棧的定義和實現
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-09-08
棧的定義和實現
前言
- 語言:Java
- 環境:IntelliJ IDEA
- JDK版本:1.8
- 原始碼:GitHub
棧的定義
棧(stack)又名堆疊,它是一種運算受限的線性表。限定僅在表尾進行插入和刪除操作的線性表。這一端被稱為棧頂,相對地,把另一端稱為棧底。向一個棧插入新元素又稱作進棧、入棧或壓棧,它是把新元素放到棧頂元素的上面,使之成為新的棧頂元素;從一個棧刪除元素又稱作出棧或退棧,它是把棧頂元素刪除掉,使其相鄰的元素成為新的棧頂元素。
佇列的特點:
- 先進後出(FILO),先入棧的資料最後出棧,後入棧的資料最先出棧
- 無論是陣列還是連結串列實現,通常需要一個變數(指標)來標記棧頂資料
佇列中的規定:
- 入棧方法名為push
- 出棧方法名為pop
- 指向棧頂的變數(指標)名為top
棧的實現
陣列實現棧
陣列實現佇列的幾種情況:
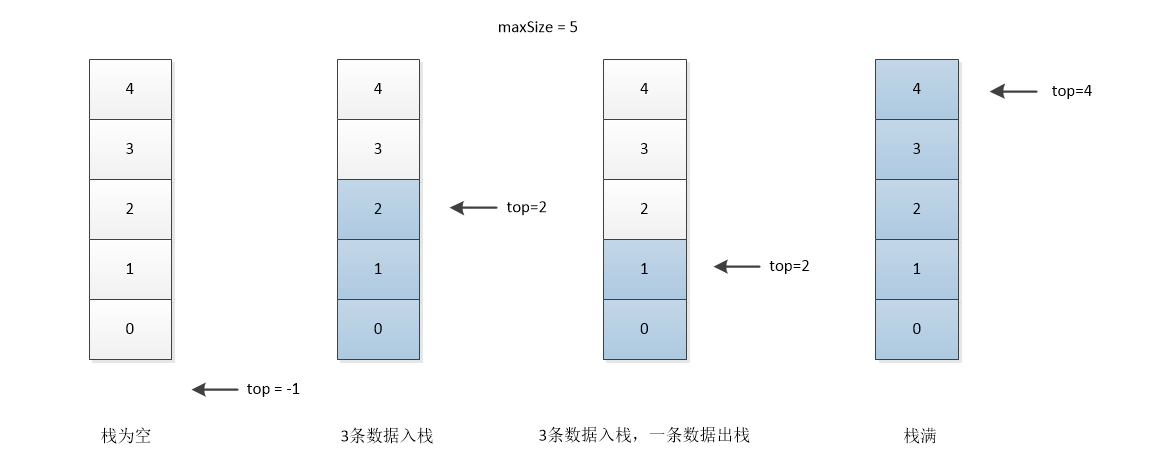
由上面四種情況可得到以下資訊:
- 初始值
top=-1 top指向棧頂資料- 判斷棧為空的條件是
top==-1 - 判斷佇列滿的條件是
top==maxSize-1 - 有效資料個數為
top+1 - 入隊時先增加
top,再在top處插入資料 - 出隊時先取出
top指向的資料,再使top-1
public class ArrayStack { private int maxSize; //棧陣列的最大容量 public int length = 0; //棧中資料的個數 private int top = -1; //棧頂索引,預設為-1,指向最頂端資料 private Employee[] stack; //棧陣列 public ArrayStack(){ this.maxSize = 10; this.stack = new Employee[this.maxSize]; } public ArrayStack(int maxSize){ this.maxSize = maxSize; this.stack = new Employee[this.maxSize]; } /** * 入棧 */ public boolean push(Employee employee){ if (isFull()){ return false; } this.top++; this.stack[this.top] = employee; this.length++; return true; } /** * 出棧 */ public Employee pop(){ if(isEmpty()){ return null; } Employee employee = this.stack[this.top]; this.top--; this.length--; return employee; } /** * 棧是否為空 */ public boolean isEmpty(){ return this.top == -1; } /** * 棧是否已滿 */ public boolean isFull(){ return this.top == this.maxSize-1; } /** * 格式化顯示棧中所有資料 */ public String formatStack(){ if (isEmpty()){ return "[]";} String str = ""; for (int i = this.length-1;i>=0;i--){ str += this.stack[i].toString()+"\n"; } return str; } }
