【演算法總結】B+樹的實現
【參考資料】
【B+樹是什麼】
b+樹是b樹的變種。b+樹與b樹最大的不同在於:b+樹的關鍵字數量跟孩子節點數量一致,這與b樹不一樣。並且,b+樹的葉子節點包含有所有關鍵字及其對應資訊,非葉子節點只包含部分關鍵字(這部分關鍵字相當於邊界索引),不含具體資料,下面這幅圖就說明了問題:
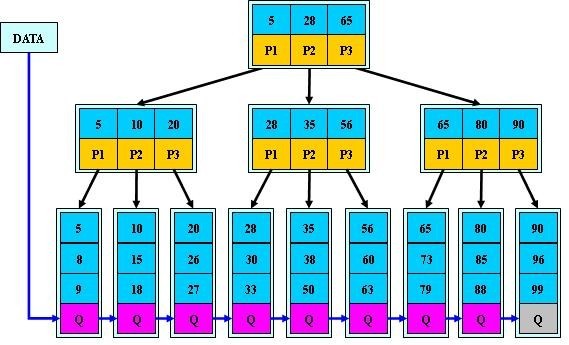
===========抄錄自july的部落格===============
【備註】:根據我連日的查詢資料及對比,我認為這幅圖片沒有出錯,這幅圖片很好地詮釋了b+樹。葉子節點的q是右邊兄弟的指標,這個很方便掃庫。
【b+樹的操作】
【新增關鍵字】
請注意,因為b+樹的葉子節點包含所有關鍵字及對應的資料,二非葉子節點包含了各個節點的邊界,一旦邊界值改變了,譬如在葉子節點“5,8,9”插入“4”,那麼從根節點到葉子節點這條路徑上的邊界“5”必須全部改變成4。--還有一點,所有的插入操作先插入到葉子,然後根據性質判斷是否邊界值改變了,還是需要分裂---分裂必然導致父親節點的邊界值改變。
【刪除關鍵字】
刪除同理,必須留意邊界值是否改變及是否需要借用關鍵字及是否需要合併節點。
【b+樹操作演示】
說明:這棵b+樹的階為3,則最多三個關鍵字,最多三個子樹,最少2個關鍵字,最少兩個子樹。
【插入操作演示】
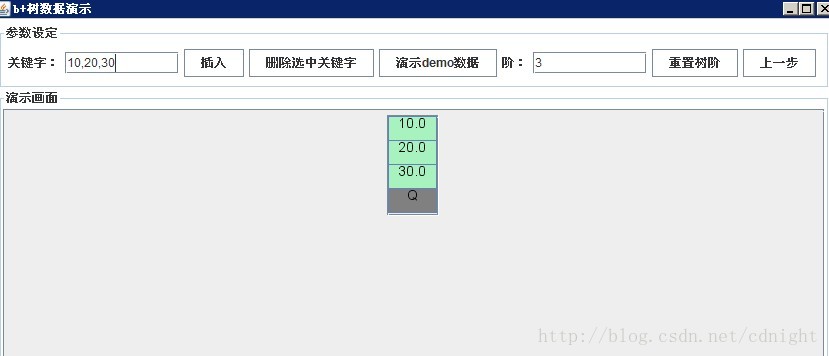
【分別插入關鍵字 10、20、30,此時根節點為葉節點,同時沒有滿足分裂條件,故放到同一個葉節點裡面】
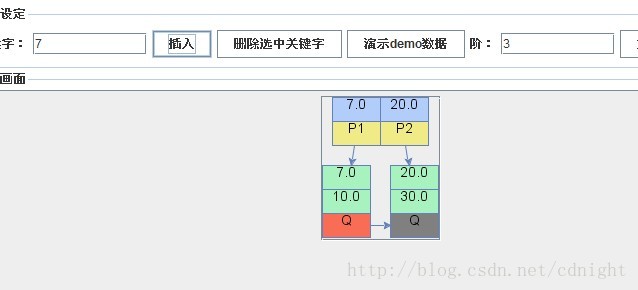
【插入關鍵字7,這時候根節點的關鍵字數量大於m(m=3),所以需要分裂成為兩個子節點(葉節點)】
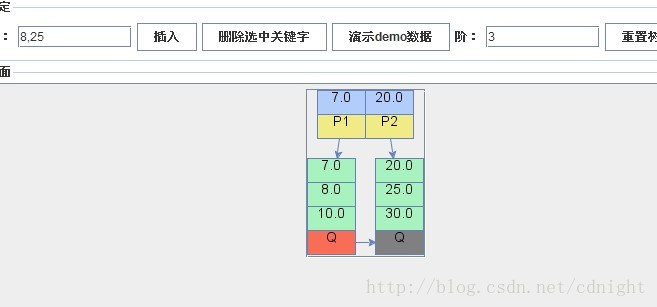
【分別插入關鍵字8、25,葉子節點被填滿,沒有符合分裂條件,不需要分裂。】
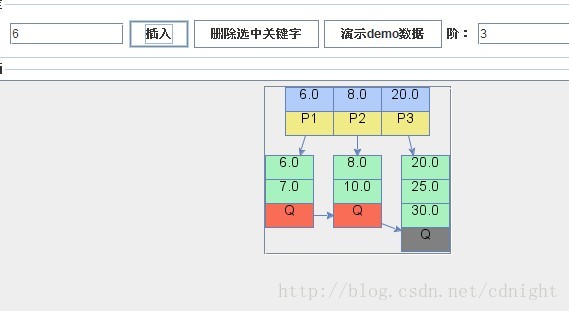
【插入關鍵字6,注意,6是少於所有關鍵字的,根據我的演算法,6將放到最左邊的葉子節點裡面,並且遞迴設定每一個父親的第一位數目(則該路徑上第一個關鍵字都改6),同時,葉子節點關鍵字大於m(m=3),需要分裂,具體演算法可以檢視我的下一篇博文的具體程式碼,裡面已經包含解釋】
【分別插入關鍵字 7.5、12】
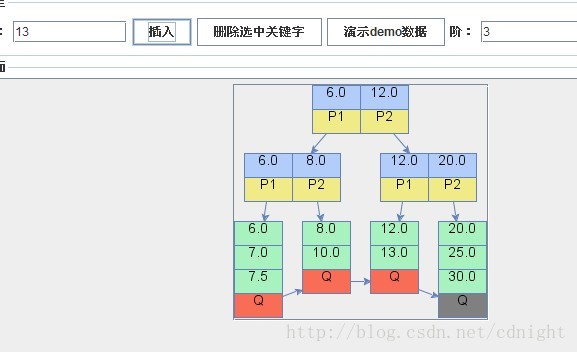
【插入關鍵字13,葉子節點滿足分裂條件,分裂以後遞迴調整b+樹的形狀】
【插入關鍵字6.5,滿足分裂條件,分裂之。】
【刪除操作演示】
【刪除關鍵字12.0,刪除後葉子節點關鍵字數量少於min(min=2),通過檢查可知,右側兄弟有多餘的關鍵字,從右側兄弟那裡借一個關鍵字,具體演算法可以參看我下一篇博文的程式碼,裡面有註釋。】
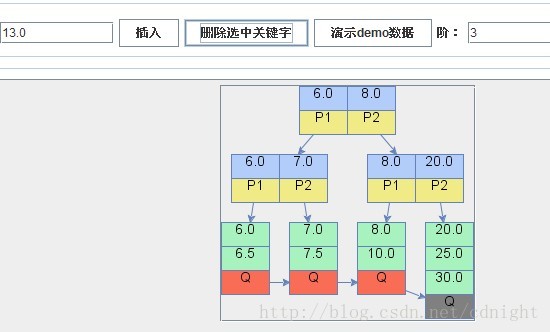
【刪除關鍵字13.0,刪除後關鍵字數量少於min,並且左右兄弟都沒有多餘的關鍵字,所以只能夠合併葉子節點,合併後需要遞迴進行樹形結構調整,具體演算法參看下一篇博文。】
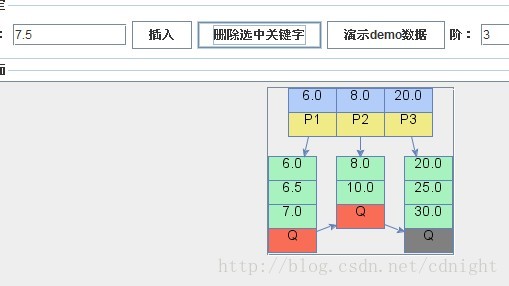
【刪除關鍵字7.5,刪除後滿足合併條件,進行合併並遞迴調整樹形。】
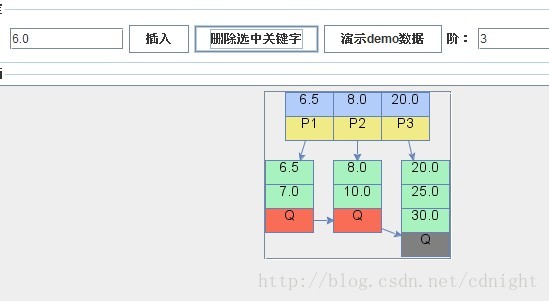
【刪除關鍵字6.0,刪除關鍵字6.0後,關鍵字數量==min,符合樹形結構,但是父節點的關鍵字代表的是界限,就本演算法而言,父親節點的關鍵字要大於或等於它對應子節點或葉子節點的所有關鍵字,所以,這裡必須進行父親節點下界關鍵字的調整,必要時(當最左邊葉子節點的第一個關鍵字改變了的情況下)甚至需要將同一路徑的所有第一個關鍵字都改變,具體演算法參看下一篇博文。】
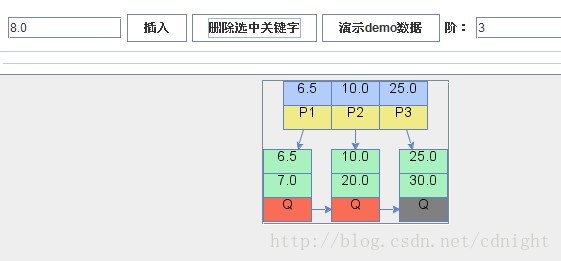
【刪除關鍵字8.0,刪除後需要向右邊兄弟借一個關鍵字。】
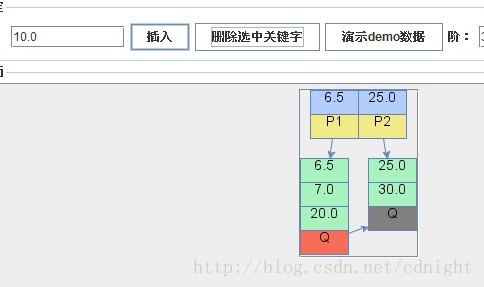
【刪除關鍵字10.0,需要合併。】
【b+樹java版實現的核心程式碼】
package BPlusTree;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class INode {
public boolean isLeaf=false;
public INode parent=null;
public ArrayList<Float> keys=new ArrayList<Float>();
public ArrayList<INode> childNodes=new ArrayList<INode>();
}
package BPlusTree;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class TreeLeaf extends INode {
