距離變換
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-11-13
分享一下我老師大神的人工智慧教程!零基礎,通俗易懂!http://blog.csdn.net/jiangjunshow
也歡迎大家轉載本篇文章。分享知識,造福人民,實現我們中華民族偉大復興!
距離變換和線性濾波器,形態學變換處於平等位置,是影象處理的一種方法,通過使用兩遍掃描光柵演算法可以快速計算到曲線或點集的距離。
應用:
水平集
快速斜切匹配
影象拼接
影象混合的羽化
臨近點配準
方法:
首先對影象進行二值化處理,然後給每個畫素賦值為離它最近的背景畫素點與其距離(Manhattan距離or歐氏距離),得到distance metric(距離矩陣),那麼離邊界越遠的點越亮。
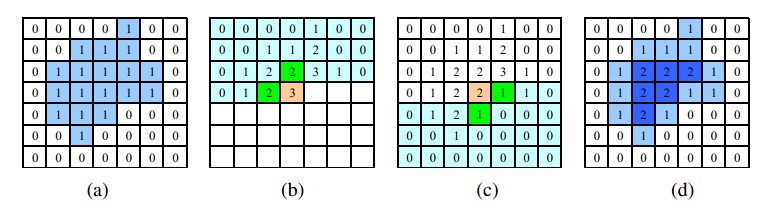
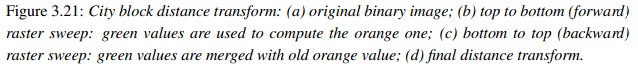
實現:
Imgori=imread('test.jpg');I=rgb2gray(Imgori);subplot(2,3,1);imshow(I);title('origin');Threshold=100;F=I>Threshold;%front%B=I<=Threshold;%backgroundsubplot(2,3,4);imshow(F,[]);title('binary'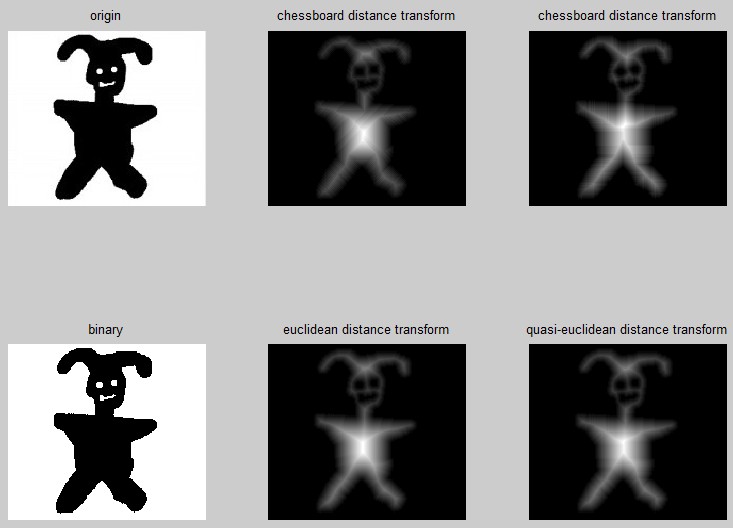 
或者單純想看這幾個距離函式的區別可以用以下code:
bw = zeros(200,200); bw(50,50) = 1; bw(50,150) = 1;bw(150,100) = 1;D1 = bwdist(bw,'euclidean');D2 = bwdist(bw,'cityblock');D3 = bwdist(bw,'chessboard');D4 = bwdist(bw,'quasi-euclidean');figuresubplot(2,2,1), subimage(mat2gray(D1)), title('Euclidean')hold on, imcontour(D1)subplot(2,2,2), subimage(mat2gray(D2)), title('City block')hold on, imcontour(D2)subplot(2,2,3), subimage(mat2gray(D3)), title('Chessboard')hold on, imcontour(D3)subplot(2,2,4), subimage(mat2gray(D4)), title('Quasi-Euclidean')hold on, imcontour(D4)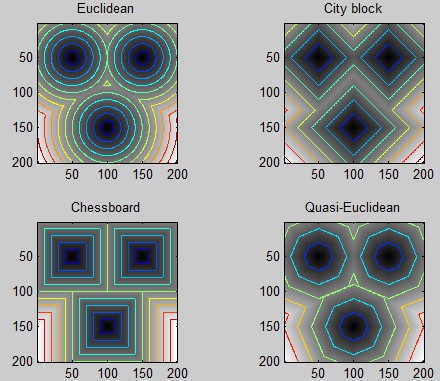
給我老師的人工智慧教程打call!http://blog.csdn.net/jiangjunshow

