影象處理二:仿射變換和透視變換
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-12-10
一、仿射變換(Affine Transformation)
放射變換(平面變換、二維座標變換):是空間直角座標系的變換,從一個二維座標變換到另一個二維座標,仿射變換是一個線性變換,保持了影象的“平行性”和“平直性”,即影象中原來的直線和平行線,變換後仍然保持原來的直線和平行線。
仿射變換比較常用的特殊變換有平移(Translation)、縮放(Scale)、翻轉(Flip)、旋轉(Rotation)和剪下(Shear);
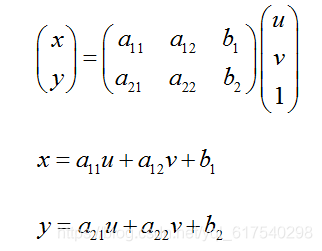
仿射變換性質:
(1)仿射變化只有6個自由度(對應變換中的6個係數),仿射變換後相互平行直線仍然是平行直線,三角形對映後仍是三角形;但卻不能保證四邊形以上的多變性對映為等邊數的多邊形;
(2)仿射變換的乘積和逆變換仍是仿射變換;
(3)仿射變換包含:平移、旋轉、縮放等幾何變換。
二、透視變換(Perspective Transformation)
透視變換(空間變換、三維座標變換):是指利用透視中心、像點、目標點三點共線的條件,按透視旋轉定律使承影面(透視面)繞跡線(透視軸)旋轉某一角度,破壞原有的投影光線束,仍能保持承影面上投影幾何圖形不變的變換。
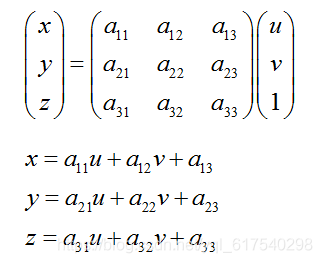
三、原始碼
影象若需儲存程式碼為:
cv2.imwrite("F:/b.jpg",res)第一個引數:路徑下,指定檔名;
第二個引數:儲存的影象。
1. 平移
import cv2 import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt img = cv2.imread('F:/a.jpg') H = np.float32([[1,0,100],[0,1,100]]) rows,cols = img.shape[:2] res = cv2.warpAffine(img,H,(rows,cols)) #需要影象、變換矩陣、變換後的大小 plt.subplot(121) plt.imshow(img) plt.subplot(122) plt.imshow(res)

2. 放縮
resize()函式可以進行影象的放大、縮小,但需要選擇合適的插值方式。
import cv2
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
img = cv2.imread('F:/a.jpg')
res1 = cv2.resize(img,None,fx=2,fy=2,interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
height,width = img.shape[:2]
res2 = cv2.resize(img,(2*width,2*height),interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
plt.subplot(131)
plt.imshow(img)
plt.subplot(132)
plt.imshow(res1)
plt.subplot(133)
plt.imshow(res2)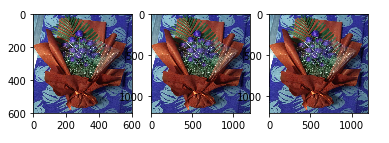
3. 旋轉
import cv2
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
img = cv2.imread('F:/a.jpg')
rows,cols = img.shape[:2]
#第一個引數旋轉中心,第二個引數旋轉角度,第三個引數:縮放比例
M = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D((cols/2,rows/2),45,1)
#第三個引數:變換後的影象大小
res = cv2.warpAffine(img,M,(rows,cols))
plt.subplot(121)
plt.imshow(img)
plt.subplot(122)
plt.imshow(res)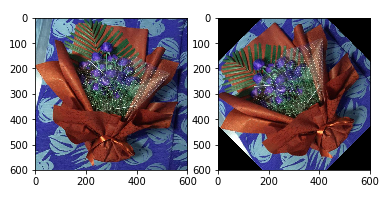
4. 仿射
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
img = cv2.imread('F:/a.jpg')
rows,cols = img.shape[:2]
pts1 = np.float32([[50,50],[200,50],[50,200]])
pts2 = np.float32([[10,100],[200,50],[100,250]])
M = cv2.getAffineTransform(pts1,pts2)
#第三個引數:變換後的影象大小
res = cv2.warpAffine(img,M,(rows,cols))
plt.subplot(121)
plt.imshow(img)
plt.subplot(122)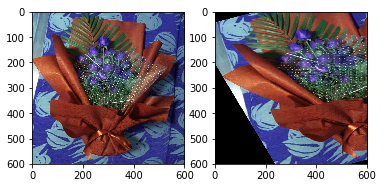
5. 投影
(1)垂直投影
import cv2
