ALGORITHMS FOR SOURCE LOCALIZATION
Two approaches for source localization, namely, nonlinear and linear, are presented in Sections 2.3.1 and 2.3.2 , respectively. Generally speaking, the nonlinear methodology [13 – 16] directly employs Equation 2.1 to solve for x by minimizing the least squares ( LS ) or the weighted least squares ( WLS ) cost function constructed from the following error function:
![]()
where is the optimization variable for x , which corresponds to the NLS or ML estimator, respectively. On the other hand, the linear techniques convert Equation 2.1 into a set of linear equations in
:
![]()
where b and A are available, while q is the transformed noise vector. Based on Equation 2.37 , we construct
![]()
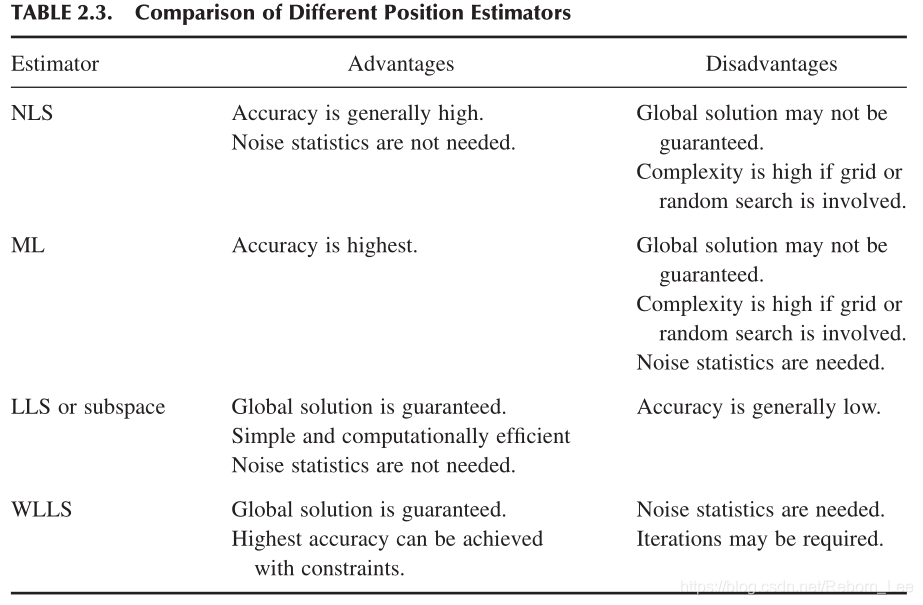
Applying the LS or WLS techniques on Equation 2.38 results in the LLS [17, 18] ,WLLS [19 – 22] and subspace [23 – 26] estimators. A comparison summary for the position estimators examined in this chapter is provided in Table 2.3 .