樹加高一層。
為了解決上面問題,我們需要不斷地回溯,這顯然比較複雜,我們可以未雨綢繆:我們不是等到發現是否真的需要分裂一個滿節點時才做插入操作。相反地,當沿著樹向下查詢要插入關鍵字所處位置時,就分裂沿途遇到的每個滿節點。這樣做後,每當要分裂一個滿節點時,就能保證其雙親不是滿節點。
分裂滿節點的過程圖解如下:
我們還要考慮特殊情況:當分裂一個滿的根時,需要先讓根成為一個新的空根節點的孩子,這樣才能被上面的分解過程分解。樹的高度增加1,分裂是樹增高的唯一途徑!其操作如下圖:
綜上所述,插入過程的具體實現如下:
//////////////////////////////插入部分///////////////////////////////////////////
/**********************************************************\
函式功能:節點分裂,防止違反B樹的性質
輸入: 父節點father ,子節點child,k表示子節點為父節點的哪個孩子
輸出:無
\**********************************************************/
void BtreeSplitChild(BtreeNode *father,BtreeNode *child,int k)
{
BtreeNode *newchild=(BtreeNode *)malloc(sizeof(BtreeNode));
newchild->isleaf=child->isleaf;//newchild為child的右節點,即child分裂為child和newchild
newchild->num=M-1;
for(int i=0;i<M-1;i++)
newchild->key[i]=child->key[i+M];
if(!child->isleaf)//當child不是葉子時,還要把指標賦給newchild
{
for(int j=0;j<M;j++)
newchild->p[j]=child->p[j+M];
}
child->num=M-1;//child的個數由2M-1變為M-1
for(int i=father->num-1;i>=k+1;i--)//改變父節點的內容
father->p[i+1]=father->p[i];
father->p[k+1]=newchild;
for(int j=father->num-1;j>=k;j--)
father->key[j+1]=father->key[j];
father->key[k]=child->key[M-1];//將child的中間節點提升到父節點
father->num=father->num+1;
}
/**********************************************************\
函式功能:x節點不是滿的情況下,插入keyword
輸入:B樹的根,要插入的關鍵字
輸出:無
\**********************************************************/
void BtreeInsertNotFull(BtreeNode *x,int keyword)
{
int i=x->num;
if(x->isleaf)//當x為葉子時,keyword插入到該節點中
{
while(i>=1&&keyword<x->key[i-1])
{
x->key[i]=x->key[i-1];
i=i-1;
}
x->key[i]=keyword;
x->num=x->num+1;
}
else//當x不是葉子時,找到keyword要插入的節點並插入
{
while(i>=1&&keyword<x->key[i-1])
{
i=i-1;
}
if(x->p[i]->num==2*M-1)//當節點為滿節點時,需要分裂
{
BtreeSplitChild(x,x->p[i],i);
if(keyword>x->key[i])
i=i+1;
}
BtreeInsertNotFull(x->p[i],keyword);
}
}
/**********************************************************\
函式功能:插入關鍵值
輸入:B樹的根,關鍵字
輸出:B樹的根
\**********************************************************/
BtreeNode * BtreeInsert(BtreeNode *TestNode,int keyword)
{
if(TestNode->num==2*M-1)//當根節點為滿時,唯一增加高度的情況
{
BtreeNode *newroot=(BtreeNode *)malloc(sizeof(BtreeNode));
newroot->isleaf=false;//產生新的根
newroot->num=0;
newroot->p[0]=TestNode;
BtreeSplitChild(newroot,TestNode,0);
BtreeInsertNotFull(newroot,keyword);
return newroot;
}
else
{
BtreeInsertNotFull(TestNode,keyword);
return TestNode;
}
}4.刪除