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
img=cv2.imread('F:/a.jpg')
GrayImage=cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) #將BGR圖轉為灰度圖
ret,thresh1=cv2.threshold(GrayImage,130,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY) #將圖片進行二值化(130,255)之間的點均變為255(背景)
(h,w)=thresh1.shape #返回高和寬
a = [0 for z in range(0, w)]
#記錄每一列的波峰
for j in range(0,w): #遍歷一列
for i in range(0,h): #遍歷一行
if thresh1[i,j]==0: #如果改點為黑點
a[j]+=1 #該列的計數器加一計數
thresh1[i,j]=255 #記錄完後將其變為白色
for j in range(0,w): #遍歷每一列
for i in range((h-a[j]),h): #從該列應該變黑的最頂部的點開始向最底部塗黑
thresh1[i,j]=0 #塗黑
plt.imshow(thresh1,cmap=plt.gray())
plt.show()
cv2.imshow('img',thresh1)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()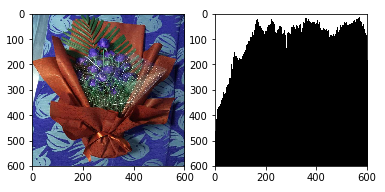
(2)水平投影
import cv2
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
img=cv2.imread('F:/a.jpg')
GrayImage=cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
ret,thresh1=cv2.threshold(GrayImage,130,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
(h,w)=thresh1.shape #返回高和寬
a = [0 for z in range(0, h)]
for j in range(0,h):
for i in range(0,w):
if thresh1[j,i]==0:
a[j]+=1
thresh1[j,i]=255
for j in range(0,h):
for i in range(0,a[j]):
thresh1[j,i]=0
plt.imshow(thresh1,cmap=plt.gray())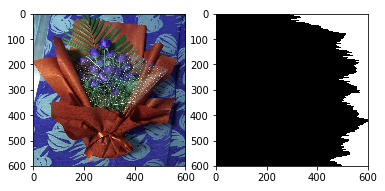
(3)基於投影的字元分割
import cv2
import numpy as np
path = 'F:/b.jpg'
root = 'F:/b/'
dsize = 28
img = cv2.imread(path)
data = np.array(img)
len_x = data.shape[0]
len_y = data.shape[1]
min_val = 10 #設定最小的文字畫素高度
start_i = -1
end_i = -1
rowPairs = [] #存放每行的起止座標
#行分割
for i in range(len_x):
if(not data[i].all() and start_i < 0):
start_i = i
elif(not data[i].all()):
end_i = i
elif (data[i].all() and start_i >= 0):
#print(end_i - start_i)
if(end_i - start_i >= min_val):
rowPairs.append((start_i, end_i))
start_i, end_i = -1, -1
#列分割
start_j = -1
end_j = -1
min_val_word = 8 #最小文字畫素長度
number = 0 #分割後儲存編號
for start, end in rowPairs:
for j in range(len_y):
if(not data[start: end, j].all() and start_j < 0):
start_j = j
elif(not data[start: end, j].all()):
end_j = j
elif(data[start: end, j].all() and start_j >= 0):
if(end_j - start_j >= min_val_word):
#print(end_j - start_j)
tmp = data[start:end, start_j: end_j]
im2save = cv2.resize(tmp, (dsize,dsize)) #歸一化處理
cv2.imwrite(root + '%d.png' % number, im2save)
number += 1
#print("%d pic" % number)
start_j, end_j = -1, -1

