Data Driven Investor
Binomial Theorem
If you’re like me — haven’t touched math/statistics in years but trying to tackle concepts for Machine Learning— here’s a really easy way to understand Binomial Theorem:
But maybe even reading the terms “Binomial” intimidate you. (I had flashing nightmares from my Calculus class four years ago
The first thing you need to remember is that a polynomial is an expression. In simple English, think of polynomials as “sentences” that contain different “words”.

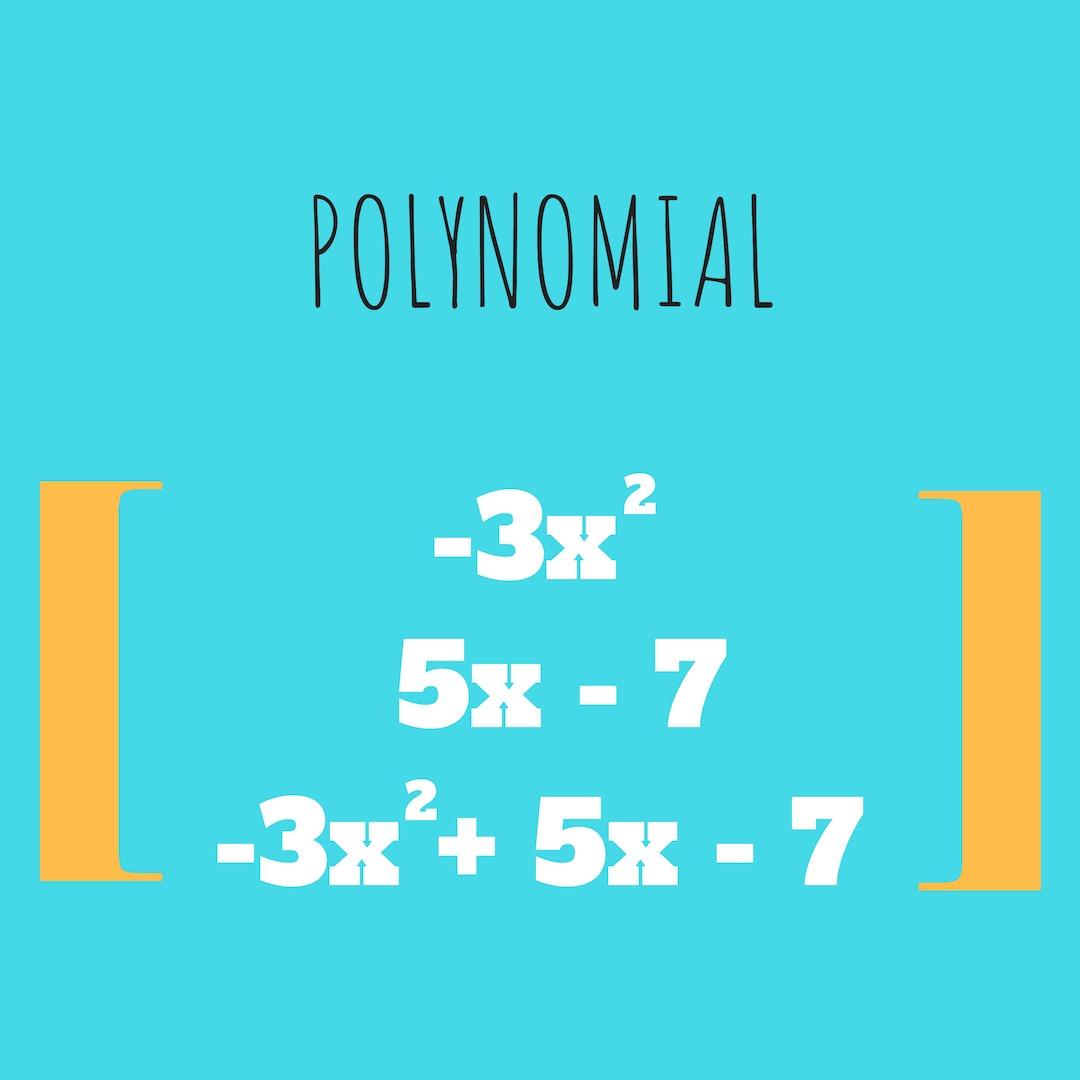
Depending on how many “words” the polynomial has, it has a different term.

