ElasticSearch 中的 Mapping
阿新 • • 發佈:2021-02-25
> **公號:碼農充電站pro**
> **主頁:**
### 1,ES 中的 Mapping
ES 中的 [Mapping](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.10/mapping.html) 相當於傳統資料庫中的**表定義**,它有以下作用:
- 定義索引中的欄位的名字。
- 定義索引中的欄位的型別,比如字串,數字等。
- 定義索引中的欄位是否建立倒排索引。
一個 Mapping 是針對一個索引中的 Type 定義的:
- ES 中的文件都儲存在索引的 Type 中
- 在 **ES 7.0** 之前,一個索引可以有多個 Type,所以一個索引可擁有多個 Mapping
- 在 **ES 7.0** 之後,一個索引只能有一個 Type,所以一個索引只對應一個 Mapping
通過下面語法可以獲取一個索引的 Mapping 資訊:
```shell
GET index_name/_mapping
```
### 2,ES 欄位的 mapping 引數
欄位的 **mapping** 可以設定很多引數,如下:
- [analyzer](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.10/analyzer.html):指定分詞器,只有 **text** 型別的資料支援。
- [enabled](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.10/enabled.html):如果設定成 `false`,表示資料僅做儲存,不支援搜尋和聚合分析(資料儲存在 **_source** 中)。
- 預設值為 `true`。
- [index](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.10/mapping-index.html):欄位是否建立倒排索引。
- 如果設定成 `false`,表示不建立倒排索引(節省空間),同時資料也**無法被搜尋**,但依然**支援聚合分析**,資料也會出現在 **_source** 中。
- 預設值為 `true`。
- [norms](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.10/norms.html):欄位是否支援算分。
- 如果欄位只用來過濾和聚合分析,而不需要被搜尋(計算算分),那麼可以設定為 `false`,可節省空間。
- 預設值為 `true`。
- [doc_values](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.10/doc-values.html):如果確定不需要對欄位進行排序或聚合,也不需要從指令碼訪問欄位值,則可以將其設定為 `false`,以節省磁碟空間。
- 預設值為 `true`。
- [fielddata](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.10/fielddata.html):如果要對 **text** 型別的資料進行排序和聚合分析,則將其設定為 `true`。
- 預設為 `false`。
- [store](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.10/mapping-store.html):預設值為 `false`,資料儲存在 **_source** 中。
- 預設情況下,欄位值被編入索引以使其可搜尋,但**它們不會被儲存**。這意味著可以查詢欄位,但無法檢索原始欄位值。
- 在某些情況下,儲存欄位是有意義的。例如,有一個帶有標題、日期和非常大的內容欄位的文件,只想檢索標題和日期,而不必從一個大的源欄位中提取這些欄位。
- [boost](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.10/mapping-boost.html):可增強欄位的算分。
- [coerce](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.10/coerce.html):是否開啟資料型別的自動轉換,比如字串轉數字。
- 預設是開啟的。
- [dynamic](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.10/dynamic.html):控制 **mapping** 的自動更新,取值有 `true`,`false`,`strict`。
- [eager_global_ordinals](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.10/eager-global-ordinals.html)
- [fields](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.10/multi-fields.html):多欄位特性。
- 讓**一個欄位**擁有**多個子欄位型別**,使得一個欄位能夠被多個不同的索引方式進行索引。
- copy_to
- format
- ignore_above
- ignore_malformed
- index_options
- index_phrases
- index_prefixes
- meta
- normalizer
- [null_value](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.10/null-value.html):定義 `null` 的值。
- position_increment_gap
- properties
- search_analyzer
- similarity
- term_vector
#### 2.1,fields 引數
讓**一個欄位**擁有**多個子欄位型別**,使得一個欄位能夠被多個不同的索引方式進行索引。
示例 1:
```shell
PUT index_name
