Huffman編碼的實現
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-11-17
Huffman編碼的實現
哈夫曼編碼(Huffman Coding),又稱霍夫曼編碼,是一種編碼方式,哈夫曼編碼是可變字長編碼(VLC)的一種。Huffman於1952年提出一種編碼方法,該方法完全依據字元出現概率來構造異字頭的平均長度最短的碼字,有時稱之為最佳編碼,一般就叫做Huffman編碼(有時也稱為霍夫曼編碼)。
最小堆的實現
#include<iostream> #include<vector> #include<string.h> #include<utility> using namespace std; template<class T> class Heap { public: Heap() {} Heap(const T* array, size_t size) { v.resize(size); for (size_t i = 0; i < size; ++i) { v[i] = array[i]; } _CreateHeap(); } //插入元素 void Push(T data) { v.push_back(data); if (v.size() < 2) return; _AdjustUp(v.size() - 1); } //刪除元素 T Pop() { if (!v.empty()) { T temp = v[0]; size_t last = v.size() - 1; swap(v[last], v[0]); v.pop_back(); _AdjustDown(0); return temp; } } //判斷堆是否為空 bool Empty() { return v.empty(); } //求堆的大小 size_t Size() { return v.size(); } //取堆頂層元素 T Top() { return v[0]; } private: //實現最小堆 void _CreateHeap() { if (v.size() <= 1) return; int root = (v.size() - 1 - 1) >> 1; for (; root >= 0; root--) { _AdjustDown(root); } } //向下調整 void _AdjustDown(size_t parent) { size_t child = parent * 2 + 1; size_t size = v.size(); while (child<size) { if (child + 1 < size&&v[child] > v[child + 1]) child += 1; if (v[parent] > v[child]) { swap(v[parent], v[child]); parent = child; child = parent * 2 + 1; } else { return; } } } //向上調整 void _AdjustUp(size_t child) { size_t parent = (child - 1) >> 1; while (0 != child) { if (v[parent] > v[child]) { swap(v[parent], v[child]); child = parent; parent = (child - 1) >> 1; } else return; } } private: vector<T> v; };
Huffman編碼的實現
#include "MinHeap.h" #include <string> template <typename E> class HuffNode { public: virtual int getWeight() = 0;//獲取當前結點的頻率 virtual bool isLeaf() = 0;//判斷是否為葉子結點 //找到結點對應的哈夫曼編碼,並運用兩個向量建立對應的哈夫曼編碼表,再用一個向量來儲存對應的頻率。 virtual void findNode(string code, vector<char> &nameTable, vector<string>&codeTable, vector<int>&fre) = 0; //找到電文對應的值,把電文翻譯為對應的值 virtual void help(HuffNode *root, string str, int &poi) = 0; }; template <typename E> class LeafNode : public HuffNode<E> { public: E value;//值 int weight;//頻率 LeafNode(const E&val, int freq) { value = val; weight = freq; } //獲取當前結點的頻率 int getWeight() { return weight; } //找到結點對應的哈夫曼編碼,並運用兩個向量建立對應的哈夫曼編碼表,再用一個向量來儲存對應的頻率。 void findNode(string code, vector<char> &nameTable, vector<string> &codeTable, vector<int>&fre) { if (value != NULL) { //如果是非空的葉子結點,把值,編碼,頻率儲存進向量 nameTable.push_back(value); codeTable.push_back(code); fre.push_back(weight); } } //判斷是否為葉子結點 bool isLeaf() { return true; } //找到電文對應的值,把電文翻譯為對應的值 void help(HuffNode *root, string str, int &poi) { //如果是葉子結點,把對應的值輸出 cout << value << " "; //如果還有電文未翻譯,再從根節點進行遍歷 if (poi <str.length()) root->help(root, str, poi); } }; template <typename E> class IntlNode :public HuffNode<E> { public: HuffNode<E> *lc; HuffNode<E> *rc; int weight; IntlNode(HuffNode<E>*l, HuffNode<E>*r) { weight = l->getWeight() + r->getWeight(); lc = l; rc = r; } //判斷是否為葉子結點 bool isLeaf() { return false; } //設立左子樹 void setLeft(HuffNode<E>* b) { lc = (HuffNode<E>*) b; } //設立右子樹 void setRight(HuffNode<E>* b) { rc = (HuffNode<E>*) b; } //獲取當前結點的頻率 int getWeight() { return weight; } //找到結點對應的哈夫曼編碼,並運用兩個向量建立對應的哈夫曼編碼表,再用一個向量來儲存對應的頻率。 