B樹的刪除比插入操作更加複雜,插入操作只需考慮三種情況,而刪除操作需要考慮的情況很多,情況如下:
和插入操作類似,根據B樹的規則,每個節點的關鍵字個數在[M-1, 2M-1]之間,故當keyword(要插入的關鍵字)要從某個葉子刪除時,如果該葉子節點只有有M-1個關鍵字,則再刪除keyword就違反了B樹的定義,這時就需要對該葉子節點進行合併。上圖中各種情況中的t就是我所說的M即最小度數。具體程式實現如下:
///////////////////////////刪除部分//////////////////////////////////////////
/**********************************************************\
函式功能:合併左右子節點
輸入:根,左右子節點,左節點是父節點的第pos個節點
輸出:無
\**********************************************************/
void BtreeMergeChild(BtreeNode *root, int pos, BtreeNode *y, BtreeNode *z)
{
// 將z中節點拷貝到y的後半部分
y->num = 2 * M - 1;
for(int i = M; i < 2 * M - 1; i++)
{
y->key[i] = z->key[i-M];
}
y->key[M-1] = root->key[pos]; // 將root->key[pos]下降為y的中間節點
if(false == z->isleaf)// 如果z是內節點即非葉子,需要拷貝指向子節點的指標p
{
for(int i = M; i < 2 * M; i++)
{
y->p[i] = z->p[i-M];
}
}
for(int j = pos + 1; j < root->num; j++) // root->key[pos]下降到y中,更新root中key和p
{
root->key[j-1] = root->key[j];
root->p[j] = root->p[j+1];
}
root->num -= 1;
free(z);
}
/**********************************************************\
函式功能:刪除關鍵字keyword
輸入:樹的根,關鍵字
輸出:樹的根
\**********************************************************/
BtreeNode *BtreeDelete(BtreeNode *root, int keyword)
{
// 唯一能降低樹高的情形
if(1 == root->num) // 當根只有一個關鍵字,兩個子女
{
BtreeNode *y = root->p[0];
BtreeNode *z = root->p[1];
if(NULL != y && NULL != z &&M - 1 == y->num && M - 1 == z->num)//兩個子女的關鍵字個數都為M-1時,合併根與兩個子女
{
BtreeMergeChild(root, 0, y, z);
free(root);//注意釋放空間
BtreeDeleteNotFull(y, keyword);
return y;
}
else
{
BtreeDeleteNotFull(root, keyword);
return root;
}
}
else
{
BtreeDeleteNotFull(root, keyword);
return root;
}
}
/**********************************************************\
函式功能: root至少有個M個關鍵字時刪除關鍵字
輸入: 樹的根,關鍵字
輸出: 無
\**********************************************************/
void BtreeDeleteNotFull(BtreeNode *root, int keyword)
{
if(true == root->isleaf) // 如果在葉子節點,直接刪除,情況1
{
int i = 0;
while(i < root->num && keyword > root->key[i]) i++;
if(keyword == root->key[i])
{
for(int j = i + 1; j < 2 * M - 1; j++)
{
root->key[j-1] = root->key[j];
}
root->num -= 1;
}
else
{
printf("keyword not found\n");
}
}
else
{ // 在分支中
int i = 0;
BtreeNode *y = NULL, *z = NULL;
while(i < root->num && keyword > root->key[i]) i++;
if(i < root->num && keyword == root->key[i])
{ // 如果在分支節點找到keyword
y = root->p[i];
z = root->p[i+1];
if(y->num > M - 1)
{
// 如果左分支關鍵字多於M-1,則找到左分支的最右節點pre,替換keyword