public ArrayList<Object> values=new ArrayList<Object>();
public TreeLeaf rightBrother=null;
}
package BPlusTree;
public class TreeNode extends INode {
}
package BPlusTree;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class TreeGen {
private int _m=4;//--最大子樹數目
private int _min=2;//--最小關鍵字
public int getM(){
return _m;
}
public int getMin(){
return _min;
}
private INode _rootNode=new TreeLeaf();
public TreeGen(int m){
_m=m;
_min=(int)Math.ceil((double)((double)_m/(double)2));
}
/**
*
* 複製當前的陣列,變成一個不同的值。
* 這個用來記錄上一步驟的結果,免得到時候找不回以前的方法了。
*
* */
public static TreeGen getCopyGen(TreeGen gen ){
TreeGen _gen1=new TreeGen(gen.getM());
ArrayList<Float> arrList=gen.getAllKeyList();
for(float f1:arrList){
_gen1.insert(f1);
}
return _gen1;
}
public void setGen(int m,int min,INode inode){
_m=m;
_min=min;
_rootNode=inode;
}
public INode getRootNode(){
return _rootNode;
}
/**
* b+樹的插入演算法,這裡解釋一下流程:
* 1、當最初插入關鍵字的時候,即根節點就是葉子節點,那麼直接插入,假如插入後根節點的關鍵字數量大於m,那麼需要分裂;
* 2、尋找需要插入到的葉子節點,假如已經包含該關鍵字,報錯,否則插入該關鍵字,檢視關鍵字數量是否達到分裂條件,假如達到,則進行分裂操作。
* 必須注意的是,我這裡的b+樹對於大小的判斷是:第一個子樹的關鍵字必然大於或等於父親的第一個關鍵字,小於父親第二個關鍵字,如此類推,
* 網上的演算法也有第一個子樹的所有關鍵字都小於或等於父親的第一個關鍵字這種。
* 我採用的演算法意味著在處理(插入)一個小於所有關鍵字的關鍵字時候,需要尋找最左邊的葉子節點,插入,然後修改該路徑所有節點的第一個索引為該關鍵字,
* 同時需要進行正常的檢查分裂操作
* */
public boolean insert(float indexNO){
//--假如是前幾次插入,根節點為空或者下面都沒有子樹,那麼就直接變成葉子節點。
if(_rootNode.childNodes.size()<=0){
if(_rootNode.isLeaf==false){
TreeLeaf myRoot=new TreeLeaf();
myRoot.isLeaf=true;
for(float keyNO:_rootNode.keys){
myRoot.keys.add(keyNO);
}
_rootNode=myRoot;
}
//--插入關鍵字。
int indexLOC=-1;
int cindex=0;
for(float f1:_rootNode.keys){
if(f1==indexNO){
return false;//包含該關鍵字,無法插入。
}
if(indexNO>f1){
indexLOC=cindex;
}
if(indexNO<f1){
break;
}
cindex++;
}
_rootNode.keys.add(indexLOC+1, indexNO);
recurse_division_after_insert(_rootNode);
return true;
}
else{
TreeLeaf theLeaf=recursion_search_suitable_leaf(_rootNode, indexNO);
if(theLeaf==null){
return false;
}
//--插入關鍵字。
int indexLOC=-1;
int cindex=0;
for(float f1:theLeaf.keys){
if(f1==indexNO){
return false;//包含該關鍵字,無法插入。
}
if(indexNO>f1){
indexLOC=cindex;
}
if(indexNO<f1){
break;
}
cindex++;
}
insertIndexNO(theLeaf, indexNO);
if(indexLOC==-1){
