201771010137 趙棟 《第十二週學習總結》
一:理論部分
1.(1) 使用者介面(User Interface)使用者與計算機系統(各種程式)互動的介面
(2)圖形使用者介面(Graphical User Interface)以圖形方式呈現的使用者介面
2.AWT:Java 的抽象視窗工具箱( Abstract WindowToolkit, AWT)包含在java.awt包中,它提供了許多用來設計GUI的元件類和容器類。
. AWT庫處理使用者介面元素的方法:把圖形元素的建立和行為委託給本地GUI工具箱進行處理。
. 應用AWT編寫依賴於本地使用者介面元素GUI會暴露出一些缺陷。例如,選單、滾動條和文字域這些
使用者介面元素,在不同的平臺上,操作行為上存在一些微妙的差異。
3.Swing:
Swing使用者介面庫是非基於對等體的GUI工具箱。
Swing具有更豐富並且更方便的使用者介面元素集合。
Swing對底層平臺的依賴很少,因此與平臺相關的bug很少。
Swing會帶來交叉平臺上的統一視覺體驗。
Swing類庫被放在javax.swing包裡。
4.AWT與Swing的關係
大部分AWT元件都有其Swing的等價元件。
Swing元件的名字一般是在AWT元件名前面新增一個字母“J”,如:JButton,JFrame,JPanel等。
二..建立框架
1.元件:構成圖形使用者介面的元素,拿來即用用圖形表示(能在螢幕上顯示,能和使用者進行互動)
2.通常把由Component類的子類或間接子類建立的物件稱為一個元件。
3.容器:容器是Java中能容納和排列元件的元件。常用的容器是框架(Frame,JFrame)
例:Frame fra = new Frame(“這是一個視窗”);
4.新增元件:
Container類提供了一個方法add(),用來在容器類元件物件中新增其他元件。
容器本身也是一個元件,可以把一個容器新增到另一個容器裡,實現容器巢狀。
5.框架(Frame)的建立:
(1)建立空框架:在Java中,常採用框架(Frame)建立初始介面,即GUI的頂層視窗。
AWT庫中有一個基於對等體的Frame類。該類的Swing版本為JFrame,JFrame是Frame子類。
(2)框架定位與框架屬性:
定位:
—常用Component類的setLocation和setBounds方法
常用屬性
—Title:框架標題
—IconImage:框架圖示
(3)確定框架的大小:通過呼叫Toolkit類的方法來得到螢幕尺寸資訊
6.在元件中顯示資訊
在AWT中可呼叫add()方法把元件直接新增到AWTFrame中,在Swing中元件則新增到內容窗格里。
其中內容窗格是用來新增元件的,新增程式碼如下:
Container contentPane = getContentPane();
Component c=…;contentPane.add(c);. 使用者也可以自行建立一個元件類,並在元件上進行繪製,此時需要過載paintComponent()。
使用者的自建元件也可新增到內容窗格里。
. paintComponent(Graphics g)定義在JComponent類中,該方法在視窗需要重新繪圖時(如擴大視窗或極小化視窗),被系統自動呼叫
.. paintComponent()方法被呼叫時,系統就自動產生一個Graphics型別的引數,傳遞給paintComponent方法中的引數g。
元件的啟用與可見性:
public void setEnabled(boolean b):設定元件是否可被啟用。
當引數b取值true時,元件可以被啟用。
當引數b取值false 時,元件不可啟用。
預設情況下,元件是可以被啟用的。
public void setVisible(boolean b):設定元件在該容器中的可見性。
當b取值true時,元件在容器中可見。
當b取值false時,元件在容器中不可見。
除了Window型元件外,其它型別元件預設是可見的。
實驗十二 圖形程式設計
實驗時間 2018-11-14
1、實驗目的與要求
(1) 掌握Java GUI中框架建立及屬性設定中常用類的API;
(2) 掌握Java GUI中2D圖形繪製常用類的API;
(3) 瞭解Java GUI中2D圖形中字型與顏色的設定方法;
(4) 瞭解Java GUI中2D影象的載入方法。
2、實驗內容和步驟
實驗1: 匯入第10章示例程式,測試程式並進行程式碼註釋。
測試程式1:
l 執行下列程式,觀察程式執行結果。
| import javax.swing.*; public class SimpleFrameTest { public static void main(String[] args) { JFrame frame = new JFrame(); frame.setBounds(0, 0,300, 200); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.setVisible(true); } } |
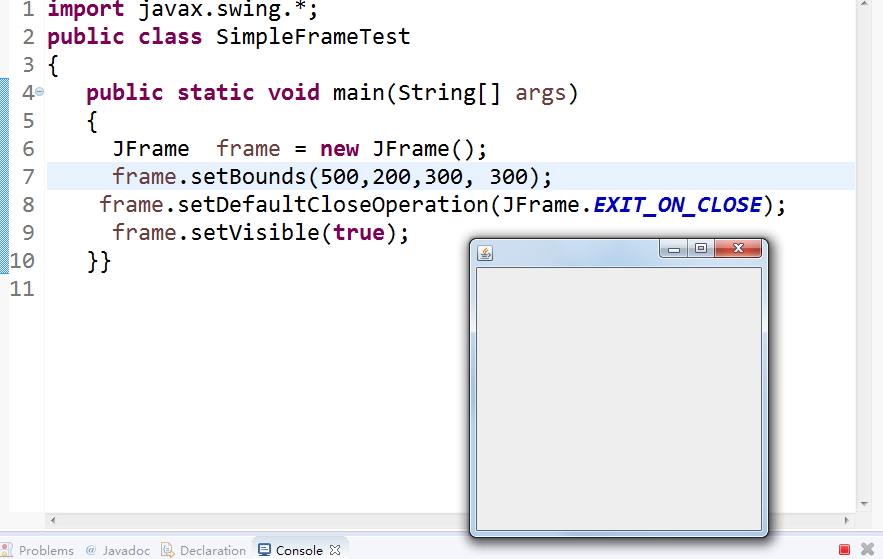
l 在elipse IDE中除錯執行教材407頁程式10-1,結合程式執行結果理解程式;與上面程式對比,思考異同;