// 並在左分支中遞迴刪除prev,情況2a
int pre = BtreeSearchPrevious(y);
root->key[i] = pre;
BtreeDeleteNotFull(y, pre);//遞迴處理
}
else if(z->num > M - 1)
{
// 如果右分支關鍵字多於M-1,則找到右分支的最左節點next,替換keyword
// 並在右分支中遞迴刪除next,情況2b
int next = BtreeSearchNext(z);
root->key[i] = next;
BtreeDeleteNotFull(z, next);
}
else // 兩個分支節點數都為M-1,則合併至y,並在y中遞迴刪除keyword,情況2c
{
BtreeMergeChild(root, i, y, z);
BtreeDelete(y, keyword);
}
}
else// 分支中沒有,在分支的子節點中的情況
{
y = root->p[i];
if(i < root->num)
{
z = root->p[i+1];//y的右兄弟
}
BtreeNode *p = NULL;//初始化
if(i > 0)
{
p = root->p[i-1];//y的左兄弟
}
if(y->num == M - 1)
{
if(i > 0 && p->num > M - 1)
{
// 左兄弟節點關鍵字個數大於M-1,情況3a
BtreeChangeToRchild(root, i-1, p, y);
}
else if(i < root->num && z->num > M - 1)
{
// 右兄弟節點關鍵字個數大於M-1,情況3a
BtreeChangeToLchild(root, i, y, z);
}
else if(i > 0)
{
BtreeMergeChild(root, i-1, p, y); //左右兄弟節點都不大於M-1,情況3b
y = p;
}
else //沒有左兄弟的情況
{
BtreeMergeChild(root, i, y, z);
}
BtreeDeleteNotFull(y, keyword);
}
else
{
BtreeDeleteNotFull(y, keyword);
}
}
}
}
/**********************************************************\
函式功能:尋找以root為根的最大關鍵字
輸入: 樹的根
輸出: 最大關鍵字
\**********************************************************/
int BtreeSearchPrevious(BtreeNode *root)
{
BtreeNode *y = root;
while(false == y->isleaf)
{
y = y->p[y->num];
}
return y->key[y->num-1];
}
/**********************************************************\
函式功能:尋找以root為根的最小關鍵字
輸入:樹的根
輸出:最小關鍵字
\**********************************************************/
int BtreeSearchNext(BtreeNode *root)
{
BtreeNode *z = root;
while(false == z->isleaf)
{
z = z->p[0];
}
return z->key[0];
}
/**********************************************************\
函式功能:z向y借節點,將root->key[pos]下降至z,將y的最大關鍵字上升至root的pos處
輸入:根,左右子節點,左節點是父節點的第pos個節點
輸出:無
\**********************************************************/
void BtreeChangeToRchild(BtreeNode *root, int pos, BtreeNode *y, BtreeNode *z)
{
z->num += 1;
for(int i = z->num -1; i > 0; i--)
{
z->key[i] = z->key[i-1];
}
z->key[0]= root->key[pos];
root->key[pos] = y->key[y->num-1];
if(false == z->isleaf)
{
for(int i = z->num; i > 0; i--)
{
z->p[i] = z->p[i-1];
}
z->p[0] = y->p[y->num];
}
y->num -= 1;
}
/**********************************************************\
函式功能:y向借節點,將root->key[pos]下降至y,將z的最小關鍵字上升至root的pos處
輸入:根,左右子節點,左節點是父節點的第pos個節點
輸出:無
\**********************************************************/