//--假如是-1,那麼表明它這一條路徑的所有父節點的第一個關鍵字都必須改為當前indexNO
recursion_changeMinimun(theLeaf, indexNO);
}
recurse_division_after_insert(theLeaf);
}
return true;
}
public INode search(float indexNO){
_research_result=null;
recursion_to_serach(_rootNode, indexNO);
return _research_result;
}
private INode _research_result=null;
private void recursion_to_serach(INode currentNode,float indexNO){
if(currentNode==null){
return;
}
if(currentNode.isLeaf==false&¤tNode.childNodes.size()>0){
int indexLoc=-1;
int cindex=0;
for(float key:currentNode.keys){
if(indexNO<key){
break;
}
if(indexNO>=key){
indexLoc=cindex;
}
cindex++;
}
/**
* 假如是-1,表示所有的數都比它大,表明b+樹裡面沒有這個數,請回。
* */
if(indexLoc==-1){
return;
}
else{
recursion_to_serach(currentNode.childNodes.get(indexLoc), indexNO);
return;
}
}
else{
int indexLoc=-1;
int cindex=0;
for(float key:currentNode.keys){
if((float)indexNO==(float)key){
indexLoc=cindex;
_research_result=currentNode;
break;
}
cindex++;
}
}
}
private void recursion_changeMinimun(INode currentNode,float indexNO){
if(currentNode==null){
return;
}
if(currentNode.keys.get(0)!=indexNO){
currentNode.keys.remove(0);
currentNode.keys.add(0, indexNO);
}
recursion_changeMinimun(currentNode.parent, indexNO);
}
private boolean insertIndexNO(INode currentNode,float indexNO){
if(currentNode==null){
return false;
}
int indexLOC=-1;
int cindex=0;
for(float f1:currentNode.keys){
if(f1==indexNO){
return false;
}
if(indexNO>f1){
indexLOC=cindex;
}
if(indexNO<f1){
break;
}
cindex++;
}
currentNode.keys.add(indexLOC+1, indexNO);
return true;
}
private TreeLeaf recursion_search_suitable_leaf(INode currentNode,float indexNO){
if(currentNode==null){
return null;
}
if(currentNode.isLeaf==true||currentNode.childNodes.size()<=0){
return (TreeLeaf)currentNode;
}
int indexLoc=-1;
int cindex=0;
for(float iNO:currentNode.keys){
if(indexNO<iNO){
break;
}
if(indexNO>iNO){
indexLoc=cindex;
}
if(indexNO==iNO){
return null;//---節點裡麵包含該關鍵字,那麼只能說,已經插入同樣的關鍵字了,返回null
}
cindex++;
}
//--假如這個關鍵字是最少的,那麼就直接找到最左邊的葉子節點。
if(indexLoc==-1){
return recursion_getLeftLeaf(currentNode);
}
else{
return recursion_search_suitable_leaf(currentNode.childNodes.get(indexLoc), indexNO);
}
}
private TreeLeaf recursion_getLeftLeaf(INode currentNode){