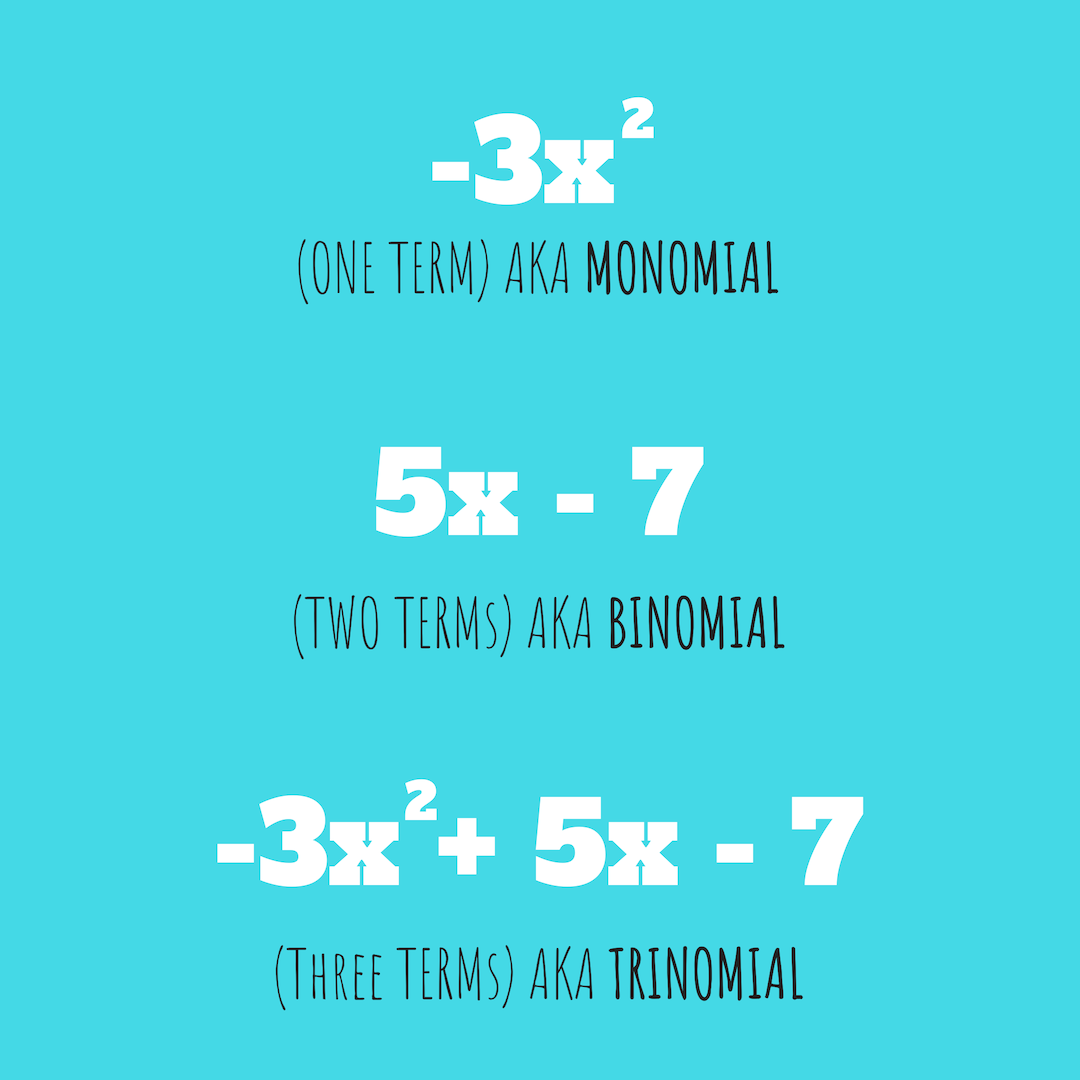
Coefficient is the number before a variable (in this case “-3” is the coefficient, “x” is the variable). Degree

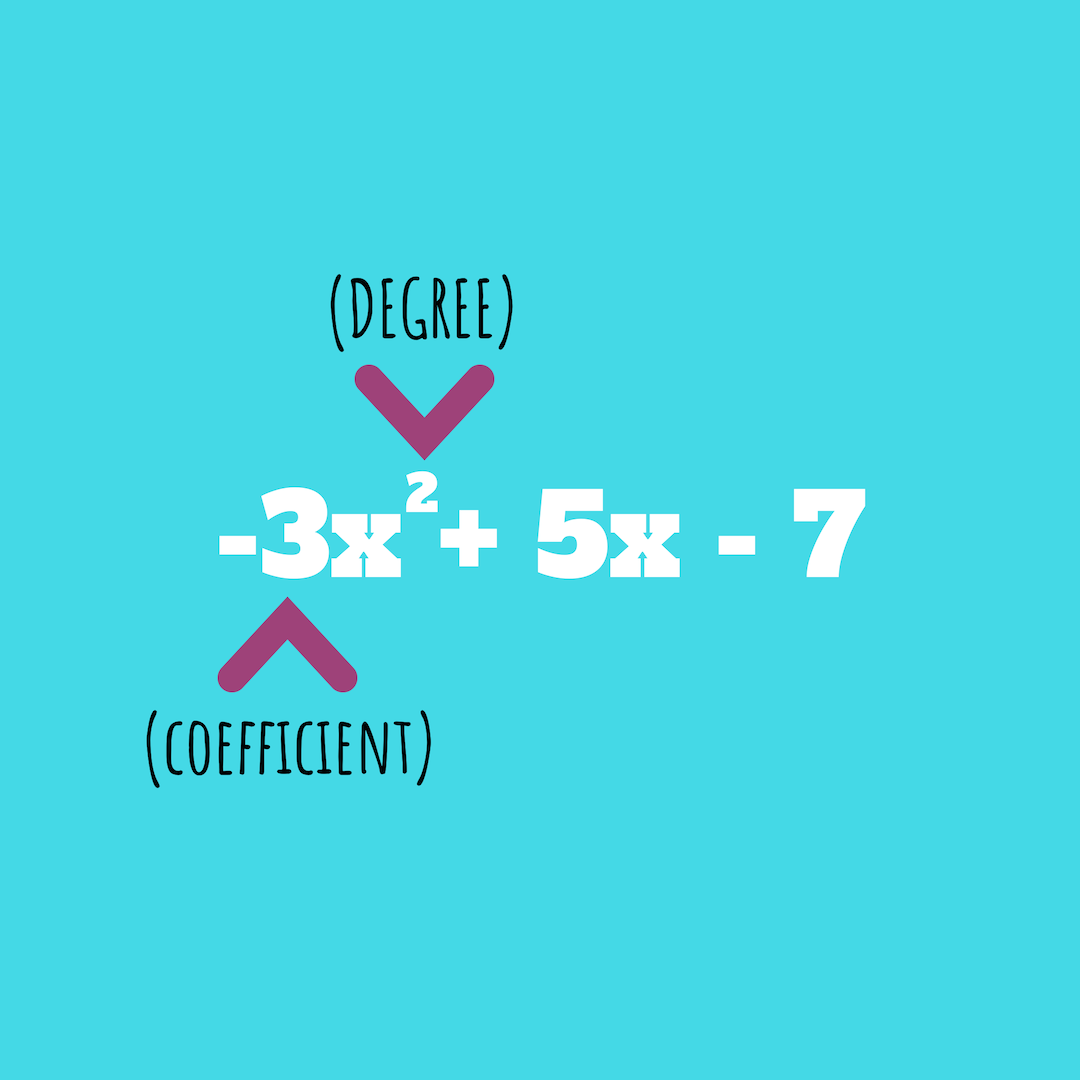
Ok, now that “binomial”, “polynomial” and “coefficient” don’t sound as intimidating, let’s now figure out Binomial Theorem:

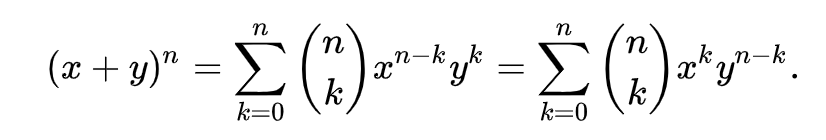
I know, it looks horrible, but it’s not that bad.
