Ray tracing in a weekend (十一)
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-12-14
Defocus Blur(散焦模糊)
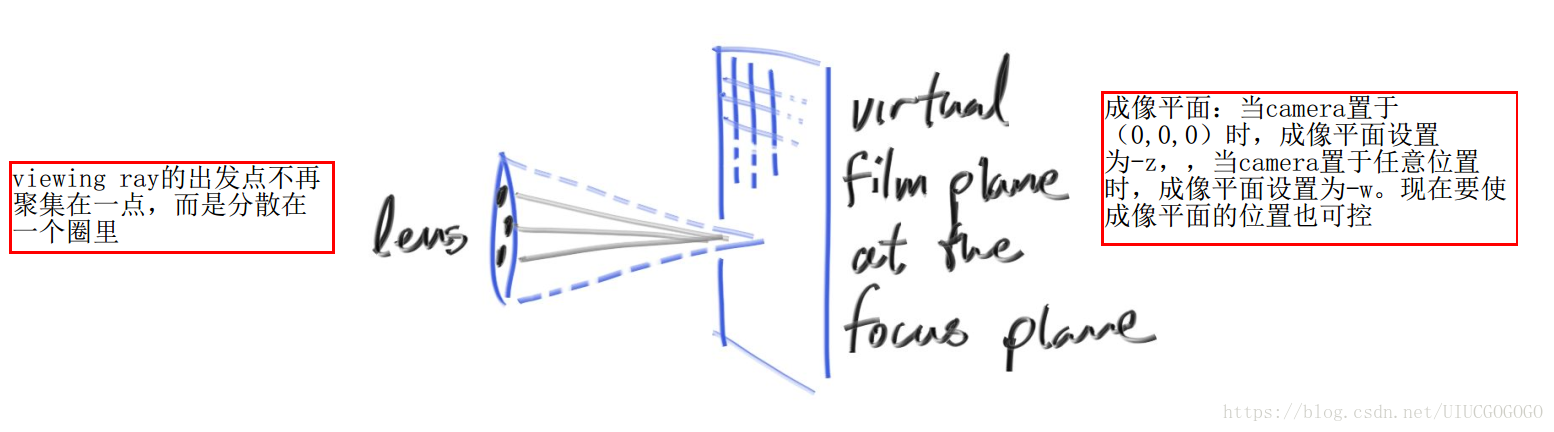
在之前渲染所得的影象中所有物體都是“清晰”的,現在要讓影象更趨近於真實的camera相片,即“有實有虛”。
camera.h
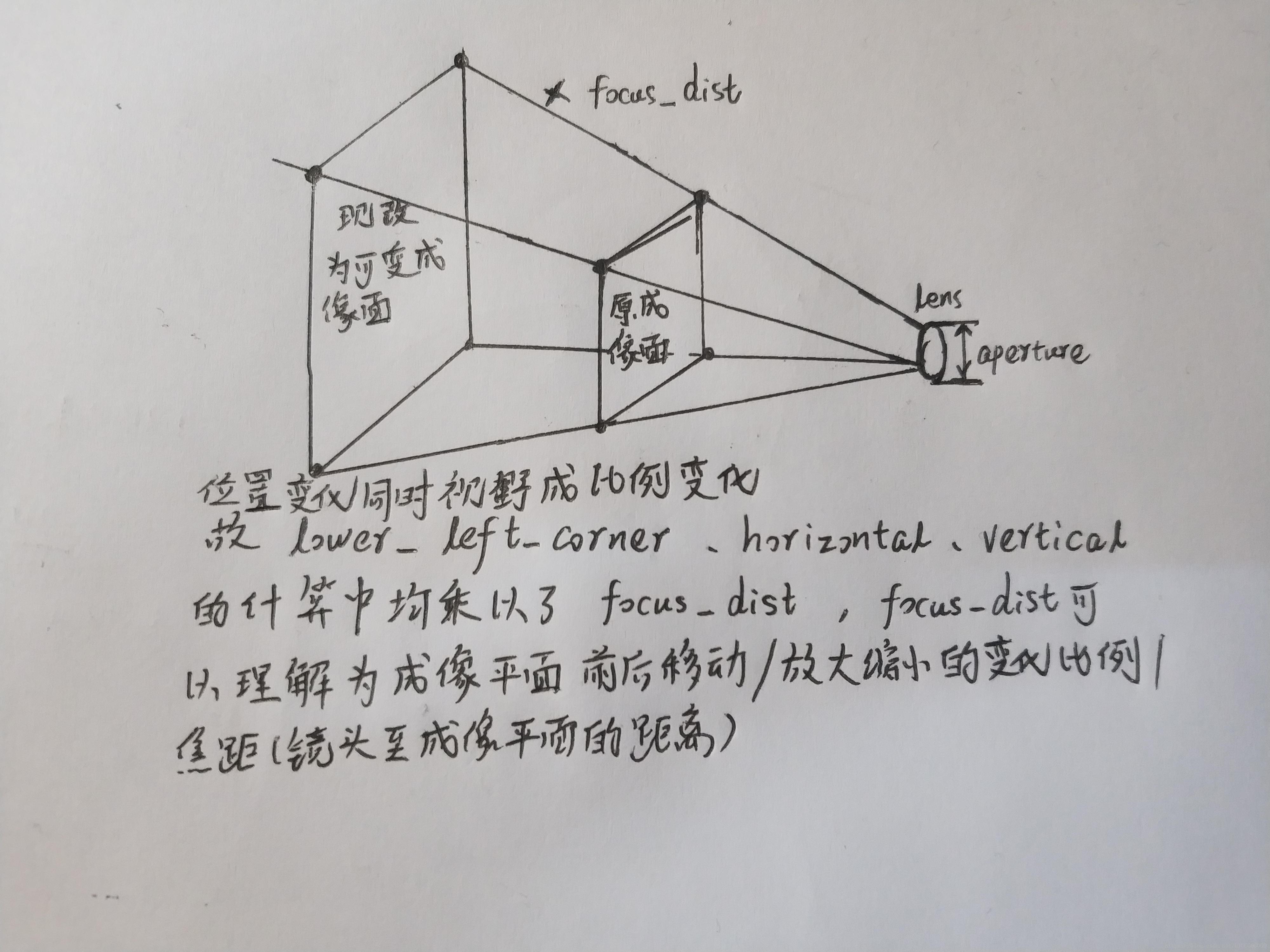
#define M_PI 3.1415926 #include"ray.h" #include"random.h" //ray的出發點限制在一個圓裡,而非集中於一點 //先求出在z=0平面,以(0,0,0)為圓心的單位圓內的任意一點 //以便在後面進行上述操作(類似之前求以(0,0,0)為球心的單位球內一點) vec3 random_in_unit_disk() { vec3 p; do { p = 2.0*vec3(drand48(), drand48(), 0) - vec3(1, 1, 0); } while (dot(p, p) >= 1.0); return p; } //之前關於image plain的資訊和viewing ray的生成 //都直接寫在main裡,現在要將它們封裝進camera //類裡,畢竟image plain本來就是camera的可視範圍 //而viewing ray也是由camera生成的 class camera { public: //vfov是角度(degree);aperture是光圈也就是鏡頭半徑,決定了ray的出發點侷限在多大的一個圈內;focus_dist是成像平面的變化比例 camera(vec3 lookfrom,vec3 lookat,vec3 vup,float vfov,float aspect,float aperture,float focus_dist) { lens_radius = aperture / 2; float theta=vfov*M_PI/180;//將角度轉化為弧度 float half_height = tan(theta / 2); float half_width = aspect*half_height; //確定視角 origin = lookfrom; w = unit_vector(lookfrom - lookat); u = unit_vector(cross(vup, w)); v = cross(w, u); //利用camera frame求出現在的lower_left_corner lower_left_corner = origin - half_width*focus_dist*u - half_height*focus_dist*v - focus_dist*w; //確定視野 horizontal = 2 * half_width*focus_dist*u;//fov/視野的寬 vertical = 2*half_height*focus_dist*v;//fov/視野的高 } ray get_ray(float s, float t) { //將單位圓中任一點換為半徑為鏡頭半徑的圓內任一點 vec3 rd = lens_radius*random_in_unit_disk(); //將圓心變為camera