if(currentNode==null){
return null;
}
if(currentNode.isLeaf==true){
return (TreeLeaf)currentNode;
}
if(currentNode.childNodes.size()<=0){
return null;
}
return recursion_getLeftLeaf(currentNode.childNodes.get(0));
}
/**
* 在插入關鍵字後,需要對當前節點及其父節點進行樹形調整。
* */
private void recurse_division_after_insert(INode currentNode){
//--當前節點符合條件,那麼不用分裂
if(currentNode.keys.size()<=_m){
return;
}
TreeLeaf currentLeaf=null;
TreeNode currentNode2=null;
INode parentNode=currentNode.parent;
if(currentNode.isLeaf==true){
currentLeaf=(TreeLeaf)currentNode;
TreeLeaf rightLeaf=new TreeLeaf();
rightLeaf.parent=currentLeaf.parent;
rightLeaf.isLeaf=true;
rightLeaf.rightBrother=currentLeaf.rightBrother;
currentLeaf.rightBrother=rightLeaf;
int cindex=0;
for(float f1:currentLeaf.keys){
if(cindex>=_min){
rightLeaf.keys.add(f1);
if(currentLeaf.values.size()>cindex){
rightLeaf.values.add(currentLeaf.values.get(cindex));
}
}
cindex++;
}
int theOriginTotal=currentLeaf.keys.size();
for(int i1=theOriginTotal-1;i1>=_min;i1--){
currentLeaf.keys.remove(i1);
if(currentLeaf.values.size()>i1){
currentLeaf.values.remove(i1);
}
}
//---假如父節點為空,那麼直接開一個父節點。
if(currentLeaf.parent==null){
TreeNode theRoot=new TreeNode();
theRoot.keys.add( currentLeaf.keys.get(0));
theRoot.keys.add(rightLeaf.keys.get(0));
theRoot.childNodes.add(currentLeaf);
theRoot.childNodes.add(rightLeaf);
currentLeaf.parent=theRoot;
rightLeaf.parent=theRoot;
_rootNode=theRoot;
return;
}
else{
int cLindex=parentNode.childNodes.indexOf(currentNode);
parentNode.keys.add(cLindex+1, rightLeaf.keys.get(0));
parentNode.childNodes.add(cLindex+1, rightLeaf);
recurse_division_after_insert(parentNode);
return;
}
}
else{
currentNode2=(TreeNode)currentNode;
TreeNode normalNode=currentNode2;
TreeNode rightBrother=new TreeNode();
rightBrother.parent=parentNode;
int originTotal=normalNode.keys.size();
for(int i1=_min;i1<=originTotal-1;i1++){
rightBrother.keys.add(normalNode.keys.get(i1));
normalNode.childNodes.get(i1).parent=rightBrother;
rightBrother.childNodes.add(normalNode.childNodes.get(i1));
}
for(int i1=originTotal-1;i1>=_min;i1--){
normalNode.childNodes.remove(i1);
normalNode.keys.remove(i1);
}
if(parentNode==null){