import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
/**
* @version 1.33 2015-05-12
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class SimpleFrameTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
EventQueue.invokeLater(() ->
{
SimpleFrame frame = new SimpleFrame();
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
}
class SimpleFrame extends JFrame
{
private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 300;
private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 200;
public SimpleFrame()
{
setSize(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT);
}
}

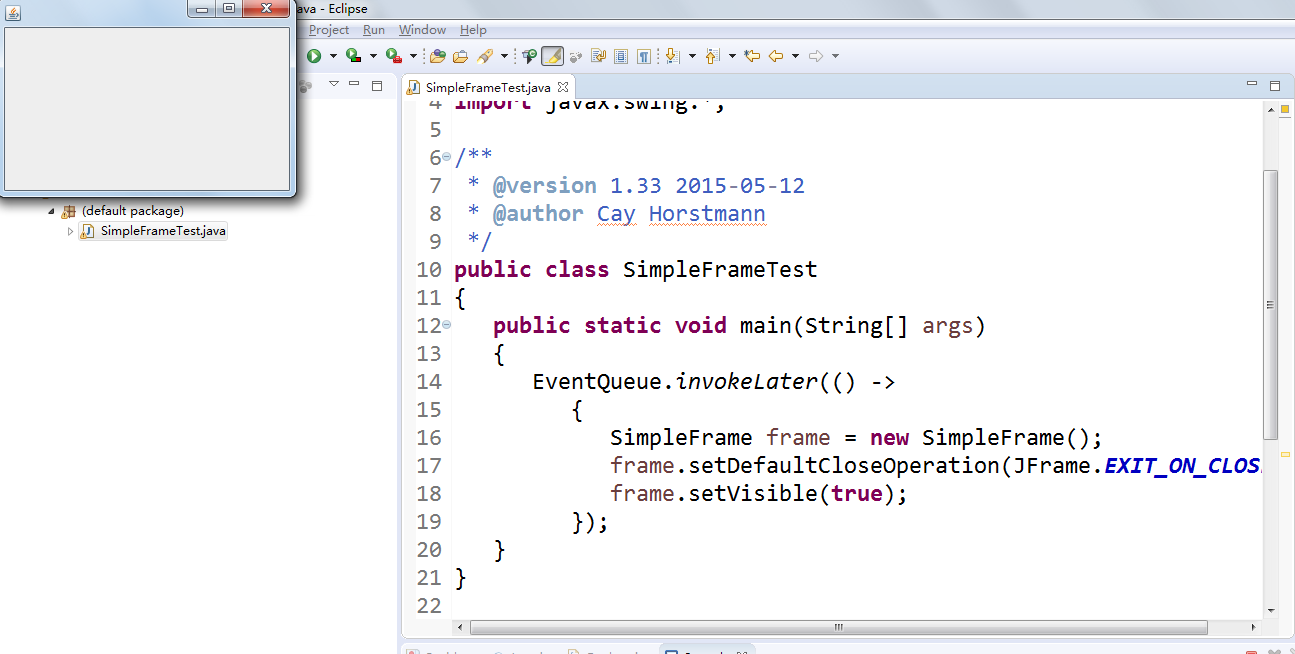
l 掌握空框架建立方法;
l 瞭解主執行緒與事件分派執行緒概念;
l 掌握GUI頂層視窗建立技術。
測試程式2:
l 在elipse IDE中除錯執行教材412頁程式10-2,結合程式執行結果理解程式;

