並查集(UnionFind)技巧總結
阿新 • • 發佈:2020-09-18
## 什麼是並查集
在電腦科學中,並查集是一種樹型的資料結構,用於處理一些不交集(Disjoint Sets)的合併及查詢問題。有一個聯合-查詢演算法(Union-find Algorithm)定義了兩個用於此資料結構的操作:
- Find:確定元素屬於哪一個子集。它可以被用來確定兩個元素是否屬於同一子集。
- Union:將兩個子集合併成同一個集合。
由於支援這兩種操作,一個不相交集也常被稱為聯合-查詢資料結構(Union-find Data Structure)或合併-查詢集合(Merge-find Set)。
## 並查集可以解決什麼問題
- 組團、配對
- 圖的連通性問題
- 集合的個數
- 集合中元素的個數
## 演算法模板
```
type UnionFind struct {
count int
parent []int
}
func ctor(n int) UnionFind {
uf := UnionFind{
count: n,
parent: make([]int, n),
}
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
uf.parent[i] = i
}
return uf
}
func (uf *UnionFind) find(p int) int {
for p != uf.parent[p] {
uf.parent[p] = uf.parent[uf.parent[p]] // 路徑壓縮
p = uf.parent[p]
}
return p
}
func (uf *UnionFind) union(p, q int) {
rootP, rootQ := uf.find(p), uf.find(q)
if rootP == rootQ {
return
}
uf.parent[rootP] = rootQ
uf.count--
}
```
## 例項
[547. 朋友圈](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/friend-circles/)

題目分析:
題目求的是有多少個朋友圈,也就是求有集合個數,可用並查集解決。
兩重遍歷所有學生,判斷倆倆是否為朋友,如為朋友將加入到集合中。這裡可以通過遍歷二維矩陣的右半邊即可,可降低遍歷數量,從而降低時間複雜度。
程式碼實現:
```
func findCircleNum(M [][]int) int {
n := len(M)
uf := ctor(n)
// 遍歷學生 i, j ,if M[i][j]==1 加入集
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
for j := i + 1; j < n; j++ {
if M[i][j] == 1 {
uf.union(i, j)
}
}
}
// 再返回有多少個集合
return uf.count
}
type UnionFind struct {
parents []int
count int
}
func ctor(n int) UnionFind {
uf := UnionFind{
parents: make([]int, n),
count: n,
}
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
uf.parents[i] = i
}
return uf
}
func (uf *UnionFind) find(p int) int {
for p != uf.parents[p] {
uf.parents[p] = uf.parents[uf.parents[p]]
p = uf.parents[p]
}
return p
}
func (uf *UnionFind) union(p, q int) bool {
rootP, rootQ := uf.find(p), uf.find(q)
if rootP == rootQ {
return false
}
uf.parents[rootP] = rootQ
uf.count--
return true
}
```
複雜度分析:
- 時間複雜度:$O(n^2)$。兩重遍歷用時 $O(n^2)$ ,```uf.union``` 和 ```uf.find``` 的時間複雜度為 $O(1)$ ,所以總的時間複雜度為 $O(n^2)$。
- 空間複雜度:$O(n)$。需要一個 $O(n)$ 大小的空間。
[200. 島嶼數量](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/number-of-islands/)

題目分析:
題目求的是島嶼數量,即集合個數,可用並查集解決。
題目可抽象為遍歷所有網格 ```(i, j)```,如果是陸地(```(i, j) == '1'```),則把其右邊的陸地(```(i+1, j) == '1'```)和下邊的陸地(```(i, j+1) == '1'```)合併到一起;如是水(```(i, j) == '0'```),則把其合併到一個哨兵集合裡。最後返回 ```集合個數 - 1```。
注:這裡關鍵是對於水的處理,把其合併到一個哨兵集合裡,讓水不會單獨存在,從而干擾島嶼個數的判斷。
程式碼實現:
```
func numIslands(grid [][]byte) int {
rows := len(grid)
if rows == 0 {
return 0
}
cols := len(grid[0])
if cols == 0 {
return 0
}
uf := ctor(rows*cols + 1)
guard := rows * cols // 哨兵:用於作為 '0' 的集合
directions := [][]int{[]int{0, 1}, []int{1, 0}}
for i := 0; i < rows; i++ {
for j := 0; j < cols; j++ {
index := i*cols + j
if grid[i][j] == '1' {
for _, direction := range directions {
newI, newJ := i+direction[0], j+direction[1]
if newI < rows && newJ < cols && grid[newI][newJ] == '1' {
newIndex := newI*cols + newJ
uf.union(index, newIndex)
}
}
} else {
uf.union(guard, index)
}
}
}
return uf.count - 1
}
type UnionFind struct {
parents []int
count int
}
func ctor(n int) UnionFind {