//--假如父節點為空,那麼只能另起節點分裂了。
TreeNode theRoot=new TreeNode();
theRoot.keys.add(normalNode.keys.get(0));
theRoot.keys.add(rightBrother.keys.get(0));
theRoot.childNodes.add(normalNode);
theRoot.childNodes.add(rightBrother);
normalNode.parent=theRoot;
rightBrother.parent=theRoot;
_rootNode=theRoot;
return;
}
else{
int cLindex=parentNode.childNodes.indexOf(normalNode);
parentNode.keys.add(cLindex+1, rightBrother.keys.get(0));
parentNode.childNodes.add(cLindex+1, rightBrother);
recurse_division_after_insert(parentNode);
return;
}
}
}
/**
* B+樹的刪除有幾種情形(假如這是演算法的話,這就是刪除演算法了)。
* 原則:
* 1、所有的刪除操作都是在葉子節點進行的,每次刪除都請先定位相關葉子節點;
* 2、必須保持b+樹的原則,具體舉例(以本文實現的B+樹演算法而言),除了根節點,所有節點的關鍵字數量必須大於或等於_min,
* 小於或等於_m,當小於_min的時候,可以這樣處理:
* 2A、假如左右葉子節點有多餘的關鍵字,可以向左右借;
* 2B、假如左右節點沒有,那麼只能合併節點,然後遞迴。(這種情況是進行遞迴的唯一情況)。
*
* 其實這些操作與B樹的操作類似。
* */
public boolean delete(float indexNO){
INode currentNode=search(indexNO);
if(currentNode==null){
return false;
}
/**
*假如該節點是根節點,那麼刪了就刪了,不用怕。
* */
if(currentNode.parent==null&¤tNode.childNodes.size()<=0){
int indexLoc=getIndexLocation(currentNode, indexNO);
if(indexLoc==-1){
return false;
}
else{
currentNode.keys.remove(indexLoc);
return true;
}
}
/**
* 假如該節點是根節點,但是並非葉節點----不可能的情況,因為刪除必須從葉節點開始!
* */
else if(currentNode.parent==null&¤tNode.childNodes.size()>0){
return false;
}
/**
* 假如該節點不是根節點,但是也並非葉節點----請明白刪除必須從葉節點開始的含義!
* */
else if(currentNode.parent!=null&¤tNode.childNodes.size()>0){
return false;
}
/**
* 假如該節點是葉子節點。
*
* */
else if(currentNode.childNodes.size()<=0){
/**
* 假如葉子節點的關鍵字數量足夠,那麼直接刪除。
* */
if(currentNode.keys.size()>_min){
int indexLoc=getIndexLocation(currentNode, indexNO);
/**
* 假如刪除的是第一個關鍵字,請注意了,這種時候,它的上一級的第一位都必須更換成新的位置
* */
if(indexLoc==0){
currentNode.keys.remove(indexLoc);
recursion_handler_firstOneDelete(null, currentNode, 0.0f);
return true;
}
/**
* 否則,直接刪除。
* */
else{
currentNode.keys.remove(indexLoc);
return true;
}
}
/**
* 關鍵字數量不足,這時候:
* 1、看看左右節點有沒有可以使用的,有的話,那麼就借用並調整樹形;
* 2、沒有的話就刪除,合併然後遞迴調整樹形。
* */
else{
INode parentNode=currentNode.parent;
int indexLoc=getIndexLocation(currentNode, indexNO);
int cNodePindex=parentNode.childNodes.indexOf(currentNode);
if(cNodePindex==-1){
return false;
}
INode leftBrother=null;
