【NOIP2018】D1T1 鋪設道路
@鋪設道路@
@題目描述@
春春是一名道路工程師,負責鋪設一條長度為 n 的道路。
鋪設道路的主要工作是填平下陷的地表。整段道路可以看作是 n 塊首尾相連的區域,一開始,第 i 塊區域下陷的深度為 di。
春春每天可以選擇一段連續區間 [L,R],填充這段區間中的每塊區域,讓其下陷深度減少 1。在選擇區間時,需要保證,區間內的每塊區域在填充前下陷深度均不為 0$。
春春希望你能幫他設計一種方案,可以在最短的時間內將整段道路的下陷深度都變為 0 。
輸入
輸入檔案包含兩行,第一行包含一個整數 n,表示道路的長度。 第二行包含 n 個整數,相鄰兩數間用一個空格隔開,第 i 個整數為 di。
輸出
輸出檔案僅包含一個整數,即最少需要多少天才能完成任務。
輸入樣例#1:
6
4 3 2 5 3 5
輸出樣例#1:
9
樣例解釋1:
一種可行的最佳方案是,依次選擇: [1,6]、[1,6]、[1,2]、[1,1]、[4,6]、[4,4]、[4,4]、[6,6]、[6,6]。
資料規模與約定
對於 30% 的資料,1 ≤ n ≤ 10;
對於 70% 的資料,1 ≤ n ≤ 1000;
對於 100% 的資料,1 ≤ n ≤ 100000 , 0 ≤ di ≤ 10000。
@考場上的思路@
我 抄 我 自 己?
雖然這是 NOIP2013 的原題“積木遊戲”……然而我並沒有做過-_-
所以考場上想了一個比較複雜的解:
顯然觀察樣例,我們可以貪心地這樣做:對於某一個區間,選擇最小值,將這個區間減去這個最小值,然後把區間按照這個最小值分為兩個區間分治求解。
因此,本來想寫線段樹來著……但是我及時地發現(其實是因為不想寫再多想會兒hhhh)區間的最小值是不會變化的。也就是說我們可以不去動態查詢區間最小值,而是建成笛卡爾樹,再在笛卡爾樹上進行操作。
程式碼(不建議參考,建議繼續往後看正常的解):
#include<cstdio>
#include @比較正常的題解@
我們實際上是求如圖的塊的個數。
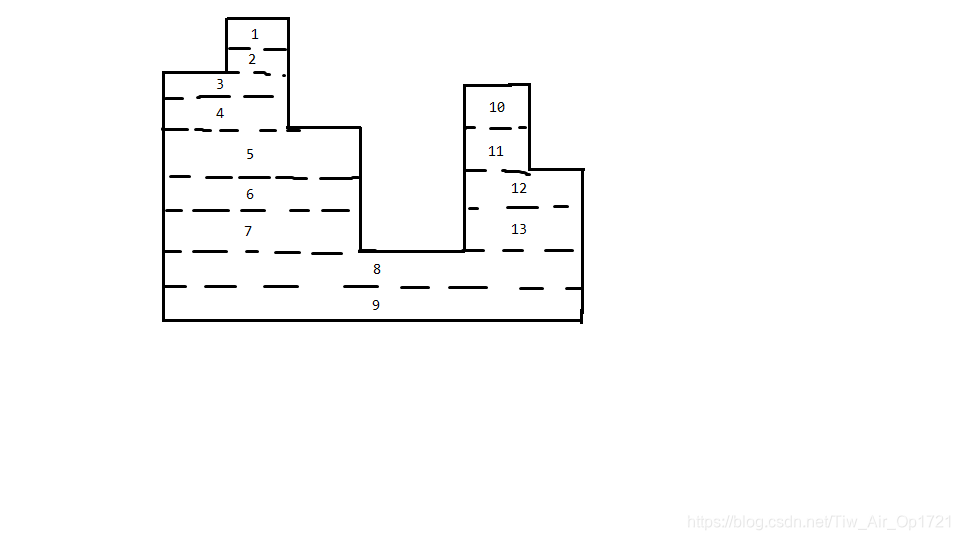
我們不妨在塊的右端點去統計每一塊對答案的貢獻。
所以就很簡單了:
(1)如果 d[i] >= d[i+1],則 ans+=(d[i]-d[i+1])
(2)如果 d[i] < d[i+1],則 continue
最後 ans+= d[n] 即可
#include<cstdio>
typedef long long ll;
const int MAXN = 100000;
int d[MAXN + 5];
int main() {
int n; ll ans = 0;
scanf("%d", &n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%d", &d[i]);
for(int i=1;i<n;i++)
if( d[i] >= d[i+1] ) ans += d[i] - d[i+1];
ans += d[n];
printf("%lld\n", ans);
}
@[email protected]
就是這樣,新的一天裡,也請多多關照哦(ノω<。)ノ))☆.。