void BtreeChangeToLchild(BtreeNode *root, int pos, BtreeNode *y, BtreeNode *z)
{
y->num += 1;
y->key[y->num-1] = root->key[pos];
root->key[pos] = z->key[0];
for(int j = 1; j < z->num; j++)
{
z->key[j-1] = z->key[j];
}
if(false == z->isleaf)
{
y->p[y->num] = z->p[0];
for(int j = 1; j <= z->num; j++)
{
z->p[j-1] = z->p[j];
}
}
z->num -= 1;
}
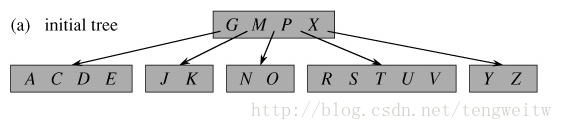
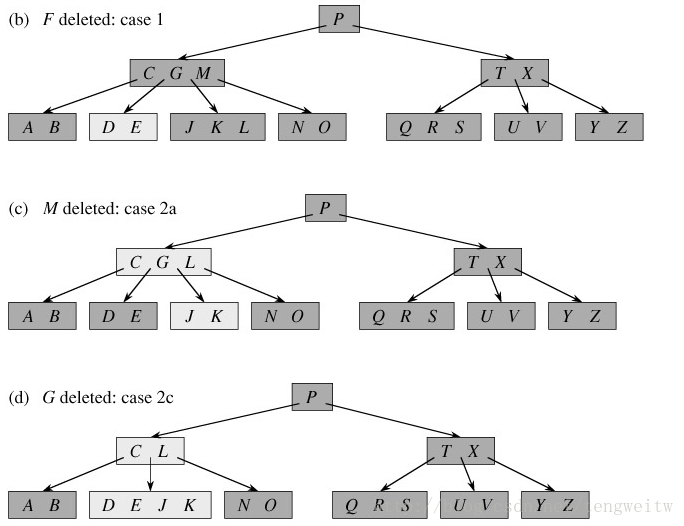
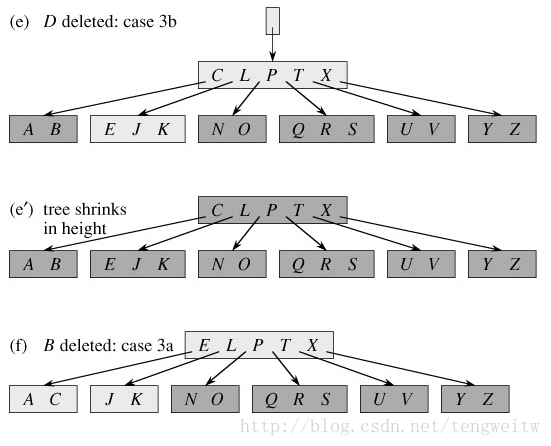
下面用具體例項來形象地說明B樹的操作:
假設初始的B樹如下:
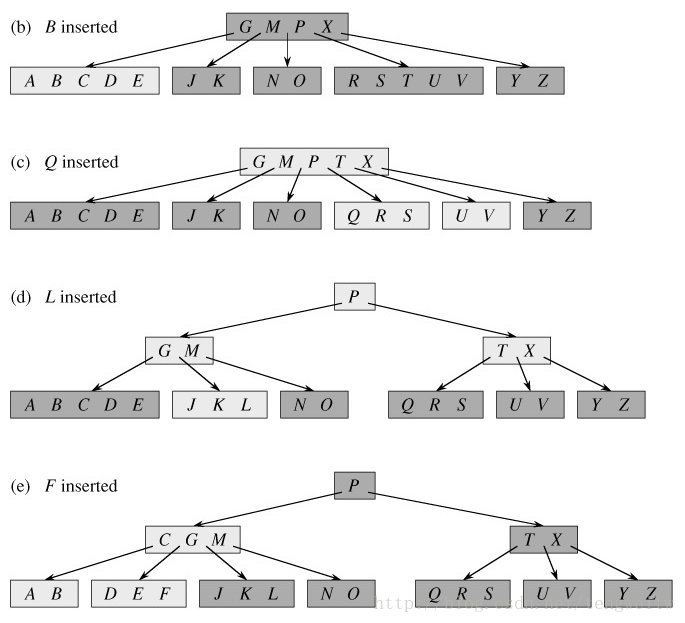
經過一系列的插入操作後:
在程式中為表示方便,將關鍵字由字母換成了數字,A、B、C……Y、Z對應於1、2、3……25、26.
經過上面的插入操作後,緊接在進行一系列刪除操作:
具體的完整例項程式實現如下:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define M 3
//節點結構體
typedef struct BtreeNode
{
int num;
struct BtreeNode *p[2*M];
int key[2*M-1];
bool isleaf;
}BtreeNode;
BtreeNode * BtreeCreate();
void BtreeSplitChild(BtreeNode *father,BtreeNode *child,int k);
void BtreeInsertNotFull(BtreeNode *x,int keyword);
BtreeNode * BtreeInsert(BtreeNode *TestNode,int keyword);
BtreeNode *BtreeSearch(BtreeNode *TestNode,int keyword);
//////
void BtreeMergeChild(BtreeNode *root, int pos, BtreeNode *y, BtreeNode *z);
BtreeNode *BtreeDelete(BtreeNode *root, int keyword);
void BtreeDeleteNotFull(BtreeNode *root, int keyword);
int BtreeSearchPrevious(BtreeNode *root);
int BtreeSearchNext(BtreeNode *root);
void BtreeChangeToRchild(BtreeNode *root, int pos, BtreeNode *y, BtreeNode *z);
void BtreeChangeToLchild(BtreeNode *root, int pos, BtreeNode *y, BtreeNode *z);
/**********************************************************\
函式功能:建立節點
輸入:無
輸出:新節點
\**********************************************************/
BtreeNode * BtreeCreate()
{
BtreeNode *node=(BtreeNode *)malloc(sizeof(BtreeNode));
if(NULL==node)
return NULL;
node->isleaf=true;
node->num=0;
for(int i=0;i<2*M;i++)
node->p[i]=NULL;
for(int i=0;i<2*M-1;i++)
node->key[i]=0;
return node;
}
//////////////////////////////插入部分///////////////////////////////////////////
/**********************************************************\
函式功能:節點分裂,防止違反B樹的性質
輸入: 父節點father ,子節點child,k表示子節點為父節點的哪個孩子
輸出:無
\**********************************************************/
void BtreeSplitChild(BtreeNode *father,BtreeNode *child,int k)
{
BtreeNode *newchild=(BtreeNode *)malloc(sizeof(BtreeNode));
newchild->isleaf=child->isleaf;//newchild為child的右節點,即child分裂為child和newchild
newchild->num=M-1;