INode rightBrother=((TreeLeaf)currentNode).rightBrother;
if(cNodePindex>0){
leftBrother=parentNode.childNodes.get(cNodePindex-1);
}
/**
* 有左側節點並且左側節點有足夠的關鍵字,借用之。
* */
if(leftBrother!=null&&leftBrother.keys.size()>_min){
currentNode.keys.remove(indexLoc);
currentNode.keys.add(0, leftBrother.keys.get(leftBrother.keys.size()-1));
leftBrother.keys.remove(leftBrother.keys.size()-1);
recursion_handler_firstOneDelete(null, currentNode, 0.0f);
return true;
}
/**
* 有右側節點並且右側節點有足夠的關鍵字,借用之。
* */
else if(rightBrother!=null&&rightBrother.keys.size()>_min){
currentNode.keys.remove(indexLoc);
currentNode.keys.add(rightBrother.keys.get(0));
rightBrother.keys.remove(0);
recursion_handler_firstOneDelete(null, rightBrother, 0.0f);
if(indexLoc==0){
recursion_handler_firstOneDelete(null, currentNode, 0.0f);
}
return true;
}
/**
* 最麻煩的情況也是需要遞迴的情況出現了,左右都沒有足夠的關鍵字,只能合併了,搞不好
* b+樹會層層合併,高度最後減-1。
* */
else{
/**
* 跟左側兄弟合併
* */
if(leftBrother!=null){
currentNode.keys.remove(indexLoc);
if(indexLoc==0){
recursion_handler_firstOneDelete(null, currentNode, 0.0f);
}
for(float f1:currentNode.keys){
leftBrother.keys.add(f1);
}
((TreeLeaf)leftBrother).rightBrother=((TreeLeaf)currentNode).rightBrother;
parentNode.keys.remove(cNodePindex);
parentNode.childNodes.remove(cNodePindex);
recursion_combination(parentNode);
return true;
}
/**
* 跟右側兄弟合併。
* */
else if(rightBrother!=null){
currentNode.keys.remove(indexLoc);
if(indexLoc==0){
recursion_handler_firstOneDelete(null, currentNode, 0.0f);
}
for(float f1:rightBrother.keys){
currentNode.keys.add(f1);
}
((TreeLeaf)currentNode).rightBrother=((TreeLeaf)rightBrother).rightBrother;
parentNode.keys.remove(cNodePindex+1);
parentNode.childNodes.remove(cNodePindex+1);
recursion_combination(parentNode);
return true;
}
else{
return false;
}
}
}
}
/**
* 其他情況不受理。
* */
else{
return false;
}
}
private void recursion_handler_after_deletion(INode curretNode){}
private void recursion_handler_firstOneDelete(INode childNode,INode currentNode,float firstIndexNO){
if(currentNode==null){
return;
}
INode parentNode=currentNode.parent;
/**
* 假如是葉節點,那麼就從這裡開始。
* */
if(currentNode.isLeaf==true){
if(parentNode!=null){
float myFirst=currentNode.keys.get(0);