優點:
- 容易理解,便於實現
缺點:
- 棧容納的資料數量有限制
- 直接規定陣列大小不利於記憶體空間的合理利用
連結串列實現棧
連結串列實現佇列的幾種情況:
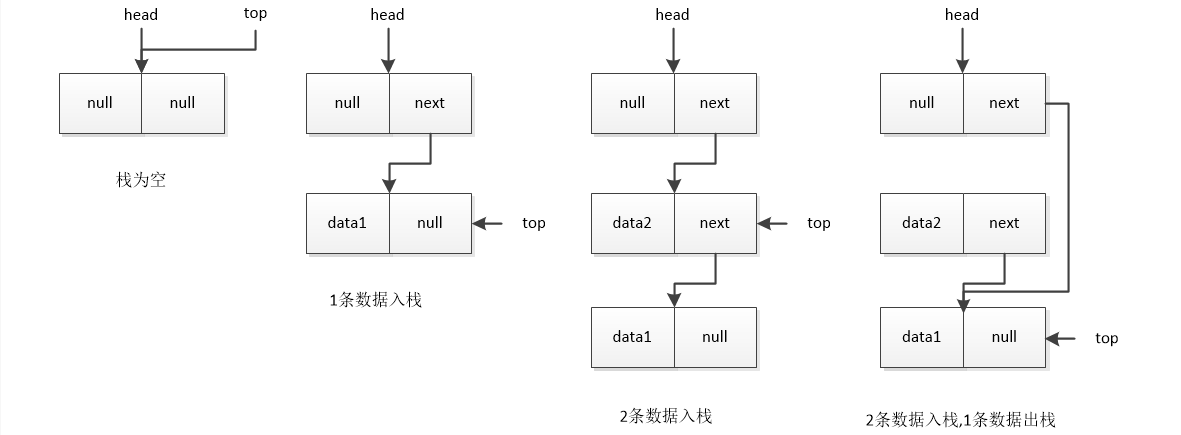
由上面四種情況可得到以下資訊:
- 初始值
top=head - head的next指向棧頂資料
- 判斷棧為空的條件是
head.next==null - 有效資料個數為
length - 入隊時要判斷棧是否為空,若為空,則直接將資料放在head.next,若不為空,則需要將資料插入到head節點之後
- 出隊時先儲存
top指向的資料,再將head.next指向top.next,並將top移動到棧的下一個資料
public class LinkedStack { private Node top; //指向棧頂資料 private Node head; //頭結點 private int length = 0; //棧中資料個數 public LinkedStack(){ this.head = new Node(); this.top = this.head; } /** * 入棧 */ public boolean push(Employee employee){ Node node = new Node(employee); if(isEmpty()){ this.head.next = node; this.top = node; length++; return true; } node.next = this.top; this.head.next = node; this.top = node; length++; return true; } /** * 出棧 */ public Employee pop(){ if(isEmpty()){ return null; } Employee employee = this.top.data; this.head.next = this.top.next; this.top = this.top.next; length--; return employee; } /** * 棧是否為空 */ public boolean isEmpty(){ return this.head.next == null; } /** * 格式化顯示棧中所有資料 */ public String formatStack(){ if (isEmpty()){ return "[]";} Node temp = this.head.next; String str = ""; while (temp!=null){ str += temp.data.toString() + "\n"; temp = temp.next; } return str; } /** * 結點 */ class Node{ private Employee data; private Node next; public Node(){} public Node(Employee employee){ this.data =employee; } } }
優點:
- 棧容量不受限制
- 利用JVM的垃圾回收機制,可以合理的利用
