ArrayList原始碼分析-jdk11 (18.9)
阿新 • • 發佈:2020-07-11
[TOC](ArrayList 原始碼分析-jdk11 (18.9))
## 1.概述
`ArrayList` 是一種變長的集合類,基於定長陣列實現。ArrayList 允許空值和重複元素,當往 ArrayList 中新增的元素數量大於其底層陣列容量時,其會通過擴容機制重新生成一個更大的陣列。另外,由於 ArrayList 底層基於陣列實現,所以其可以保證在 `O(1)` 複雜度下完成隨機查詢操作。其他方面,ArrayList 是非執行緒安全類,併發環境下,多個執行緒同時操作 ArrayList,會引發不可預知的錯誤。
ArrayList 是大家最為常用的集合類,作為一個變長集合類,其核心是擴容機制。所以只要知道它是怎麼擴容的,以及基本的操作是怎樣實現就夠了。本文後續內容將圍繞`jdk11 (18.9)`中ArrayList的原始碼展開敘述。
## 2.原始碼分析
### 2.1引數
1、ArrayList預設容量為10`DEFAULT_CAPACITY註釋`
2、ArrayList並不是在初始化的時候就建立了 `DEFAULT_CAPACITY=10` 的陣列。而是在往裡邊 `add` 第一個資料的時候會擴容到 10 `elementData註釋`
```java
private static final long serialVersionUID = 8683452581122892189L;
/**
* 預設初始化容量
*/
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
/**
* 用於空例項的共享空陣列例項。
*/
private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
/**
* Shared empty array instance used for default sized empty instances. We
* distinguish this from EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA to know how much to inflate when
* first element is added.
* 用於預設大小的空例項的共享空陣列例項。我們將其與EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA分開來,以瞭解新增第一個元素時要膨脹多少。
*/
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
/**
* The array buffer into which the elements of the ArrayList are stored.
* The capacity of the ArrayList is the length of this array buffer. Any
* empty ArrayList with elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
* will be expanded to DEFAULT_CAPACITY when the first element is added.
儲存ArrayList元素的陣列緩衝區,ArrayList的容量是這個陣列緩衝區的長度。當第一個元素被新增的時候,elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA 將被擴充套件成 DEFAULT_CAPACITY
*/
transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access
/**
* The size of the ArrayList (the number of elements it contains).
* 陣列大小
* @serial
*/
private int size;
```
### 2.2 構造方法
ArrayList 有三個構造方法,`無參構造方法`、`構造空的具有特定初始容量值方法`、`構造一個包含指定集合元素的列表,按照集合的迭代器返回它們的順序`。
#### 2.2.1 無參構造方法
注意下圖中的註釋`Constructs an empty list with an initial capacity of ten` 呼叫無參構造方法,預設構造一個容量為10的空list.
```java
/**
* Constructs an empty list with an initial capacity of ten.
*/
public ArrayList() {
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
```
#### 2.2.2 構造空的具有特定初始容量值方法
1、在知道將會向 ArrayList 插入多少元素的情況下 2、在有大量資料寫入 時;**一定要初始化指定長度**。
```java
/**
* Constructs an empty list with the specified initial capacity.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the list
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the specified initial capacity
* is negative
*/
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity > 0) {
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
} else if (initialCapacity == 0) {
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
}
}
```
#### 2.2.3構造一個包含指定集合元素的列表,按照集合的迭代器返回它們的順序
```java
/**
* Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified
* collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's
* iterator.
構造一個包含指定集合元素的列表,按照集合的迭代器返回它們的順序
* @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this list
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public ArrayList(Collection c) {
elementData = c.toArray();
if ((size = elementData.length) != 0) {
// defend against c.toArray (incorrectly) not returning Object[]
//防禦c.toArray(錯誤地)不返回Object[]
// (see e.g. https://bugs.openjdk.java.net/browse/JDK-6260652)
// jdk bug(Arrays內部實現的ArrayList的toArray()方法的行為與規範不一致) 15年修復;
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class);
} else {
// replace with empty array.