import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
/**
* @version 1.34 2015-06-16
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class SizedFrameTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
EventQueue.invokeLater(() ->
{
JFrame frame = new SizedFrame();
frame.setTitle("SizedFrame");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
}
class SizedFrame extends JFrame
{
public SizedFrame()
{
// get screen dimensions
Toolkit kit = Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit();
Dimension screenSize = kit.getScreenSize();
int screenHeight = screenSize.height;
int screenWidth = screenSize.width;
// set frame width, height and let platform pick screen location
setSize(screenWidth / 2, screenHeight / 2);
setLocationByPlatform(true);
// set frame icon
Image img = new ImageIcon("icon.gif").getImage();
setIconImage(img);
}
}

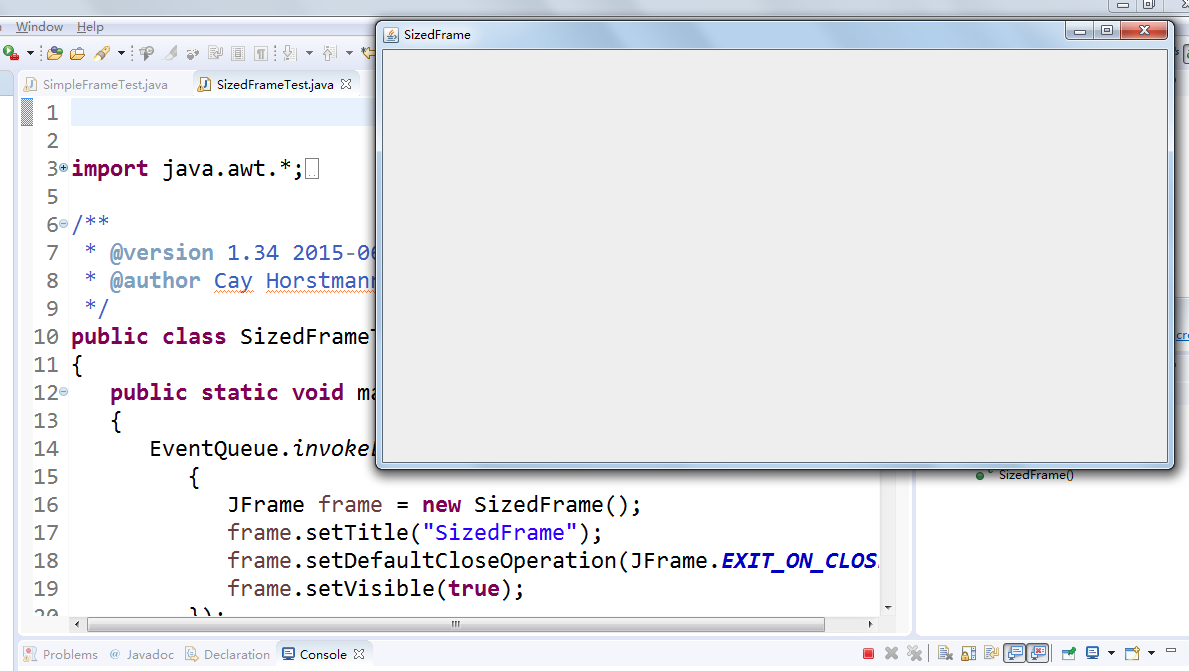
l 掌握確定框架常用屬性的設定方法。
測試程式3:
l 在elipse IDE中除錯執行教材418頁程式10-3,結合執行結果理解程式;
l 掌握在框架中新增元件;
l 掌握自定義元件的用法。
測試程式4:
l 在elipse IDE中除錯執行教材424 -425頁程式10-4,結合程式執行結果理解程式;