{
"mappings": { # 設定 mappings
"properties": { # 屬性,固定寫法
"city": { # 欄位名
"type": "text", # city 欄位的型別為 text
"fields": { # 多欄位域,固定寫法
"raw": { # 子欄位名稱
"type": "keyword" # 子欄位型別
}
}
}
}
}
}
```
示例 2 :
```shell
PUT index_name
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"title": { # 欄位名稱
"type": "text", # 欄位型別
"analyzer": "english", # 欄位分詞器
"fields": { # 多欄位域,固定寫法
"std": { # 子欄位名稱
"type": "text", # 子欄位型別
"analyzer": "standard" # 子欄位分詞器
}
}
}
}
}
}
```
### 3,ES 欄位的資料型別
ES 中欄位的[資料型別](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.10/mapping-types.html)有以下這些:
- 簡單型別
- [Numeric](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.10/number.html)
- [Boolean](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.10/boolean.html)
- [Date](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.10/date.html)
- [Text](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.10/text.html)
- [Keyword](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.10/keyword.html)
- [Binary](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.10/binary.html)
- 等
- 複雜型別
- [Object](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.10/object.html)
- [Arrays](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.10/array.html)
- [Nested](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.10/nested.html):一種物件資料型別。
- [Join](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.10/parent-join.html):為同一索引中的文件定義父/子關係。
- 特殊型別
- [Geo-point](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.10/geo-point.html)
- [Geo-shape](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.10/geo-shape.html)
- [Percolator](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.10/percolator.html)
***text 型別與 keyword 型別***
字串資料可以定義成 **text** 或 **keyword** 型別,**text** 型別資料會做**分詞處理**,而 **keyword** 型別資料不會做分詞處理。
***陣列型別***
對於陣列型別 **Arrays**,ES 並沒有提供專門的陣列型別,但是**任何欄位**都可以包含多個**相同型別**的資料,比如:
```shell
["one", "two"] # 一個字串陣列
[1, 2] # 一個整數陣列
[1, [ 2, 3 ]] # 相當於 [ 1, 2, 3 ]
[{ "name": "Mary", "age": 12 }, { "name": "John", "age": 10 }] # 一個物件陣列
```
當在 Mapping 中檢視這些陣列的型別時,其實**還是陣列中的元素的型別,而不是一個數組型別**。
#### 3.1,Nested 型別
**Nested** 是一種物件型別,它保留了子欄位之間的關係。
##### 1,為什麼需要 Nested 型別
假如我們有如下結構的資料:
```shell
POST my_movies/_doc/1
{
"title":"Speed",
"actors":[ # actors 是一個數組型別,陣列中的元素是物件型別
{
"first_name":"Keanu",
"last_name":"Reeves"
},
{
"first_name":"Dennis",
"last_name":"Hopper"
}
]
}
```
將資料插入 ES 之後,執行下面的查詢:
```shell
# 查詢電影資訊
POST my_movies/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{"match": {"actors.first_name": "Keanu"}},
{"match": {"actors.last_name": "Hopper"}}
]
}
}
}
```
按照上面的查詢語句,我們想查詢的是 `first_name=Keanu` 且 `last_name=Hopper` 的資料,所以我們剛才插入的 **id** 為 1 的文件應該不符合這個查詢條件。
但是在 ES 中執行上面的查詢語句,卻能查出 **id** 為 1 的文件。這是為什麼呢?
