演算法設計與優化程式設計 第十講 Subway
Subway
Problem Description
jiefangxuanyan and yiyi cat are universally acknowledged model couples(配偶). Once jiefangxuanyan has time, he takes a train to yiyi cat’s city and meets her. This time, as usual, jiefangxuanyan gets out from the railway station, and enters the subway, only to find that the subway stations of the whole city changes their names!
As a direction idiot(白痴), jiefangxuanyan felt helpless with this situation. He called yiyi cat for help. Because the subway map is so complicated, she can’t remember it either. Fortunately, only the names of the stations changed, the structure of subway lines is the same. So she picks out the old map to make a mapping.
But mapping such a confused(迷亂的) subway map is definitely a difficult task. So she has to use the computer. Unfortunately, she just spilt(潑出,灑出) wonton(餛飩) soup(湯) into her computer. So, yiyi cat asked you for help, hoping you can help her with this problem.
The subway in the city forms a tree, with N subway stations and N-1 subway lines. Any pair of stations are connected with one or more subway lines. You need to find a bijective(雙射) mapping from the old names to the new names, that for each pair of stations connected by exactly one line in the old map, their new names are also connected by exactly one line in the new map.
Input
The input has multiple test cases, please process to the end of file.
For each test case, the first line is an integer N (1≤N≤100000) .
In the following N−1 lines, each line has two space-separated strings, as two stations connected by one line in the old map.
In the following N−1 lines, each line has two space-separated strings, as two stations connected by one line in the new map.
Station names are no longer than 10 characters, and only consists of lowercase letters (a~z).
Output
For each test case, output N lines.
Each line consists two space-separated strings, as the old name and its corresponding new name.
Both the names appeared in the old and new subway map should appear exactly once in the output.
You can output the names in any order. And if there are multiple valid mappings, output any one.
Names in the old map and the new map may be the same, but this does not mean these two stations are the same.
Sample Input
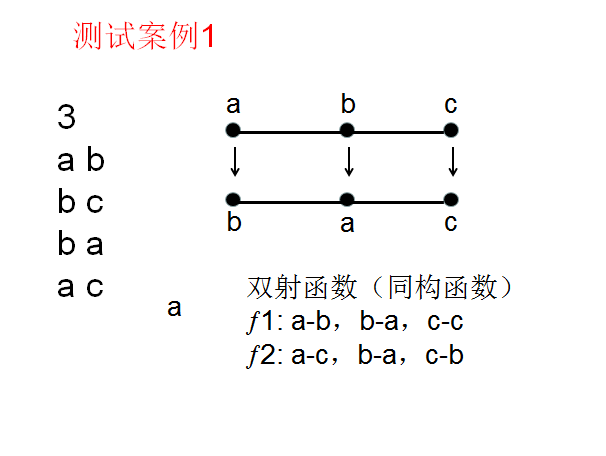
3
a b
b c
b a
a c
Sample Output
b a
a b
c c
思路:
這個題是一個樹的同構判斷,想辦法用一個和節點順序無關的雜湊函式將樹表示出來即可。
這裡提供一種方法:首先求解樹的中點,然後將中點作為根。只有一個結點的子樹雜湊值為1。選一個比較大的質數P和一個特別大的質數Q。對於每一顆樹,把它的所有子樹的雜湊值排序。然後hash=sum(P^i∗hash[i])%Q,就能算出來總體的雜湊值。有兩個中點的樹兩個中點都試一下。為了保險可以檢查下雜湊值有沒有重的。
程式碼
#include <cstring>
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <map>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <new>
using std::string;
using std::cin;
using std::cout;
const int N=110000;
struct Metro{
std::map<string,int> mp;
std::vector<string> vec;
//呼叫分配程式,把字元編號的頂點換成整數編號的頂點
int alloc(const string &name){
//迭代器iterator
std::pair<std::map<string,int>::iterator,bool> got=mp.insert(std::make_pair(name,mp.size()));
//如果得到第二個點
if(got.second){
