Python遺傳演算法程式碼例項講解
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-12-24
目錄
例項:
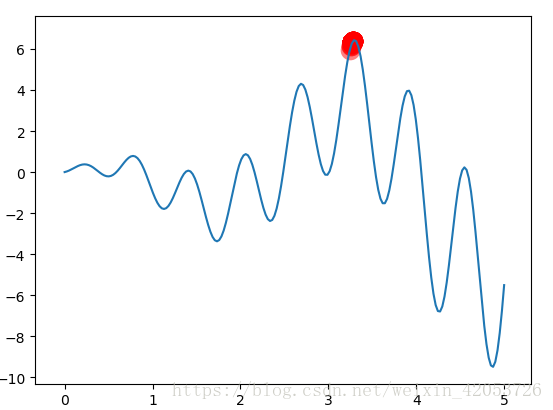
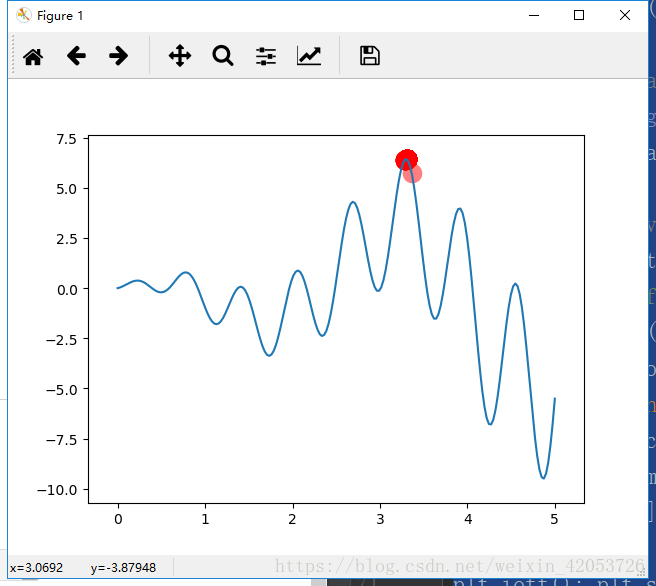
求解函式的最大值y=xsin(10x)+xsin(2x),自變數取值:0--5,用Python畫出的影象如下
(注:此程式碼好像有一些感覺不對的地方,首先:沒有保留那些適應度低的個體
pop = select(pop, fitness) '''這一行程式碼,壓根就是把適應度低的個體給乾沒了。'''
for parent in pop: child = crossover(parent, pop_copy) child = mutate(child) parent[:] = child '''這個for迴圈,沒有對交叉變異後的個體進行適應度篩選啊'''
)
程式碼講解:
''' 1初始化種群:返回一個元素為 二進位制的矩陣,每一行代表一個個體,每個個體由二進位制數字表示x值 2:代表二進位制,POP_SIZE:矩陣行數,DNA_SIZE:矩陣列數。 ''' pop = np.random.randint(2, size=(POP_SIZE, DNA_SIZE)) ''' 2,計算適應度並且原則優良種群,(有放回的抽取),迴圈很多代 pop:代表二進位制種群,translateDNA(pop):將其轉化十進位制,在計算適應度,在select選擇優良種群 ''' F_values = F(translateDNA(pop)) #求函式值 fitness = get_fitness(F_values) #得到使用度,這裡例子函式值就是適應度 pop = select(pop, fitness) #此時的pop是經過篩選的好的總群,也是一個二進位制表現方式,裡面有很多一樣的個體,因為使用放回抓取 ''' 3,經過一波篩選後,接下來該交叉變異了,為了得到更好的x值,因為初始化的x值使得個體分佈不均勻 ''' pop_copy = pop.copy() #複製一份優良種群,用於交叉變異 for parent in pop: child = crossover(parent, pop_copy) #交叉 child = mutate(child) #交叉後的種群在進行變異 parent[:] = child #將child賦值給parent
難度較大的程式碼:
crossover() mutate() parent[:] = child ''' crossover 交叉:parent:表示每一個二進位制個體,pop:優良的種群,如100個個體 返回交叉後的一個個體,也是二進位制表示方式 這個函式的功能就是 parent[cross_points] = pop[i_, cross_points] ''' def crossover(parent, pop): # mating process (genes crossover) if np.random.rand() < CROSS_RATE: i_ = np.random.randint(0, POP_SIZE, size=1) # select another individual from pop # 從0-POP_SIZE,隨機選擇一個數字, cross_points = np.random.randint(0, 2, size=DNA_SIZE).astype(np.bool) #array([ True, False, False, True, True, False, False, True, True, #True]) #隨機生成一個10個元素的陣列,元素為0和1,在轉化成bool型 # choose crossover points parent[cross_points] = pop[i_, cross_points] #這個語句有難度: ''' 將parent為True的元素,將被改變,False的元素不變.將被改變的元素改變成 pop矩陣第 i_ 行裡面被選擇為true的元素, 注意,parent的是cross_points, pop 也是cross_points,必須保持一致,才可以實現交叉生成一個新的個體,這個個體是父母基因的交叉結果 ''' # mating and produce one child return parent #將新個體返回出去
'''
變異:將交叉後得到的個體,(這個個體不一定就是好的個體,很可能是不好的適應度不高的個體)
進行變異,
核心程式碼:
child[point] = 1 if child[point] == 0 else 0
'''
def mutate(child):
for point in range(DNA_SIZE):
if np.random.rand() < MUTATION_RATE:
child[point] = 1 if child[point] == 0 else 0
'''
point是把child這個個體基因遍歷一遍,按照機率進行將0變成1,