frame的原點 vec3 offset = rd.x()*u + rd.y()*v; return ray(origin+offset, lower_left_corner + s*horizontal + t*vertical - origin-offset); } vec3 origin; vec3 lower_left_corner; vec3 horizontal; vec3 vertical; vec3 u, v, w;//camera frame各軸 float lens_radius; };
RayTracer.cpp
#include"vector.h" #include"ray.h" #include"sphere.h" #include"hitable_list.h" #include"camera.h" #include"material.h" #include"random.h" #include<random> #include<cfloat> #include<math.h> #include<iostream> #include<fstream> using namespace std; //此處的world就是把整個場景裡的所有object視為一體(即hitable_list) //depth是ray的傳播深度,scatter一次加一 vec3 color(const ray& r,hitable *world,int depth) { hit_record rec; //如果viewing ray(反向光線)與hitable object相交 //tmin採用0.001是基於對showdow的考量,見fundamentals p86 //然而當前還沒有引入light,陰影部分是因為當光線到達此處時經歷了太多次反射 if (world->hit(r, 0.001, FLT_MAX, rec)) { //當前還不能確定是difusse還是reflection,取決於hitable的material ray scattered; vec3 attenuation;//削弱 //如果scatter次數小於50 //並且ray接觸的hitable object的material能成功呼叫scattered函式 if (depth < 50 && rec.mat_ptr->scatter(r, rec, attenuation, scattered)) { return attenuation*color(scattered, world, depth + 1); } else//scatter超過50次,能量全被吸完了;scattered函式呼叫失敗 { return vec3(0, 0, 0);//黑 } } else//注意當前還是沒有引入light,依然是由最後一條ray的direction的y值決定color //實際上可以認為是background在發光 { vec3 unit_direction = unit_vector(r.direction());//得到單位方向向量,將y限定在-1至1之間 float t = 0.5*(unit_direction.y() + 1.0);//間接用t代表y,將其限制在0至1之間 return (1.0 - t)*vec3(1.0, 1.0, 1.0) + t*vec3(0.5, 0.7, 