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
}
```
#### JDK-6260652 `(see e.g. https://bugs.openjdk.java.net/browse/JDK-6260652)`
簡單來說就是,就是下圖程式碼會產生的情況。
```java
Object[] objects = new String[]{"string"};
objects[0] = 1;
/**
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArrayStoreException: java.lang.Integer
*/
```
#### 產生原因
```java
public Object[] toArray() {
return a.clone();
}
```
Arrays內部實現的ArrayList的toArray()方法的行為與規範不一致。根據JLS規範String[]的clone方法返回的也是String[]型別,所以toArray()方法返回的真實型別是String[],所以個toArray()[0]賦值時可能會導致型別不匹配的錯誤
jdk11中的Arrays內部實現的ArrayList的toArray()方法。所以呼叫copyOf()返回值型別為Object[]
```java
public Object[] toArray() {
return Arrays.copyOf(a, a.length, Object[].class);
}
```
### 2.3常見方法
#### 2.3.1插入
對於陣列(線性表)結構,插入操作分為兩種情況。一種是在元素序列尾部插入,另一種是在元素序列其他位置插入。ArrayList 的原始碼裡也體現了這兩種插入情況,如下:
```java
/**
* This helper method split out from add(E) to keep method
* bytecode size under 35 (the -XX:MaxInlineSize default value),
* which helps when add(E) is called in a C1-compiled loop.
(這個輔助方法是從add(E)方法分離而來的,為了保持方法位元組碼低於35,這將有助於add(E)方法呼叫C1編譯迴圈)
*/
private void add(E e, Object[] elementData, int s) {
if (s == elementData.length)
elementData = grow();
/**
private Object[] grow() {
return grow(size + 1);
}**/
//將新元素插入序列尾部
elementData[s] = e;
size = s + 1;
}
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this
* list. Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and
* any subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices).
在此列表的指定位置插入指定的元素。將當前位於該位置的元素(如果有)和任何後續元素向右移動(在其索引中新增一個元素)
* @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted
* @param element element to be inserted
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public void add(int index, E element) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
modCount++;
final int s;
Object[] elementData;
if ((s = size) == (elementData = this.elementData).length)
elementData = grow();
// 2. 將 index 及其之後的所有元素都向後移一位
System.arraycopy(elementData, index,
elementData, index + 1,
s - index);
// 3. 將新元素插入至 index 處
elementData[index] = element;
size = s + 1;
}
```
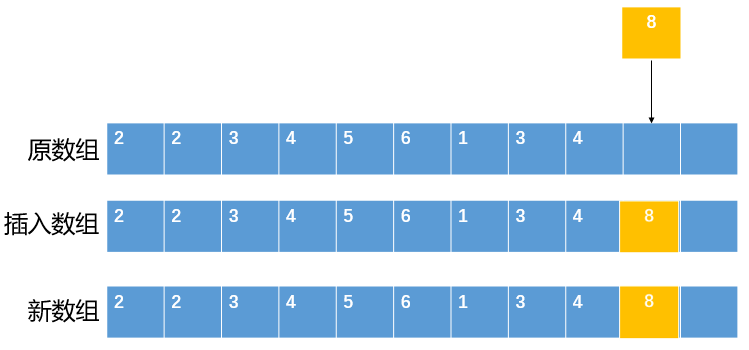
##### 2.3.1.1元素序列尾部插入
1. 檢測陣列是否有足夠的空間插入
2. 將新元素插入至序列尾部
如下圖:
##### 2.3.1.2元素序列指定位置(假設該位置合理)插入
1. 檢測陣列是否有足夠的空間
2. 將 index 及其之後的所有元素向後移一位
3. 將新元素插入至 index 處
如下圖:
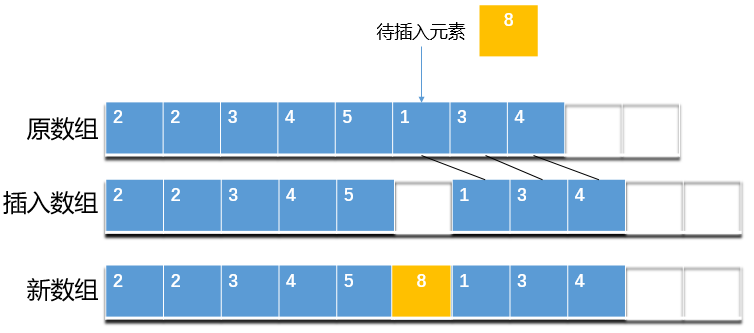
從上圖可以看出,將新元素插入至序列指定位置,需要先將該位置及其之後的元素都向後移動一位,為新元素騰出位置。這個操作的時間`複雜度為O(N)`,頻繁移動元素可能會導致效率問題,特別是集合中元素數量較多時。在日常開發中,若非所需,我們應當儘量避免在大集合中呼叫第二個插入方法。
#### 2.3.2 ArrayList 的擴容機制
對於變長資料結構,當結構中沒有空餘空間可供使用時,就需要進行擴容。在 ArrayList 中,當空間用完,其會按照原陣列空間的1.5倍進行擴容。相關原始碼如下:
```java
/** 擴容的入口方法 */
/**
* Increases the capacity of this {@code ArrayList} instance, if
* necessary, to ensure that it can hold at least the number of elements
* specified by the minimum capacity argument.