這是因為,ES 對於這種 **actors** 欄位這樣的結構的資料,ES 並沒有考慮**物件的邊界**。
實際上,在 ES 內部,**id** 為 1 的那個文件是這樣儲存的:
```shell
"title":"Speed"
"actors.first_name":["Keanu","Dennis"]
"actors.last_name":["Reeves","Hopper"]
```
所以這種儲存方式,並不是我們想象的那樣。
如果我們檢視 ES 預設為上面(id 為 1)結構的資料生成的 mappings,如下:
```shell
{
"my_movies" : {
"mappings" : {
"properties" : {
"actors" : { # actors 內部又嵌套了一個 properties
"properties" : {
"first_name" : { # 定義 first_name 的型別
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {"type" : "keyword", "ignore_above" : 256}
}
},
"last_name" : { # 定義 last_name 的型別
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {"type" : "keyword", "ignore_above" : 256}
}
}
}
}, # end actors
"title" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {"type" : "keyword", "ignore_above" : 256}
}
}
}
}
}
}
```
那如何才能真正的表達一個物件型別呢?這就需要使用到 **Nested** 型別。
##### 2,使用 Nested 型別
**Nested** 型別允許物件陣列中的物件被獨立(看作一個整體)索引。
我們對 **my_movies** 索引設定這樣的 **mappings**:
```shell
DELETE my_movies
PUT my_movies
{
"mappings" : {
"properties" : {
"actors" : {
"type": "nested", # 將 actors 設定為 nested 型別
"properties" : { # 這時 actors 陣列中的每個物件就是一個整體了
"first_name" : {"type" : "keyword"},
"last_name" : {"type" : "keyword"}
}},
"title" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {"keyword":{"type":"keyword","ignore_above":256}}
}
}
}
}
```
寫入資料後,在進行這樣的搜尋,就不會搜尋出資料了:
```shell
# 查詢電影資訊
POST my_movies/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{"match": {"actors.first_name": "Keanu"}},
{"match": {"actors.last_name": "Hopper"}}
]
}
}
}
```
但是這樣的查詢也查不出資料:
```shell
POST my_movies/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{"match": {"actors.first_name": "Keanu"}},
{"match": {"actors.last_name": "Reeves"}}
]
}
}
}
```
##### 3,搜尋 Nested 型別
這是因為,查詢 Nested 型別的資料,要像下面這樣查詢:
```shell
POST my_movies/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"nested": { # nested 查詢
"path": "actors", # 自定 actors 欄位路徑
"query": { # 查詢語句
"bool": {
"must": [
{"match": {"actors.first_name": "Keanu"}},
{"match": {"actors.last_name": "Hopper"}}
]
}
}
} # end nested
}
] # end must
} # end bool
}
}
```
##### 4,聚合 Nested 型別
對 Nested 型別的資料進行聚合,示例:
```shell
# Nested Aggregation
POST my_movies/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"actors": { # 自定義聚合名稱
"nested": { # 指定 nested 型別
"path": "actors" # 聚合的欄位名稱