1.0); //所謂插值法,不同的ray對應的t不同,這些t決定了其對應的color為(1.0,1.0,1.0)和(0.5,0.7,1.0)之間某一RGB顏色 //RGB各分量實際就是一個介於0.0至1.0的小數 } } int main() { int nx = 200;//200列 int ny = 100;//100行 int ns = 100; ofstream out("d:\\theFirstPpm.txt"); out << "P3\n" << nx << " " << ny << "\n255" << endl; hitable *list[5];//我們自己定義world是什麼,此處定義為兩個sphere list[0] = new sphere(vec3(0, 0, -1), 0.5,new lambertian(vec3(0.1,0.2,0.5))); list[1] = new sphere(vec3(0, -100.5, -1), 100, new lambertian(vec3(0.8, 0.8, 0.0))); list[2] = new sphere(vec3(1, 0, -1), 0.5, new metal(vec3(0.8, 0.6, 0.2),0.3)); list[3] = new sphere(vec3(-1, 0, -1), 0.5, new dielectric(1.5)); list[4] = new sphere(vec3(-1, 0, -1), -0.45, new dielectric(1.5)); hitable *world = new hitable_list(list, 5);//初始化world vec3 lookfrom(3, 3, 2); vec3 lookat(0, 0, -1); float dist_to_focus = (lookfrom - lookat).length();//焦距 float aperture = 2.0; camera cam(lookfrom,lookat,vec3(0,1,0),20,float(nx)/float(ny),aperture,dist_to_focus); for (int j = ny - 1;j >= 0;j--)//行從上到下 { for (int i = 0;i < nx;i++)//列從左到右 { vec3 col(0, 0, 0); for (int s = 0;s < ns;s++) { float u = float(i + drand48()) / float(nx); float v = float(j + drand48()) / float(ny); ray r = cam.get_ray(u, v); vec3 p = r.point_at_parameter(2.0); col += color(r,world,0); } col /= float(ns); //進行gamma校正,一般來說取gamma=2,原理及公式見fundamentals p63 col = vec3(sqrt(col[0]), sqrt(col[1]), sqrt(col[2])); int ir = int(255.99*col[0]); int ig = int(255.99*col[1]); int ib = int(255.99*col[2]); out << ir << " " << ig << " " << ib << endl; } } return 0; }