Let’s use an example:

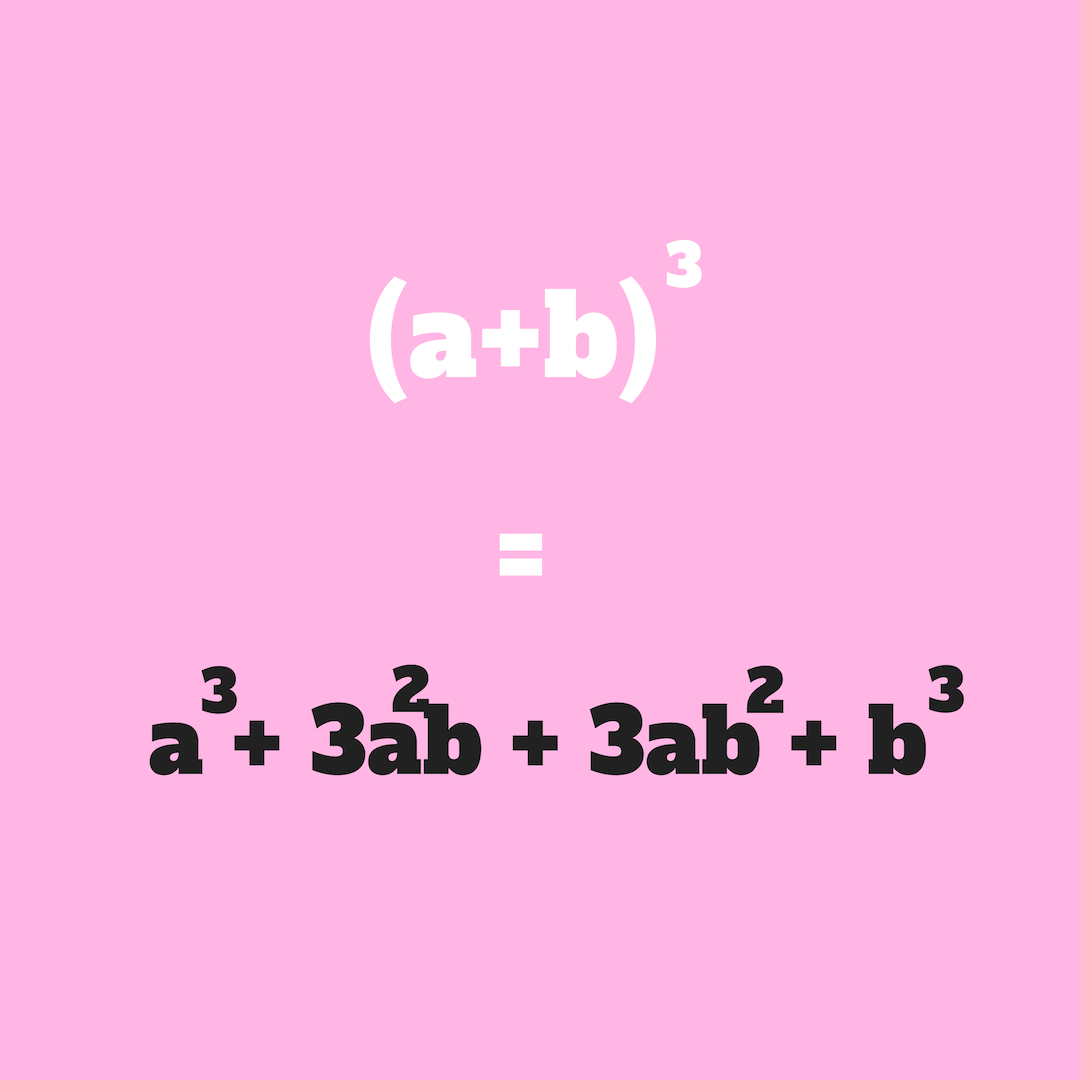
The theorem becomes easier to