for(int i=0;i<M-1;i++)
newchild->key[i]=child->key[i+M];
if(!child->isleaf)//當child不是葉子時,還要把指標賦給newchild
{
for(int j=0;j<M;j++)
newchild->p[j]=child->p[j+M];
}
child->num=M-1;//child的個數由2M-1變為M-1
for(int i=father->num;i>=k+1;i--)//改變父節點的內容
{
father->p[i+1]=father->p[i];
}
father->p[k+1]=newchild;
for(int j=father->num-1;j>=k;j--)
father->key[j+1]=father->key[j];
father->key[k]=child->key[M-1];//將child的中間節點提升到父節點
father->num=father->num+1;
}
/**********************************************************\
函式功能:x節點不是滿的情況下,插入keyword
輸入:B樹的根,要插入的關鍵字
輸出:無
\**********************************************************/
void BtreeInsertNotFull(BtreeNode *x,int keyword)
{
int i=x->num;
if(x->isleaf)//當x為葉子時,keyword插入到該節點中
{
while(i>=1&&keyword<x->key[i-1])
{
x->key[i]=x->key[i-1];
i=i-1;
}
x->key[i]=keyword;
x->num=x->num+1;
}
else//當x不是葉子時,找到keyword要插入的節點並插入
{
i=x->num;
while(i>=1&&keyword<x->key[i-1])
{
i=i-1;
}
if(x->p[i]->num==2*M-1)//當節點為滿節點時,需要分裂
{
BtreeSplitChild(x,x->p[i],i);
if(keyword>x->key[i])
i=i+1;
}
BtreeInsertNotFull(x->p[i],keyword);
}
}
/**********************************************************\
函式功能:插入關鍵值
輸入:B樹的根,關鍵字
輸出:B樹的根
\**********************************************************/
BtreeNode * BtreeInsert(BtreeNode *TestNode,int keyword)
{
if(TestNode->num==2*M-1)//當根節點為滿時,唯一增加高度的情況
{
BtreeNode *newroot=(BtreeNode *)malloc(sizeof(BtreeNode));
newroot->isleaf=false;//產生新的根
newroot->num=0;
newroot->p[0]=TestNode;
BtreeSplitChild(newroot,TestNode,0);
BtreeInsertNotFull(newroot,keyword);
return newroot;
}
else
{
BtreeInsertNotFull(TestNode,keyword);
return TestNode;
}
}
/**********************************************************\
函式功能:查詢關鍵字所在的節點
輸入: 樹的根,關鍵字
輸出: 關鍵字所在的節點
\**********************************************************/
BtreeNode *BtreeSearch(BtreeNode *TestNode,int keyword)
{
int i=0;
while(i<TestNode->num&&keyword>TestNode->key[i])
i=i+1;
if(i<=TestNode->num&&keyword==TestNode->key[i])
return TestNode;
if(TestNode->isleaf)
{
printf("Not founded!\n");
return NULL;
}
else
{
return BtreeSearch(TestNode->p[i],keyword);
}
}
///////////////////////////刪除部分//////////////////////////////////////////
/**********************************************************\
函式功能:合併左右子節點
輸入:根,左右子節點,左節點是父節點的第pos個節點
輸出:無
\**********************************************************/