int pIndex=parentNode.childNodes.indexOf(currentNode);
recursion_handler_firstOneDelete(currentNode,parentNode, myFirst);
}
return;
}
else{
int childIndexLoc=currentNode.childNodes.indexOf(childNode);
if(childIndexLoc==-1){
return;
}
if((float)currentNode.keys.get(childIndexLoc)==firstIndexNO){}
else{
if(childIndexLoc>0){
currentNode.keys.remove(childIndexLoc);
currentNode.keys.add(childIndexLoc,firstIndexNO);
if(parentNode!=null){
float cIndexNO=currentNode.keys.get(0);
recursion_handler_firstOneDelete(currentNode,parentNode, cIndexNO);
}
return;
}
else if(childIndexLoc==0){
currentNode.keys.remove(0);
currentNode.keys.add(0,firstIndexNO);
float cIndexNO=currentNode.keys.get(0);
recursion_handler_firstOneDelete(currentNode, parentNode, cIndexNO);
return;
}
else{
return;
}
}
}
}
private int getIndexLocation(INode currentNode,float indexNO){
int indexLoc=-1;
if(currentNode==null){
return indexLoc;
}
int cindex=0;
for(float f1:currentNode.keys){
if(f1==indexNO){
indexLoc=cindex;
break;
}
cindex++;
}
return cindex;
}
/**
* 當葉子節點需要合併,那麼必須遞迴進行處理合並。
* */
private void recursion_combination(INode currentNode){
if(currentNode==null){
return;
}
INode parentNode=currentNode.parent;
if(currentNode.keys.size()>=_min){
return;
}
/**
* 假如這個節點只有1,這種情況只會發生在剛好分成兩份的根節點被刪除一個然後需要合併,葉子節點合併後的情況,那麼
* 只能rootNode改變一下。
* */
if(currentNode.keys.size()==1&&parentNode==null){
_rootNode=currentNode.childNodes.get(0);
_rootNode.parent=null;
return;
}
/**
* 否則,這個是根節點,有兩個關鍵字是可以的。
* */
if(parentNode==null&¤tNode.keys.size()>=2){
return;
}
INode leftBrother=null;
INode rightBrother=null;
int theCPindex=parentNode.childNodes.indexOf(currentNode);
if(theCPindex==-1){
return;
}
if(theCPindex==0){
rightBrother=parentNode.childNodes.get(1);
}
else if(theCPindex==parentNode.childNodes.size()-1){
leftBrother=parentNode.childNodes.get(theCPindex-1);
}
else{
leftBrother=parentNode.childNodes.get(theCPindex-1);
rightBrother=parentNode.childNodes.get(theCPindex+1);
}
/**
* 假如左側有空餘的關鍵字,那麼就借用。
* */
if(leftBrother!=null&&leftBrother.keys.size()>_min){
currentNode.keys.add(0, leftBrother.keys.get(leftBrother.keys.size()-1));
currentNode.childNodes.add(0,leftBrother.childNodes.get(leftBrother.childNodes.size()-1));
