影象分割必備知識點 | Dice損失 理論+程式碼
阿新 • • 發佈:2020-11-25
本文包含程式碼案例和講解,建議收藏,也順便點個贊吧。歡迎各路朋友愛好者加我的微信討論問題:cyx645016617.
在很多關於醫學影象分割的競賽、論文和專案中,發現 Dice 係數(Dice coefficient) 損失函數出現的頻率較多,這裡整理一下。**使用影象分割,繞不開Dice損失,這個就好比在目標檢測中繞不開IoU一樣**。
## 1 概述
Dice損失和Dice係數(Dice coefficient)是同一個東西,他們的關係是:
$$DiceLoss = 1-DiceCoefficient$$
### 1.2 Dice 定義
- Dice係數, 根據 Lee Raymond Dice命名,是一種**集合相似度度量函式**,通常用於計算兩個樣本的相似度(值範圍為 [0, 1])。
$$DiceCoefficient = \frac{2|X \bigcap Y|}{|X| + |Y|}$$
其中$|X| \bigcap |Y|$表示X和Y集合的交集,|X|和|Y|表示其元素個數,**對於分割任務而言,|X|和|Y|表示分割的ground truth和predict_mask**。
此外,**我們可以得到Dice Loss的公式:**
$$DiceLoss = 1- \frac{2|X \bigcap Y|}{|X| + |Y|}$$
## 2 手推案例
這個Dice網上有一個非常好二分類的Dice Loss的手推的案例,非常好理解,過程分成兩個部分:
1. 先計算$|X|\bigcap|Y|$
2. 再計算$|X|$和$|Y|$
計算loss我們必然已經有了這兩個引數,模型給出的output,也就是預測的mask;資料集中的ground truth(GT),也就是真實的mask。
在很多關於醫學影象分割的競賽、論文和專案中,發現 Dice 係數(Dice coefficient) 損失函數出現的頻率較多,這裡整理一下。**使用影象分割,繞不開Dice損失,這個就好比在目標檢測中繞不開IoU一樣**。
## 1 概述
Dice損失和Dice係數(Dice coefficient)是同一個東西,他們的關係是:
$$DiceLoss = 1-DiceCoefficient$$
### 1.2 Dice 定義
- Dice係數, 根據 Lee Raymond Dice命名,是一種**集合相似度度量函式**,通常用於計算兩個樣本的相似度(值範圍為 [0, 1])。
$$DiceCoefficient = \frac{2|X \bigcap Y|}{|X| + |Y|}$$
其中$|X| \bigcap |Y|$表示X和Y集合的交集,|X|和|Y|表示其元素個數,**對於分割任務而言,|X|和|Y|表示分割的ground truth和predict_mask**。
此外,**我們可以得到Dice Loss的公式:**
$$DiceLoss = 1- \frac{2|X \bigcap Y|}{|X| + |Y|}$$
## 2 手推案例
這個Dice網上有一個非常好二分類的Dice Loss的手推的案例,非常好理解,過程分成兩個部分:
1. 先計算$|X|\bigcap|Y|$
2. 再計算$|X|$和$|Y|$
計算loss我們必然已經有了這兩個引數,模型給出的output,也就是預測的mask;資料集中的ground truth(GT),也就是真實的mask。

當然還沒完,還要把結果加和:
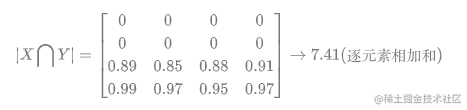
對於二分類問題,GT分割圖是隻有 0, 1 兩個值的,因此可以有效的將在 Pred 分割圖中未在 GT 分割圖中啟用的所有畫素清零. 對於啟用的畫素,主要是懲罰低置信度的預測,較高值會得到更好的 Dice 係數.
關於計算$|X|$和$|Y|$,如下:
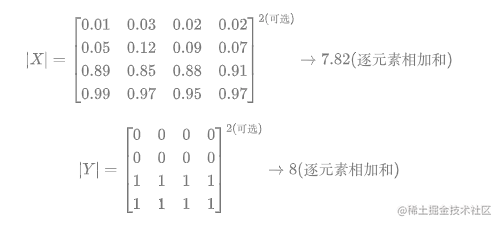
**其中需要注意的是,一半情況下,這個是直接對所有元素求和,當然有對所有元素先平方再求和的做法。總之就這麼多,非常的簡單好用。不過上面的內容是針對分割二分類的情況,對於多分類的情況和二分類基本相同**。
## 3 二分類程式碼實現
在實現的時候,往往會加上一個smooth,防止分母為0的情況出現。所以公式變成:
$$DiceLoss = 1- \frac{2|X \bigcap Y|+smooth}{|X| + |Y|+smooth}$$
**一般smooth為1**
### 3.1 PyTorch實現
先是dice coefficient的實現,pred和target的shape為【batch_size,channels,...】,2D和3D的都可以用這個。
```python
def dice_coeff(pred, target):
smooth = 1.
num = pred.size(0)
m1 = pred.view(num, -1) # Flatten
m2 = target.view(num, -1) # Flatten
intersection = (m1 * m2).sum()
return (2. * intersection + smooth) / (m1.sum() + m2.sum() + smooth)
```
當然dice loss就是1-dice ceofficient,所以可以寫成:
```python
def dice_coeff(pred, target):
smooth = 1.
num = pred.size(0)
m1 = pred.view(num, -1) # Flatten
m2 = target.view(num, -1) # Flatten
intersection = (m1 * m2).sum()
return 1-(2. * intersection + smooth) / (m1.sum() + m2.sum() + smooth)
```
### 3.2 keras實現
```python
smooth = 1. # 用於防止分母為0.
def dice_coef(y_true, y_pred):
y_true_f = K.flatten(y_true) # 將 y_true 拉伸為一維.
y_pred_f = K.flatten(y_pred)
intersection = K.sum(y_true_f * y_pred_f)
return (2. * intersection + smooth) / (K.sum(y_true_f * y_true_f) + K.sum(y_pred_f * y_pred_f) + smooth)
def dice_coef_loss(y_true, y_pred):
return 1. - dice_coef(y_true, y_pred)
```
### 3.3 tensorflow實現
```python
def dice_coe(output, target, loss_type='jaccard', axis=(1, 2, 3), smooth=1e-5):
"""
Soft dice (Sørensen or Jaccard) coefficient for comparing the similarity of two batch of data,
usually be used for binary image segmentation
i.e. labels are binary.
The coefficient between 0 to 1, 1 means totally match.
Parameters
-----------
output : Tensor
A distribution with shape: [batch_size, ....], (any dimensions).
target : Tensor
The target distribution, format the same with `output`.
loss_type : str
``jaccard`` or ``sorensen``, default is ``jaccard``.
axis : tuple of int
All dimensions are reduced, default ``[1,2,3]``.
smooth : float
This small value will be added to the numerator and denominator.
- If both output and target are empty, it makes sure dice is 1.
- If either output or target are empty (all pixels are background), dice = ```smooth/(small_value + smooth)``, then if smooth is very small, dice close to 0 (even the image values lower than the threshold), so in this case, higher smooth can have a higher dice.
Examples
---------
>>> outputs = tl.act.pixel_wise_softmax(network.outputs)
>>> dice_loss = 1 - tl.cost.dice_coe(outputs, y_)
References
-----------
- `Wi