*增加{@code ArrayList}例項的容量,如果必需的,以確保它至少可以容納minimum capacity引數指定的元素數
* @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity
*/
public void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity > elementData.length
&& !(elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
&& minCapacity <= DEFAULT_CAPACITY)) {
modCount++;
grow(minCapacity);
}
}
/** 擴容的核心方法 */
/**
* Returns a capacity at least as large as the given minimum capacity.
* Returns the current capacity increased by 50% if that suffices.
* Will not return a capacity greater than MAX_ARRAY_SIZE unless
* the given minimum capacity is greater than MAX_ARRAY_SIZE.
返回至少等於給定最小值的容量容量。返回當前容量增加50%,如果夠了。不會返回大於MAX_ARRAY_SIZE的容量,除非給定的最小容量大於MAX_ARRAY_SIZE
* @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity
* @throws OutOfMemoryError if minCapacity is less than zero
*/
private int newCapacity(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1); //舊容量大小+在舊容量基礎上增加50%(左移1位相當於除以2)
if (newCapacity - minCapacity <= 0) {
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA)
return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
return minCapacity;
}
return (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE <= 0)
? newCapacity
: hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
}
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
// 如果最小容量超過 MAX_ARRAY_SIZE,則將陣列容量擴容至 Integer.MAX_VALUE
return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?
Integer.MAX_VALUE :
MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
```
#### 2.3.3刪除
不同於插入操作,ArrayList 沒有無參刪除方法。所以其只能刪除指定位置的元素或刪除指定元素,這樣就無法避免移動元素(除非從元素序列的尾部刪除)。相關程式碼如下:
```java
/** 刪除指定位置的元素 */
/**
* Removes the element at the specified position in this list.
* Shifts any subsequent elements to the left (subtracts one from their
* indices).
*
* @param index the index of the element to be removed
* @return the element that was removed from the list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E remove(int index) {
Objects.checkIndex(index, size);
final Object[] es = elementData;
// 返回被刪除的元素值
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E oldValue = (E) es[index];
fastRemove(es, index);
return oldValue;
}
/** 從列表中刪除第一個出現的指定元素(如果存在)。
如果列表不包含元素,則不變。更準確地說,刪除索引最低的元素 */
/**
* Removes the first occurrence of the specified element from this list,
* if it is present. If the list does not contain the element, it is
* unchanged. More formally, removes the element with the lowest index
* {@code i} such that
* {@code Objects.equals(o, get(i))}
* (if such an element exists). Returns {@code true} if this list
* contained the specified element (or equivalently, if this list
* changed as a result of the call).
*
* @param o element to be removed from this list, if present
* @return {@code true} if this list contained the specified element
*/
public boolean remove(Object o) {
final Object[] es = elementData;
final int size = this.size;
int i = 0;
// 遍歷陣列,查詢要刪除元素的位置
found: {
if (o == null) {
for (; i < size; i++)
if (es[i] == null)
break found;
} else {
for (; i < size; i++)
if (o.equals(es[i]))
break found;
}
return false;
}
fastRemove(es, i);
return true;
}
/**
* Private remove method that skips bounds checking and does not
* return the value removed.