void BtreeMergeChild(BtreeNode *root, int pos, BtreeNode *y, BtreeNode *z)
{
// 將z中節點拷貝到y的後半部分
y->num = 2 * M - 1;
for(int i = M; i < 2 * M - 1; i++)
{
y->key[i] = z->key[i-M];
}
y->key[M-1] = root->key[pos]; // 將root->key[pos]下降為y的中間節點
if(false == z->isleaf)// 如果z是內節點即非葉子,需要拷貝指向子節點的指標p
{
for(int i = M; i < 2 * M; i++)
{
y->p[i] = z->p[i-M];
}
}
for(int j = pos + 1; j < root->num; j++) // root->key[pos]下降到y中,更新root中key和p
{
root->key[j-1] = root->key[j];
root->p[j] = root->p[j+1];
}
root->num -= 1;
free(z);
}
/**********************************************************\
函式功能:刪除關鍵字keyword
輸入:樹的根,關鍵字
輸出:樹的根
\**********************************************************/
BtreeNode *BtreeDelete(BtreeNode *root, int keyword)
{
// 唯一能降低樹高的情形
if(1 == root->num) // 當根只有一個關鍵字,兩個子女
{
BtreeNode *y = root->p[0];
BtreeNode *z = root->p[1];
if(NULL != y && NULL != z &&M - 1 == y->num && M - 1 == z->num)//兩個子女的關鍵字個數都為M-1時,合併根與兩個子女
{
BtreeMergeChild(root, 0, y, z);
free(root);//注意釋放空間
BtreeDeleteNotFull(y, keyword);
return y;
}
else
{
BtreeDeleteNotFull(root, keyword);
return root;
}
}
else
{
BtreeDeleteNotFull(root, keyword);
return root;
}
}
/**********************************************************\
函式功能: root至少有個M個關鍵字時刪除關鍵字
輸入: 樹的根,關鍵字
輸出: 無
\**********************************************************/
void BtreeDeleteNotFull(BtreeNode *root, int keyword)
{
if(true == root->isleaf) // 如果在葉子節點,直接刪除,情況1
{
int i = 0;
while(i < root->num && keyword > root->key[i]) i++;
if(keyword == root->key[i])
{
for(int j = i + 1; j < 2 * M - 1; j++)
{
root->key[j-1] = root->key[j];
}
root->num -= 1;
}
else
{
printf("keyword not found\n");
}
}
else
{ // 在分支中
int i = 0;
BtreeNode *y = NULL, *z = NULL;
while(i < root->num && keyword > root->key[i]) i++;
if(i < root->num && keyword == root->key[i])
{ // 如果在分支節點找到keyword
y = root->p[i];
z = root->p[i+1];
if(y->num > M - 1)
{
// 如果左分支關鍵字多於M-1,則找到左分支的最右節點pre,替換keyword
// 並在左分支中遞迴刪除prev,情況2a
int pre = BtreeSearchPrevious(y);
root->key[i] = pre;
BtreeDeleteNotFull(y, pre);//遞迴處理
}
else if(z->num > M - 1)
{
// 如果右分支關鍵字多於M-1,則找到右分支的最左節點next,替換keyword
// 並在右分支中遞迴刪除next,情況2b
int next = BtreeSearchNext(z);
root->key[i] = next;
BtreeDeleteNotFull(z, next);
}
else // 兩個分支節點數都為M-1,則合併至y,並在y中遞迴刪除keyword,情況2c
{
BtreeMergeChild(root, i, y, z);
BtreeDelete(y, keyword);
}
}
else// 分支中沒有,在分支的子節點中的情況
{
y = root->p[i];
if(i < root->num)
{