uf := UnionFind{parents: make([]int, n), count: n}
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
uf.parents[i] = i
}
return uf
}
func (uf *UnionFind) find(p int) int {
for p != uf.parents[p] {
uf.parents[p] = uf.parents[uf.parents[p]]
p = uf.parents[p]
}
return p
}
func (uf *UnionFind) union(p, q int) bool {
rootP, rootQ := uf.find(p), uf.find(q)
if rootP == rootQ {
return false
}
uf.parents[rootP] = rootQ
uf.count--
return true
}
```
複雜度分析:
- 時間複雜度:$O(n*m)$,其中 ```n``` 和 ```m``` 分別表示二維陣列的行數和列數。
- 空間複雜度:$O(n*m)$。並查集需要 ```n * m``` 大小的陣列空間。
[130. 被圍繞的區域](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/surrounded-regions/)
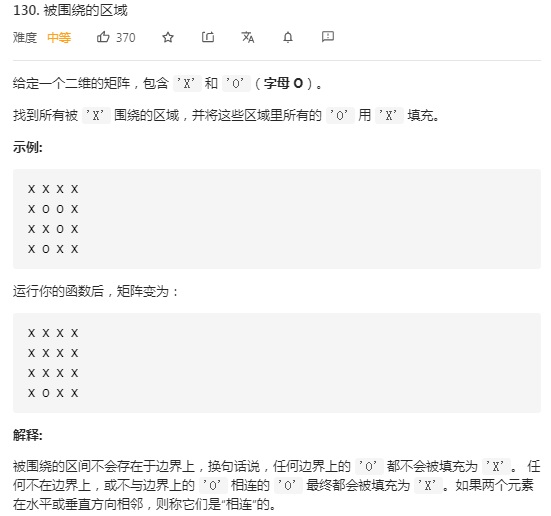
題目分析:
題目可理解為把邊界上的 ```'O'``` 保留,其他都填充為 ```'X'``` ,可以把邊界上的 ```'O'``` 作為一個集合,不是這個集合的填充為 ```'X'``` ,因此可使用並查集解決。
1. 遍歷邊界上的點,把 ```'O'``` 合併到一個哨兵集合裡。
2. 遍歷二維矩陣裡的點,把 ```'O'``` 的右和下合併到一起。
3. 遍歷二維矩陣,把不在哨兵集合裡的全部填充為 ```'X'```
程式碼實現:
```
func solve(board [][]byte) {
n := len(board)
if n == 0 {
return
}
m := len(board[0])
if m == 0 {
return
}
uf := ctor(n*m + 1)
guard := n * m
directions := [][]int{[]int{0, 1}, []int{1, 0}}
getIndex := func(i, j int) int {
return i*m + j
}
// 1. 遍歷邊界上的點,把 'O' 合併到一個哨兵集合裡。
for j := 0; j < m; j++ {
if board[0][j] == 'O' {
uf.union(getIndex(0, j), guard)
}
if board[n-1][j] == 'O' {
uf.union(getIndex(n-1, j), guard)
}
}
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
if board[i][0] == 'O' {
uf.union(getIndex(i, 0), guard)
}
if board[i][m-1] == 'O' {
uf.union(getIndex(i, m-1), guard)
}
}
// 2. 遍歷二維矩陣裡的點,把 ```'O'``` 的右和下合併到一起。
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
for j := 0; j < m; j++ {
if board[i][j] == 'O' {
for _, direction := range directions {
newI, newJ := i+direction[0], j+direction[1]
if newI < n && newJ < m && board[newI][newJ] == 'O' {
uf.union(getIndex(newI, newJ), getIndex(i, j))
}
}
}
}
}
// 3. 遍歷二維矩陣,把不在哨兵集合裡的全部填充為 'X'
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
for j := 0; j < m; j++ {
if !uf.isConnect(getIndex(i, j), guard) {
board[i][j] = 'X'
}
}
}
}
type UnionFind struct {
parents []int
count int
}
func ctor(n int) UnionFind {
uf := UnionFind{
parents: make([]int, n),
count: n,
}
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
uf.parents[i] = i
}
return uf
}
func (uf *UnionFind) find(p int) int {
for p != uf.parents[p] {
uf.parents[p] = uf.parents[uf.parents[p]]
p = uf.parents[p]
}
return p
}
func (uf *UnionFind) union(p, q int) bool {
rootP, rootQ := uf.find(p), uf.find(q)
if rootP == rootQ {
return false
}
uf.parents[rootP] = rootQ
uf.count--
return true
}
func (uf *UnionFind) isConnect(p, q int) bool {
return uf.find(p) == uf.find(q)
}
```
複雜度分析:
- 時間複雜度:$O(n^2)$,其中 ```n``` 和 ```m``` 分別表示二維陣列的行數和列數。
- 空間複雜度:$O(n^2)$。並查集需要 ```n * m``` 大小的陣列空間。
## 總結
1. 要熟練掌握並查集的模板,要能夠快速寫出來。
2. 要掌握並查集的應用場景。例如組團、配對、圖的連通性問題、集合個數、集合中元素的個數等。
3. 對於二維的問題轉一維解決,例如 ```200. 島嶼數量``` 和 ```130. 被圍繞的區域```。
4. 找出元素間的“配對”關係是解決問題的關鍵。例如二維陣列,找當前位置與其右和其下配對。例如 ```200. 島嶼數量``` 和 ```130. 被圍繞的區域```。
## 參考資料
- [並查集 - 力扣](https://leetcode-cn.com/tag/union-find/)
- [並查集概念及用法分析](https://juejin.im/post/6844903954774491149)