import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
/**
* @version 1.34 2015-06-16
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class SizedFrameTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
EventQueue.invokeLater(() ->
{
JFrame frame = new SizedFrame();
frame.setTitle("SizedFrame");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
}
class SizedFrame extends JFrame
{
public SizedFrame()
{
// get screen dimensions
Toolkit kit = Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit();
Dimension screenSize = kit.getScreenSize();
int screenHeight = screenSize.height;
int screenWidth = screenSize.width;
// set frame width, height and let platform pick screen location
setSize(screenWidth / 2, screenHeight / 2);
setLocationByPlatform(true);
// set frame icon
Image img = new ImageIcon("icon.gif").getImage();
setIconImage(img);
}
}


l 掌握2D圖形的繪製方法。
測試程式5:
l 在elipse IDE中除錯執行教材432頁-433程式10-5,結合程式執行結果理解程式;

import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.font.*;
import java.awt.geom.*;
import javax.swing.*;
/**
* @version 1.34 2015-05-12
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class FontTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
EventQueue.invokeLater(() ->
{
JFrame frame = new FontFrame();
frame.setTitle("FontTest");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
}
/**
* A frame with a text message component
*/
class FontFrame extends JFrame
{
public FontFrame()
{
add(new FontComponent());
pack();
}
}
/**
* A component that shows a centered message in a box.
*/
class FontComponent extends JComponent
{
private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 300;
private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 200;
public void paintComponent(Graphics g)
{
Graphics2D g2 = (Graphics2D) g;
String message = "Hello, World!";
Font f = new Font("Serif", Font.BOLD, 36);
g2.setFont(f);
// measure the size of the message
FontRenderContext context = g2.getFontRenderContext();
Rectangle2D bounds = f.getStringBounds(message, context);
// set (x,y) = top left corner of text
double x = (getWidth() - bounds.getWidth()) / 2;
double y = (getHeight() - bounds.getHeight()) / 2;
// add ascent to y to reach the baseline
double ascent = -bounds.getY();
double baseY = y + ascent;
// draw the message
g2.drawString(message, (int) x, (int) baseY);
g2.setPaint(Color.LIGHT_GRAY);
// draw the baseline
g2.draw(new Line2D.Double(x, baseY, x + bounds.getWidth(), baseY));
// draw the enclosing rectangle
Rectangle2D rect = new Rectangle2D.Double(x, y, bounds.getWidth(), bounds.getHeight());
g2.draw(rect);
}
public Dimension getPreferredSize() { return new Dimension(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT); }
}