void findNode(string code, vector<char> &nameTable, vector<string> &codeTable, vector<int>&fre) { string lNewCode = code + '0';//沿左子結點對應編碼加1 string rNewCode = code + '1';//沿右子結點對應編碼加0 //如果是中間節點,則先進行左子樹的迭代,再進行右子樹的迭代。 lc->findNode(lNewCode, nameTable, codeTable, fre); rc->findNode(rNewCode, nameTable, codeTable, fre); } //找到電文對應的值,把電文翻譯為對應的值 void help(HuffNode *root, string str, int& poi) { //是中間節點時,當前電文為0則往左遞迴,1則往右。 if (str[poi++] == '0') { lc->help(root, str, poi); } else { rc->help(root, str, poi); } } }; template <typename E> class HuffTree { private: public: HuffNode<E>* Root;//根節點 HuffTree() { Root = NULL; } HuffTree(HuffTree<E>* root) { Root = root; } HuffTree(E val, int freq) { Root = new LeafNode<E>(val, freq); } HuffTree(HuffTree<E>* l, HuffTree<E>*r) { Root = new IntlNode<E>(l->root(), r->root()); } //返回根節點 HuffNode<E>* root() { return Root; } //返回頻率 int weight() { return Root->getWeight(); } //運算子過載 bool operator <=(HuffTree<E> &r) { return weight() <= r.weight(); } bool operator <(HuffTree<E> &r) { return weight()<r.weight(); } bool operator >=(HuffTree<E> &r) { return weight() >= r.weight(); } bool operator >(HuffTree<E> &r) { return weight()>r.weight(); } }; //構建哈夫曼樹 template <typename E> HuffTree<E>* buildHuff(Heap<HuffTree<E>> &minHeap, string str, vector<char> & str1, vector<string> & str2, vector<int>&fre) { HuffTree<E> *temp1, *temp2, *temp3 = NULL;//最小堆中的最小的兩個樹,以及它們合成的新樹 while (minHeap.Size() > 1) { temp1 = &minHeap.Pop(); temp2 = &minHeap.Pop(); //移出最小堆中的最小的兩個樹 HuffTree<E> *temp3 = new HuffTree<E>(temp1, temp2);//把它們合成為新樹 minHeap.Push(*temp3); //把它們合成的新樹插入最小堆中 } //生成哈夫曼編碼 createNode(dynamic_cast< IntlNode<char> *>(minHeap.Top().root()), str, str1, str2, fre); return temp3; }; template <typename E> void createNode(HuffNode<E> *node, string code, vector<char> &nameTable, vector<string> &codeTable, vector<int> &fre) { if (node != NULL) { node->findNode(code, nameTable, codeTable, fre); } };
測試函式
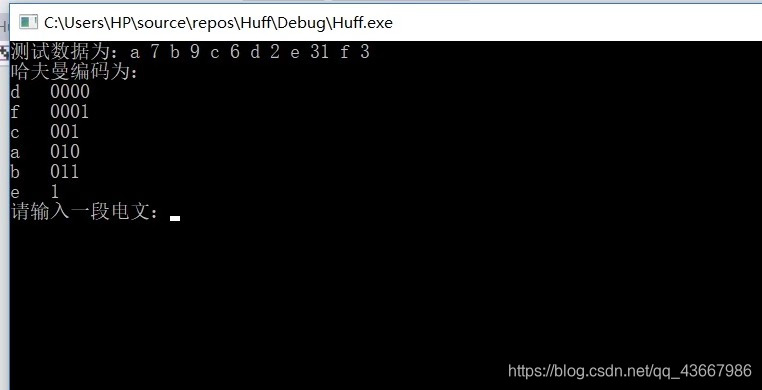
int main() { HuffTree<char> a('a', 7); HuffTree<char> b('b', 9); HuffTree<char> c('c', 6); HuffTree<char> d('d', 2); HuffTree<char> e('e', 31); HuffTree<char> f('f', 3); HuffTree<char> min[6] = { a,b,c,d,e,f }; Heap<HuffTree<char>> heap(min, 6); //cout<<heap.Top().weight()<<endl; //cout << heap.Size(); string str; vector<char> str1; vector<string> str2; vector<int> fre; HuffTree<char> *final(buildHuff(heap, str, str1, str2, fre)); cout << "測試資料為:a 7 b 9 c 6 d 2 e 31 f 3" << endl; cout << "哈夫曼編碼為:" << endl; for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) { cout << str1[i] << " " << str2[i] << endl; } string temp; cout << "請輸入一段電文:"; cin >> temp; int curr = 0; heap.Top().root()->help(heap.Top().root(), temp, curr); cout << "平均長度為"; double sum = 0; for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) { sum += str2[i].length()*fre[i]; } cout << sum << "/";; cout << heap.Top().root()->getWeight() << "="; cout << sum / heap.Top().root()->getWeight(); //cout << heap.root().weight(); //cout << endl; //cout << heap.deleteTop().weight() << endl; }
實驗結果