currentNode.childNodes.get(0).parent=currentNode;
leftBrother.keys.remove(leftBrother.keys.size()-1);
leftBrother.childNodes.remove(leftBrother.childNodes.size()-1);
parentNode.keys.remove(theCPindex);
parentNode.keys.add(theCPindex,currentNode.keys.get(0));
return;
}
/**
* 假如右側有空餘關鍵字。
* */
else if(rightBrother!=null&&rightBrother.keys.size()>_min){
currentNode.keys.add(rightBrother.keys.get(0));
currentNode.childNodes.add(rightBrother.childNodes.get(0));
currentNode.childNodes.get(currentNode.childNodes.size()-1).parent=currentNode;
rightBrother.keys.remove(0);
rightBrother.childNodes.remove(0);
parentNode.keys.remove(theCPindex+1);
parentNode.keys.add(theCPindex+1,rightBrother.keys.get(0));
return;
}
/**
* 都沒有多餘的話,只能合併了,需要遞迴檢查。
* */
else{
/**
* 假如左側兄弟有,那麼與左邊兄弟合併。
* */
if(leftBrother!=null){
for(Float key1:currentNode.keys){
leftBrother.keys.add(key1);
}
for(INode tmpNode:currentNode.childNodes){
tmpNode.parent=leftBrother;
leftBrother.childNodes.add(tmpNode);
}
parentNode.keys.remove(theCPindex);
parentNode.childNodes.remove(theCPindex);
/**
* 合併完畢,遞迴到上一級再合併。
* */
recursion_combination(parentNode);
return;
}
/**
* 假如有右邊兄弟,那麼與右邊合併。
* */
else if(rightBrother!=null){
for(Float key1:rightBrother.keys){
currentNode.keys.add(key1);
}
for(INode tmpNode:rightBrother.childNodes){
tmpNode.parent=currentNode;
currentNode.childNodes.add(tmpNode);
}
parentNode.keys.remove(theCPindex+1);
parentNode.childNodes.remove(theCPindex+1);
/**
* 合併完畢,遞迴。
* */
recursion_combination(parentNode);
return;
}
else{
return;
}
}
}
private TreeLeaf _leaf_tmp=null;
private void recursion_search_first_leaf(INode currNode){
if(currNode==null){
return;
}
if(currNode.isLeaf){
_leaf_tmp=(TreeLeaf)currNode;
return;
}
else{
if(currNode.childNodes.size()<=0){
return;
}
else{
recursion_search_first_leaf(currNode.childNodes.get(0));
return;
}
}
}
public TreeLeaf getFirstLeaf(){
_leaf_tmp=null;
recursion_search_first_leaf(_rootNode);
return _leaf_tmp;
}
public ArrayList<Float> getAllKeyList(){
ArrayList<Float> flist=new ArrayList<Float>();
TreeLeaf fLeaf=getFirstLeaf();
while(fLeaf!=null){
for(float f2:fLeaf.keys){
flist.add(f2);
}
fLeaf=fLeaf.rightBrother;
}
return flist;
}
}