vec.push_back(name);
}
return got.first->second;
}
};
//定義item結構體
struct item{
int tgt;
item *next;
item(){}
item(int tgt,item *next):tgt(tgt),next(next){}
}*ls[N],*lt[N],storage[4*N];
//插入邊
void insert(item **list,int a,int b,item *&loc){
list[a]=new(loc++) item(b,list[a]);
list[b]=new(loc++) item(a,list[b]);
}
int farSel[N];
std::pair<int,int> findFarthest(item **list,int a,int prev){
std::pair<int,int> r(a,-1);
for(item *p=list[a];p;p=p->next){
if(p->tgt!=prev){
std::pair<int,int> cur=findFarthest(list,p->tgt,a);
if(cur.second>r.second){
farSel[a]=p->tgt;
r=cur;
}
}
}
r.second++;
return r;
}
//找樹的中點
std::pair<int,int> findRoot(item **list){
int a=findFarthest(list,0,-1).first;
std::pair<int,int> t=findFarthest(list,a,-1);
for(int i=0;i<t.second/2;i++){
a=farSel[a];
}
return std::make_pair(a,t.second%2?farSel[a]:-1);
}
const int M=1000000007,MM=100000007;
struct HashPair{
int a,h;
HashPair(){}
HashPair(int a,int h):a(a),h(h){}
bool operator<(const HashPair &x)const{
return h<x.h;
}
};
//求雜湊值
std::vector<HashPair> hs[N],ht[N];
int hash(item **list,int a,int prev,std::vector<HashPair> *tgt){
std::vector<HashPair> vec;
for(item *p=list[a];p;p=p->next){
if(p->tgt!=prev){
vec.push_back(HashPair(p->tgt,hash(list,p->tgt,a,tgt)));
}
}
std::sort(vec.begin(),vec.end());
int r=1;
for(int i=0;i<(int)vec.size();i++){
r=((long long)r*MM+vec[i].h)%M;
}
tgt[a].swap(vec);
return r;
}
bool match(std::vector<HashPair> &vs,std::vector<HashPair> &vt,int *res){
if(vs.size()!=vt.size()){
return false;
}
for(int i=0;i<(int)vs.size();i++){
for(int j=i;j<(int)vt.size()&&vt[j].h==vs[i].h;j++){
std::swap(vt[i].a,vt[j].a);
if(match(hs[vs[i].a],ht[vt[i].a],res)){
goto lblMatch;
}
}
return false;
lblMatch:
res[vs[i].a]=vt[i].a;
}
return true;
}
int mapping[N];
int main(){
int size = 8 << 20;
char *p = (char*)malloc(size) + size;
//__asm__("movl %0, %%esp\n" :: "r"(p));
//std::ifstream fin("in.txt");
//std::ofstream fout("out.txt");
int n;
//輸入邊
while(cin>>n){
memset(ls,0,sizeof(ls));
item *loc=storage;
Metro src;
//轉換成整數
for(int i=0;i<n-1;i++){
string name;
cin>>name;
int a=src.alloc(name);
cin>>name;
int b=src.alloc(name);
insert(ls,a,b,loc);
}
memset(lt,0,sizeof(lt));
Metro tgt;
//轉換成整數
for(int i=0;i<n-1;i++){
string name;
cin>>name;
int a=tgt.alloc(name);
cin>>name;
int b=tgt.alloc(name);
insert(lt,a,b,loc);
}
//找樹根(中點)
std::pair<int,int> rs=findRoot(ls),rt=findRoot(lt);
std::vector<HashPair> vs,vt;
//求樹根雜湊值
vs.push_back(HashPair(rs.first,hash(ls,rs.first,rs.second,hs)));
//處理第一個中點
if(rs.second!=-1){
vs.push_back(HashPair(rs.second,hash(ls,rs.second,rs.first,hs)));
}
//排序,提高速度
std::sort(vs.begin(),vs.end());
vt.push_back(HashPair(rt.first,hash(lt,rt.first,rt.second,ht)));
//處理第二個中點
if(rs.second!=-1){
vt.push_back(HashPair(rt.second,hash(lt,rt.second,rt.first,ht)));
}
//排序,提高速度
std::sort(vt.begin(),vt.end());
//判斷是否同構
if(match(vs,vt,mapping)){
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
//列印同構
cout<<src.vec[i]<<' '<<tgt.vec[mapping[i]]<<'\n';
}
}else{
cout<<"TAT\n";
}
}
return 0;
}