},
"aggs": { # 子聚合
"actor_name": { # 自定義子聚合名稱
"terms": { # terms 聚合
"field": "actors.first_name", # 子欄位名稱
"size": 10
}
}
}
}
}
}
```
使用普通的聚合方式則**無法工作**:
```shell
POST my_movies/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"actors": { # 自定義聚合名稱
"terms": { # terms 聚合
"field": "actors.first_name",
"size": 10
}
}
}
}
```
#### 3.2,Join 型別
**Nested** 型別的物件與**其父/子級文件**的關係,使得每次文件有更新的時候需要重建**整個文件**(包括根物件和巢狀物件)的索引。
**Join** 資料型別(類似關係型資料庫中的 Join 操作)為同一索引中的文件定義父/子關係。
Join 資料型別可以維護一個父/子關係,從而分離兩個物件,它的優點是:
- 父文件和子文件是兩個完全獨立的文件,這使得更新父文件不會影響到子文件,更新子文件也不會影響到父文件。
**Nested** 型別與 **Join**(Parent/Child) 型別的**優缺點對比**:
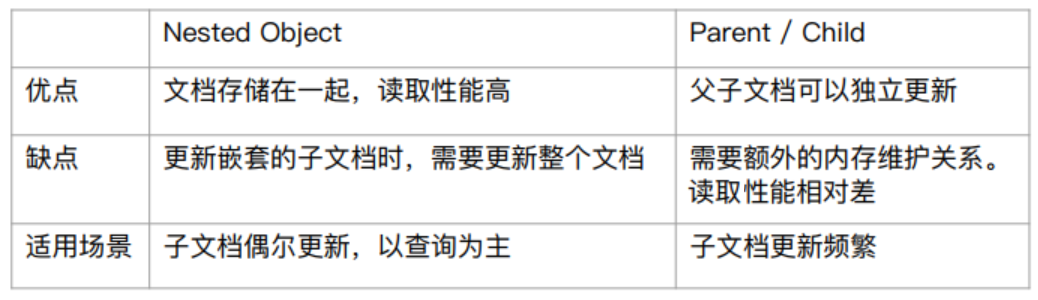
##### 1,定義 Join 型別
定義 Join 型別的語法如下:
```shell
DELETE my_blogs
# 設定 Parent/Child Mapping
PUT my_blogs
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"blog_comments_relation": { # 欄位名稱
"type": "join", # 定義 join 型別
"relations": { # 定義父子關係
"blog": "comment" # blog 表示父級文件,comment 表示子級文件
}
},
"content": {
"type": "text"
},
"title": {
"type": "keyword"
}
}
}
}
```
##### 2,插入 Join 資料
先插入兩個父文件:
```shell
# 插入 blog1
PUT my_blogs/_doc/blog1
{
"title":"Learning Elasticsearch",
"content":"learning ELK @ geektime",
"blog_comments_relation":{
"name":"blog" # name 為 blog 表示父文件
}
}
# 插入 blog2
PUT my_blogs/_doc/blog2
{
"title":"Learning Hadoop",
"content":"learning Hadoop",
"blog_comments_relation":{
"name":"blog" # name 為 blog 表示父文件
}
}
```
插入子文件:
- 其中需要注意 **routing 的值是父文件 id**;
- 這樣可以**確保父子文件被索引到相同的分片**,從而**確保 join 查詢的效能**。
```shell
# 插入comment1
PUT my_blogs/_doc/comment1?routing=blog1 # routing 的值是父文件 id
{ # 確保父子文件被索引到相同的分片
"comment":"I am learning ELK",
"username":"Jack",
"blog_comments_relation":{
"name":"comment", # name 為 comment 表示子文件
"parent":"blog1" # 指定父文件的 id,表示子文件屬於哪個父文件
}
}
# 插入 comment2
PUT my_blogs/_doc/comment2?routing=blog2 # routing 的值是父文件 id
{ # 確保父子文件被索引到相同的分片
"comment":"I like Hadoop!!!!!",
"username":"Jack",
"blog_comments_relation":{
"name":"comment", # name 為 comment 表示子文件
"parent":"blog2" # 指定父文件的 id,表示子文件屬於哪個父文件
}
}
# 插入 comment3
PUT my_blogs/_doc/comment3?routing=blog2 # routing 的值是父文件 id
{ # 確保父子文件被索引到相同的分片
"comment":"Hello Hadoop",
"username":"Bob",
"blog_comments_relation":{
"name":"comment", # name 為 comment 表示子文件
"parent":"blog2" # 指定父文件的 id,表示子文件屬於哪個父文件
}
}
```