z = root->p[i+1];//y的右兄弟
}
BtreeNode *p = NULL;//初始化
if(i > 0)
{
p = root->p[i-1];//y的左兄弟
}
if(y->num == M - 1)
{
if(i > 0 && p->num > M - 1)
{
// 左兄弟節點關鍵字個數大於M-1,情況3a
BtreeChangeToRchild(root, i-1, p, y);
}
else if(i < root->num && z->num > M - 1)
{
// 右兄弟節點關鍵字個數大於M-1,情況3a
BtreeChangeToLchild(root, i, y, z);
}
else if(i > 0)
{
BtreeMergeChild(root, i-1, p, y); //左右兄弟節點都不大於M-1,情況3b
y = p;
}
else //沒有左兄弟的情況
{
BtreeMergeChild(root, i, y, z);
}
BtreeDeleteNotFull(y, keyword);
}
else
{
BtreeDeleteNotFull(y, keyword);
}
}
}
}
/**********************************************************\
函式功能:尋找以root為根的最大關鍵字
輸入: 樹的根
輸出: 最大關鍵字
\**********************************************************/
int BtreeSearchPrevious(BtreeNode *root)
{
BtreeNode *y = root;
while(false == y->isleaf)
{
y = y->p[y->num];
}
return y->key[y->num-1];
}
/**********************************************************\
函式功能:尋找以root為根的最小關鍵字
輸入:樹的根
輸出:最小關鍵字
\**********************************************************/
int BtreeSearchNext(BtreeNode *root)
{
BtreeNode *z = root;
while(false == z->isleaf)
{
z = z->p[0];
}
return z->key[0];
}
/**********************************************************\
函式功能:z向y借節點,將root->key[pos]下降至z,將y的最大關鍵字上升至root的pos處
輸入:根,左右子節點,左節點是父節點的第pos個節點
輸出:無
\**********************************************************/
void BtreeChangeToRchild(BtreeNode *root, int pos, BtreeNode *y, BtreeNode *z)
{
z->num += 1;
for(int i = z->num -1; i > 0; i--)
{
z->key[i] = z->key[i-1];
}
z->key[0]= root->key[pos];
root->key[pos] = y->key[y->num-1];
if(false == z->isleaf)
{
for(int i = z->num; i > 0; i--)
{
z->p[i] = z->p[i-1];
}
z->p[0] = y->p[y->num];
}
y->num -= 1;
}
/**********************************************************\
函式功能:y向借節點,將root->key[pos]下降至y,將z的最小關鍵字上升至root的pos處
輸入:根,左右子節點,左節點是父節點的第pos個節點
輸出:無
\**********************************************************/
void BtreeChangeToLchild(BtreeNode *root, int pos, BtreeNode *y, BtreeNode *z)
{
y->num += 1;
y->key[y->num-1] = root->key[pos];
root->key[pos] = z->key[0];
for(int j = 1; j < z->num; j++)
{
z->key[j-1] = z->key[j];
}
if(false == z->isleaf)
{
y->p[y->num] = z->p[0];
for(int j = 1; j <= z->num; j++)
{
z->p[j-1] = z->p[j];
}
}
z->num -= 1;
}
//按層次遍歷B樹
void Print(BtreeNode *root)
{
int front,rear;
int num=0;
int num1=0;
int flag=0;
BtreeNode *queue[100];
BtreeNode *s;
if(root!=NULL)
{
rear=1;