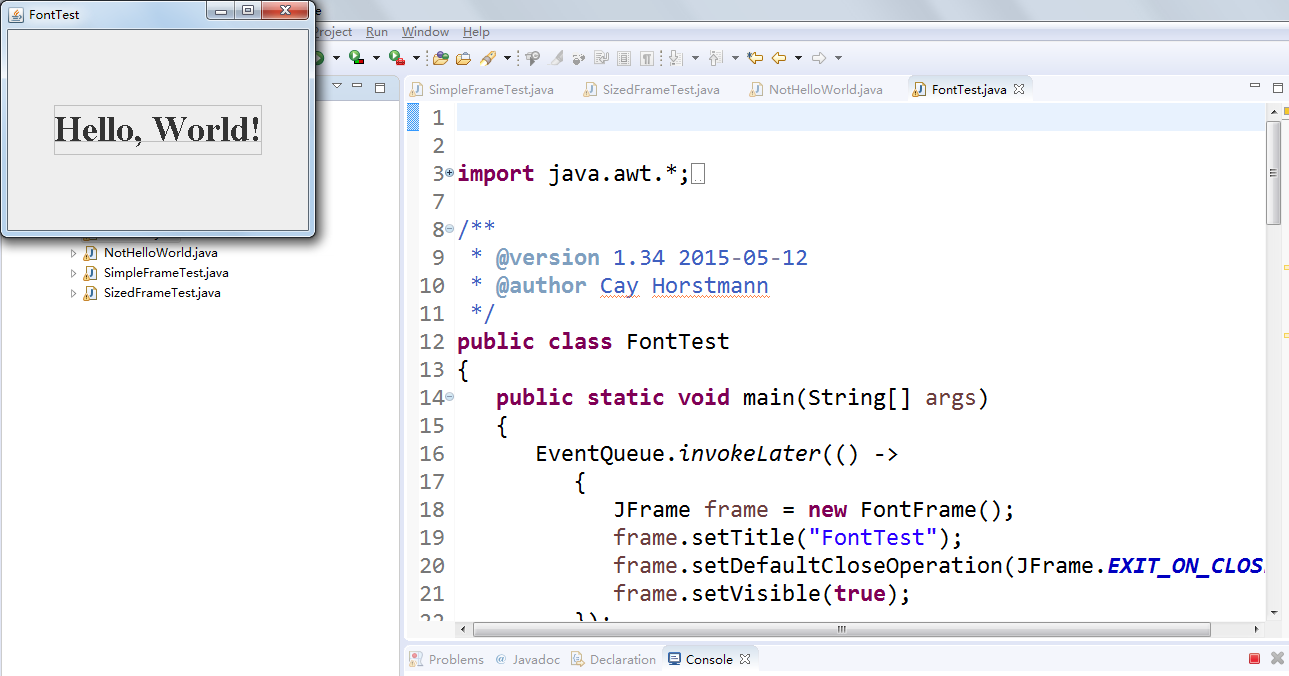
l 瞭解2D圖形中字型的設定的方法;
測試程式6:
l 在elipse IDE中除錯執行教材436頁-437程式10-6,結合程式執行結果理解程式;
l 瞭解2D圖形影象的顯示方法。

import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
/**
* @version 1.34 2015-05-12
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class ImageTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
EventQueue.invokeLater(() ->
{
JFrame frame = new ImageFrame();
frame.setTitle("ImageTest");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
}
/**
* A frame with an image component
*/
class ImageFrame extends JFrame
{
public ImageFrame()
{
add(new ImageComponent());
pack();
}
}
/**
* A component that displays a tiled image
*/
class ImageComponent extends JComponent
{
private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 300;
private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 200;
private Image image;
public ImageComponent()
{
image = new ImageIcon("book.jpg.jpg").getImage();
}
public void paintComponent(Graphics g)
{
if (image == null) return;
int imageWidth = image.getWidth(null);
int imageHeight = image.getHeight(null);
// draw the image in the upper-left corner
g.drawImage(image, 0, 0, null);
// tile the image across the component
for (int i = 0; i * imageWidth <= getWidth(); i++)
for (int j = 0; j * imageHeight <= getHeight(); j++)
if (i + j > 0)
g.copyArea(0, 0, imageWidth, imageHeight, i * imageWidth, j * imageHeight);
}
public Dimension getPreferredSize() { return new Dimension(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT); }
}

實驗總結:掌握了Java GUI中框架建立及屬性設定中常用類的API、Java GUI中2D圖形繪製常用類的API; 瞭解了Java GUI中2D圖形中字型與顏色的設定方法以及Java GUI中2D影象的載入方法。在老師與學長的演示講解之下也熟悉了這章所要學習的的新知識,通過在實驗平臺上也對與以前的知識有所回顧。