##### 3,parent_id 查詢
根據父文件 id 來查詢父文件,**普通的查詢**無法查出子文件的資訊:
```shell
GET my_blogs/_doc/blog2
```
如果想查到子文件的資訊,需要使用 **parent_id** 查詢:
```shell
POST my_blogs/_search
{
"query": {
"parent_id": { # parent_id 查詢
"type": "comment", # comment 表示是子文件,即是表示想查詢子文件資訊
"id": "blog2" # 指定父文件的 id
} # 這樣可以查詢到 blog2 的所有 comment
}
}
```
##### 4,has_child 查詢
**has_child** 查詢可以**通過子文件的資訊,查到父文件資訊**。
```shell
POST my_blogs/_search
{
"query": {
"has_child": { # has_child 查詢
"type": "comment", # 指定子文件型別,表示下面的 query 中的資訊要在 comment 子文件中匹配
"query" : {
"match": {"username" : "Jack"}
} # 在子文件中匹配資訊,最終返回所有的相關父文件資訊
}
}
}
```
##### 5,has_parent 查詢
**has_parent** 查詢可以**通過父文件的資訊,查到子文件資訊**。
```shell
POST my_blogs/_search
{
"query": {
"has_parent": { # has_parent 查詢
"parent_type": "blog", # 指定子文件型別,表示下面的 query 中的資訊要在 blog 父文件中匹配
"query" : {
"match": {"title" : "Learning Hadoop"}
} # 在父文件中匹配資訊,最終返回所有的相關子文件資訊
}
}
}
```
##### 6,通過子文件 id 查詢子文件資訊
普通的查詢**無法查到**:
```shell
GET my_blogs/_doc/comment3
```
需要指定 **routing** 引數,提供父文件 **id**:
```shell
GET my_blogs/_doc/comment3?routing=blog2
```
##### 7,更新子文件資訊
**更新子文件不會影響到父文件**。
示例:
```shell
# URI 中指定子文件 id,並通過 routing 引數指定父文件 id
PUT my_blogs/_doc/comment3?routing=blog2
{
"comment": "Hello Hadoop??",
"blog_comments_relation": {
"name": "comment",
"parent": "blog2"
}
}
```
### 4,ES 動態 Mapping
ES 中的[動態 Mapping](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.1/dynamic-mapping.html) 指的是:
- 在寫入新文件的時候,如果索引不存在,ES 會自動建立索引。
- **動態 Mapping** 使得我們可以不定義 Mapping,ES 會自動根據文件資訊,推斷出欄位的型別。
- 但有時候也會**推斷錯誤**,不符合我們的預期,比如地理位置資訊等。
ES 型別的[自動識別規則](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.1/dynamic-field-mapping.html)如下:
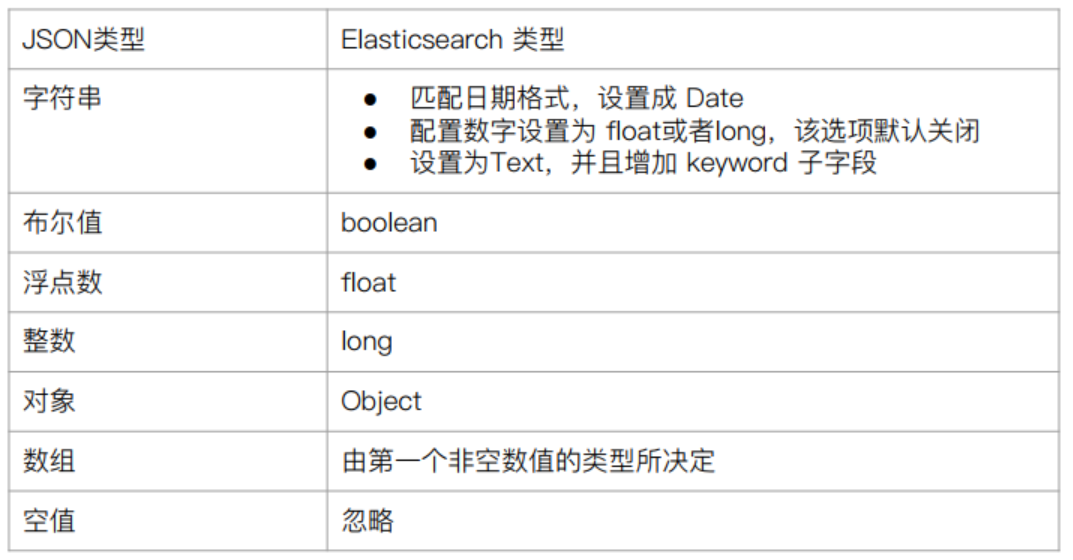
### 5,修改文件欄位型別
欄位型別是否能夠修改,分兩種情況:
- 對於新增欄位:
- 如果 `mappings._doc.dynamic` 為 `ture`,當有新欄位寫入時,`Mappings` 會自動更新。
- 如果 `mappings._doc.dynamic` 為 `false`,當有新欄位寫入時,`Mappings` 不會更新;新增欄位不會建立倒排索引,但是資訊會出現在 `_source` 中。
- 如果 `mappings._doc.dynamic` 為 `strict`,當有新欄位寫入時,寫入失敗。
- 對於已有欄位:
- 欄位的型別**不允許**再修改。因為如果修改了,會導致已有的資訊無法被搜尋。
- 如果希望修改欄位型別,需要 `Reindex` 重建索引。
`dynamic` 有 3 種取值,使用下面 API 可以修改 `dynamic` 的值:
```shell
PUT index_name/_mapping
{
"dynamic": false/true/strict
}
```
通過下面語法可以獲取一個索引的 Mapping:
```shell
GET index_name/_mapping
```
### 6,自定義 Mapping
自定義 Mapping 的語法如下:
```shell
PUT index_name
{
"mappings" : {
# 定義
}
}
```
