PAT 1018 Public Bike Management (30 分)
1018 Public Bike Management (30 分)
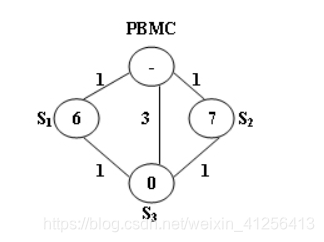
There is a public bike service in Hangzhou City which provides great convenience to the tourists from all over the world. One may rent a bike at any station and return it to any other stations in the city.
The Public Bike Management Center (PBMC) keeps monitoring the real-time capacity of all the stations. A station is said to be in perfect condition if it is exactly half-full. If a station is full or empty, PBMC will collect or send bikes to adjust the condition of that station to perfect. And more, all the stations on the way will be adjusted as well.
When a problem station is reported, PBMC will always choose the shortest path to reach that station. If there are more than one shortest path, the one that requires the least number of bikes sent from PBMC will be chosen.

解析
很紮實的30分題。圖應用題。
這題的要求是你從PBMT出發:沿著最短路徑開始排程自行車。遇上一個station:如果這裡自行車有多的:則拿走一些。如果自行車少了:就先從手頭看看有沒有之前在其他station收的自行車。如果沒有:就要sent了。
這個行為是要一個station到另一個station:是不滿足dijkstra區域性最優解的。所以用dijkstra只能算最短路徑。
而且不能說前面station的自行車不夠:用後面的station的自行車補給。這是不對的。
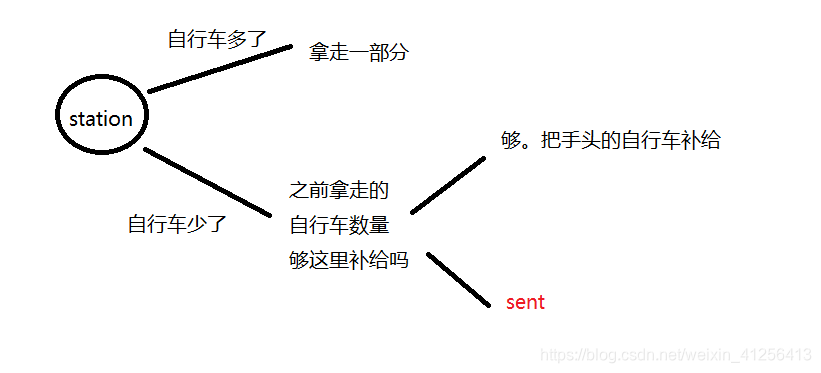
這題有三個標尺:第一個是最短路徑,可以用Dijkstra演算法解決。
第二個是最少sent,第三個是最少take back。當時我一想:sent和take back不是矛盾的嗎。其實我是忽略了不能說前面station的自行車不夠:用後面的station的自行車補給。
所以:在所有最短路徑中:看誰的sent是最少的。如果一樣:就挑誰的take back最小。DFS
Code:
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<utility> 