front=0;
queue[rear]=root;
while(front<rear)
{
front++;
s=queue[front];
if(!s->isleaf)
{
for(int j=0;j<=s->num;j++)
{
if(s->p[j]!=NULL)
{
rear++;
queue[rear]=s->p[j];
}
}
}
}
for(int k=1;k<=rear;k++)//使輸出簡單易看
{
for(int i=0;i<queue[k]->num;i++)
printf("%d ",queue[k]->key[i]);
printf("| ");
if(k>num)
{
while(flag<k)
{
num=num+queue[flag+1]->num+1;
flag++;
}
printf("\n");
flag=k;
}
}
}
}
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
void main()
{
/**************************初始化**************************/
BtreeNode *TestNode=BtreeCreate();
BtreeNode *Node1=BtreeCreate();
BtreeNode *Node2=BtreeCreate();
BtreeNode *Node3=BtreeCreate();
BtreeNode *Node4=BtreeCreate();
BtreeNode *Node5=BtreeCreate();
BtreeNode *root=BtreeCreate();
BtreeNode *SearchNode=BtreeCreate();
TestNode->isleaf=false;
TestNode->num=4;
TestNode->key[0]=7;
TestNode->key[1]=13;
TestNode->key[2]=16;
TestNode->key[3]=24;
TestNode->p[0]=Node1;
TestNode->p[1]=Node2;
TestNode->p[2]=Node3;
TestNode->p[3]=Node4;
TestNode->p[4]=Node5;
Node1->isleaf=true;
Node1->num=4;
Node1->key[0]=1;
Node1->key[1]=3;
Node1->key[2]=4;
Node1->key[3]=5;
Node2->isleaf=true;
Node2->num=2;
Node2->key[0]=10;
Node2->key[1]=11;
Node3->isleaf=true;
Node3->num=2;
Node3->key[0]=14;
Node3->key[1]=15;
Node4->isleaf=true;
Node4->num=5;
Node4->key[0]=18;
Node4->key[1]=19;
Node4->key[2]=20;
Node4->key[3]=21;
Node4->key[4]=22;
Node5->isleaf=true;
Node5->num=2;
Node5->key[0]=25;
Node5->key[1]=26;
root=TestNode;
/*******************************初始化結束***********************/
printf("原始B樹:\n");
Print(root);
root=BtreeInsert(root,2);
printf("\n插入關鍵字為2後的B樹:\n");
Print(root);
root=BtreeInsert(root,17);
printf("\n插入關鍵字為17後的B樹:\n");
Print(root);
root=BtreeInsert(root,12);
printf("\n插入關鍵字為12後的B樹:\n");
Print(root);
root=BtreeInsert(root,6);
printf("\n插入關鍵字為6後的B樹:\n");
Print(root);
printf("\n\n");
//刪除操作
root=BtreeDelete(root,6);
printf("\n刪除關鍵字為6後的B樹:\n");
Print(root);
root=BtreeDelete(root,13);
printf("\n刪除關鍵字為13後的B樹:\n");
Print(root);
root=BtreeDelete(root,7);
printf("\n刪除關鍵字為7後的B樹:\n");
Print(root);
root=BtreeDelete(root,4);
printf("\n刪除關鍵字為4後的B樹:\n");
Print(root);
root=BtreeDelete(root,2);
printf("\n刪除關鍵字為2後的B樹:\n");
Print(root);
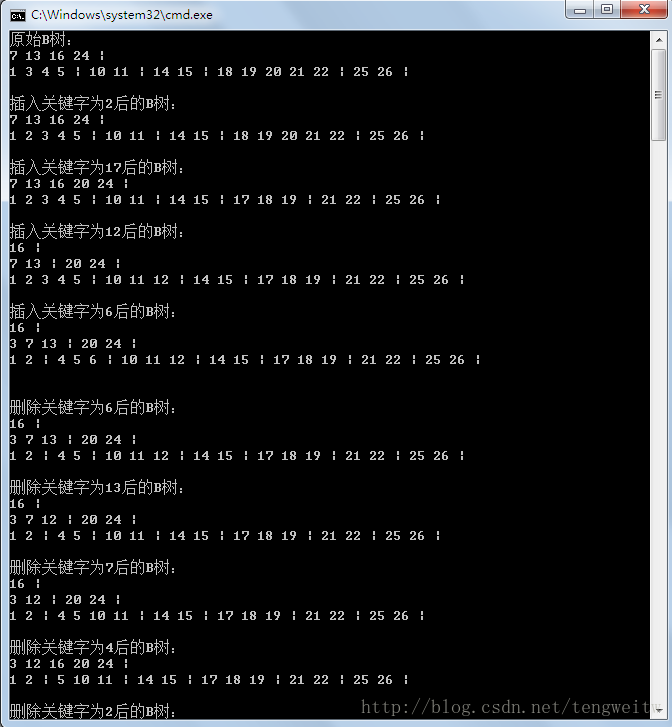
}程式結果如下(| 用於分開不同節點的關鍵字,下圖顯示是按樹的層次遍歷的,可以看出結果與上面插入和刪除的圖解過程完全相同!):
注:如果程式出錯,可能是使用的開發平臺版本不同,請點選如下連結: 解釋說明
作者:nineheadedbird