自定義 Mapping 的小技巧:
1. 建立一個臨時索引,寫入一些測試資料
2. 獲取該索引的 Mapping 值,修改後,使用它建立新的索引
3. 刪除臨時索引
**Mappings** 有很多引數可以設定,可以參考[這裡](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.10/mapping-params.html)。
#### 6.1,一個巢狀物件的 mappings
如果我們要在 ES 中插入如下結構的資料:
```shell
PUT blog/_doc/1
{
"content":"I like Elasticsearch",
"time":"2019-01-01T00:00:00",
"user": { # 是一個物件型別
"userid":1,
"username":"Jack",
"city":"Shanghai"
}
}
```
其中的 **user** 欄位是一個**物件型別**。
這種結構的資料對應的 **mappings** 應該像下面這樣定義:
```shell
PUT /blog
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"content": {
"type": "text"
},
"time": {
"type": "date"
},
"user": { # user 內部又嵌套了一個 properties
"properties": {
"city": {
"type": "text"
},
"userid": {
"type": "long"
},
"username": {
"type": "keyword"
}
}
}
}
}
}
```
#### 6.2,一個物件陣列的 mappings
如果我們要在 ES 中插入如下結構的資料:
```shell
POST my_movies/_doc/1
{
"title":"Speed",
"actors":[ # actors 是一個數組型別,陣列中的元素是物件型別
{
"first_name":"Keanu",
"last_name":"Reeves"
},
{
"first_name":"Dennis",
"last_name":"Hopper"
}
]
}
```
其中的 **actors** 欄位是一個數組型別,陣列中的元素是物件型別。
像這種結構的資料對應的 **mappings** 應該像下面這樣定義:
```shell
PUT my_movies
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"actors": { # actors 欄位
"properties": { # 嵌入了一個 properties
"first_name": {"type": "keyword"},
"last_name": {"type": "keyword"}
}
},
"title": {
"type": "text",
"fields": {
"keyword": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 256
}
}
}
}
}
}
```
### 7,控制欄位是否可被索引
可以通過設定欄位的 [index](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.10/mapping-index.html) 值,來控制某些欄位是否可被搜尋。
`index` 有兩種取值:`true / false`,預設為 `true`。
當某個欄位的 `index` 值為 `false` 時,ES 就不會為該欄位建立倒排索引(節省空間),該欄位也不能被搜尋(如果搜尋的話會**報錯**)。
設定語法如下:
```shell
PUT index_name
{
"mappings" : { # 固定寫法
"properties" : { # 固定寫法
"firstName" : { # 欄位名
"type" : "text"
},
"lastName" : { # 欄位名
"type" : "text"
},
"mobile" : { # 欄位名
"type" : "text",
"index": false # 設定為 false
}
}
}
}
```
### 8,控制倒排索引項的內容
我們可以通過設定 [index_options](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.10/index-options.html) 的值來控制**倒排索引項**的內容,它有 4 種取值:
- `docs`:只記錄`文件 id`
- `freqs`:記錄`文件 id` 和 `詞頻`
- `positions`:記錄`文件 id`,`詞頻` 和 `單詞 position`
- `offsets`:記錄`文件 id`,`詞頻`,`單詞 position` 和 `字元 offset`
`Text` 型別的資料,`index_options` 的值**預設**為 `positions`;`其它`型別的資料,`index_options` 的值**預設**為 `docs`。
>