*/
private void fastRemove(Object[] es, int i) {
modCount++;
final int newSize;
if ((newSize = size - 1) > i)
// 將 index + 1 及之後的元素向前移動一位,覆蓋被刪除值
System.arraycopy(es, i + 1, es, i, newSize - i);
// 將最後一個元素置空,並將 size 值減1
es[size = newSize] = null;
}
```
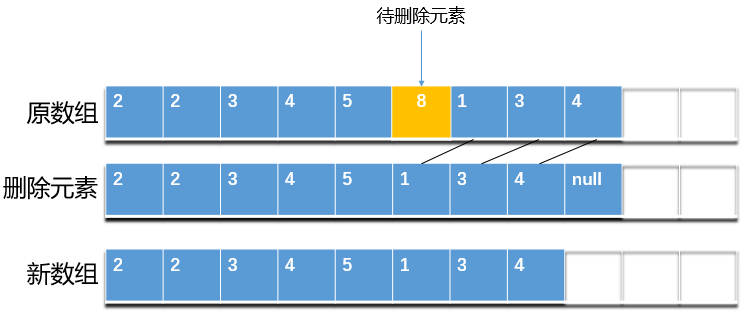
上面的刪除方法並不複雜,這裡以第一個刪除方法為例,刪除一個元素步驟如下:
1. 獲取指定位置 index 處的元素值
2. 將 index + 1 及之後的元素向前移動一位
3. 將最後一個元素置空,並將 size 值減 1
4. 返回被刪除值,完成刪除操作
如下圖:
現在,考慮這樣一種情況。我們往 ArrayList 插入大量元素後,又刪除很多元素,此時底層陣列會空閒處大量的空間。因為 ArrayList 沒有自動縮容機制,導致底層陣列大量的空閒空間不能被釋放,造成浪費。對於這種情況,ArrayList 也提供了相應的處理方法,如下:
```java
/** 將陣列容量縮小至元素數量 */
/**
* Trims the capacity of this {@code ArrayList} instance to be the
* list's current size. An application can use this operation to minimize
* the storage of an {@code ArrayList} instance.
*/
public void trimToSize() {
modCount++;
if (size < elementData.length) {
elementData = (size == 0)
? EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
: Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size);
}
}
```
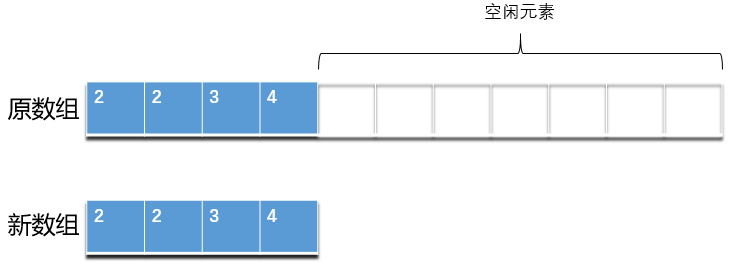
我們可以使用`trimToSize()`手動觸發 ArrayList 的縮容機制,釋放多餘的空間。
#### 2.3.4 遍歷
ArrayList 實現了 RandomAccess 介面(該介面是個標誌性介面),表明它具有`快速隨機訪問`的能力。ArrayList 底層基於陣列實現,所以它可在常數階的時間內完成隨機訪問,效率很高。對 ArrayList 進行遍歷時,一般情況下,我們喜歡使用 foreach 迴圈遍歷,但這並不是推薦的遍歷方式。ArrayList 具有隨機訪問的能力,如果在一些效率要求比較高的場景下,更推薦下面這種方式:
```java
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
list.get(i);
}
```
官網還特意說明了,如果是實現了這個介面的 **List**,那麼使用for迴圈的方式獲取資料會優於用迭代器獲取資料
## 3.其他細節
### 3.1 快速失敗機制
在 Java 集合框架中,很多類都實現了快速失敗機制。該機制被觸發時,會丟擲併發修改異常`ConcurrentModificationException`,這個異常大家在平時開發中多多少少應該都碰到過。關於快速失敗機制,ArrayList 的註釋裡對此做了解釋,這裡引用一下:
> The iterators returned by this class’s iterator() and
> listIterator(int) methods are fail-fast
> if the list is structurally modified at any time after the iterator is
> created, in any way except through the iterator’s own
> ListIterator remove() or ListIterator add(Object) methods,
> the iterator will throw a ConcurrentModificationException. Thus, in the face of
> concurrent modification, the iterator fails quickly and cleanly, rather
> than risking arbitrary, non-deterministic behavior at an undetermined
> time in the future.
上面註釋大致意思是,ArrayList 迭代器中的方法都是均具有快速失敗的特性,當遇到併發修改的情況時,迭代器會快速失敗,以避免程式在將來不確定的時間裡出現不確定的行為。
以上就是 Java 集合框架中引入快速失敗機制的原因,並不難理解,這裡不多說了。
### 3.2 關於遍歷時刪除
遍歷時刪除是一個不正確的操作,即使有時候程式碼不出現異常,但執行邏輯也會出現問題。關於這個問題,阿里巴巴 Java 開發手冊裡也有所提及。這裡引用一下:
> 【強制】不要在 foreach 迴圈裡進行元素的 remove/add 操作。remove 元素請使用 Iterator 方式,如果併發操作,需要對 Iterator 物件加鎖。
相關程式碼(稍作修改)如下:
```j