注意:並不是將所有的0變成1,而是有機率的 if np.random.rand() < MUTATION_RATE:
'''
return child全部程式碼:
"""
Visualize Genetic Algorithm to find a maximum point in a function.
Visit my tutorial website for more: https://morvanzhou.github.io/tutorials/
"""
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
DNA_SIZE = 10 # DNA length
POP_SIZE = 100 # population size
CROSS_RATE = 0.8 # mating probability (DNA crossover)
MUTATION_RATE = 0.003 # mutation probability
N_GENERATIONS = 200
X_BOUND = [0, 5] # x upper and lower bounds
def F(x): return np.sin(10*x)*x + np.cos(2*x)*x # to find the maximum of this function
# find non-zero fitness for selection
def get_fitness(pred): return pred + 1e-3 - np.min(pred)
# convert binary DNA to decimal and normalize it to a range(0, 5)
def translateDNA(pop): return pop.dot(2 ** np.arange(DNA_SIZE)[::-1]) / float(2**DNA_SIZE-1) * X_BOUND[1]
def select(pop, fitness): # nature selection wrt pop's fitness
idx = np.random.choice(np.arange(POP_SIZE), size=POP_SIZE, replace=True,
p=fitness/fitness.sum())
return pop[idx]
def crossover(parent, pop): # mating process (genes crossover)
if np.random.rand() < CROSS_RATE:
i_ = np.random.randint(0, POP_SIZE, size=1) # select another individual from pop
cross_points = np.random.randint(0, 2, size=DNA_SIZE).astype(np.bool) # choose crossover points
parent[cross_points] = pop[i_, cross_points] # mating and produce one child
return parent
def mutate(child):
for point in range(DNA_SIZE):
if np.random.rand() < MUTATION_RATE:
child[point] = 1 if child[point] == 0 else 0
return child
pop = np.random.randint(2, size=(POP_SIZE, DNA_SIZE)) # initialize the pop DNA
plt.ion() # something about plotting
x = np.linspace(*X_BOUND, 200)
plt.plot(x, F(x))
for _ in range(N_GENERATIONS):
F_values = F(translateDNA(pop)) # compute function value by extracting DNA
# something about plotting
if 'sca' in globals(): sca.remove()
sca = plt.scatter(translateDNA(pop), F_values, s=200, lw=0, c='red', alpha=0.5); plt.pause(0.05)
# GA part (evolution)
fitness = get_fitness(F_values)
print("Most fitted DNA: ", pop[np.argmax(fitness), :])
pop = select(pop, fitness)
pop_copy = pop.copy()
for parent in pop:
child = crossover(parent, pop_copy)
child = mutate(child)
parent[:] = child # parent is replaced by its child
plt.ioff(); plt.show()