understand once you break down the answer into “a”s and “b”:
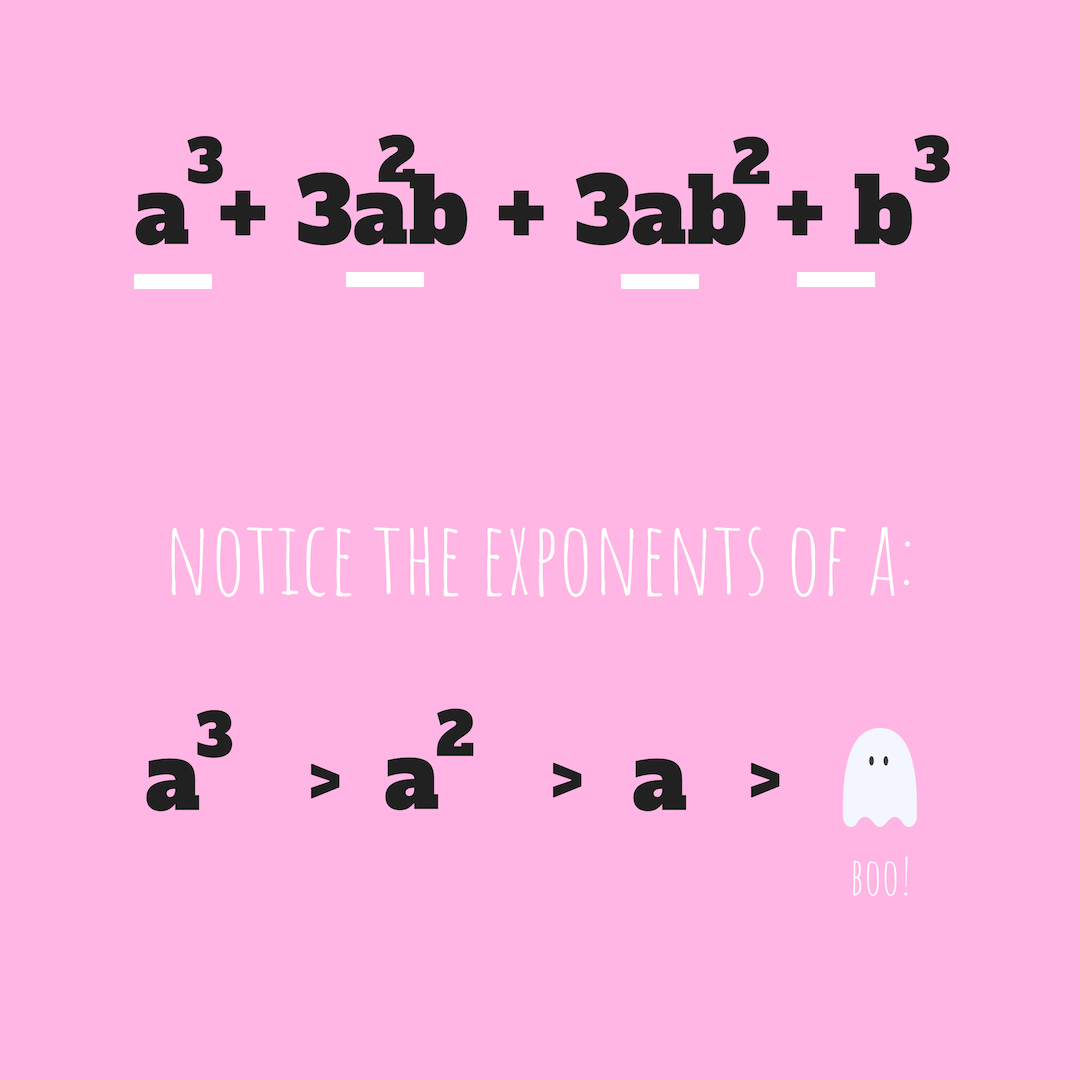

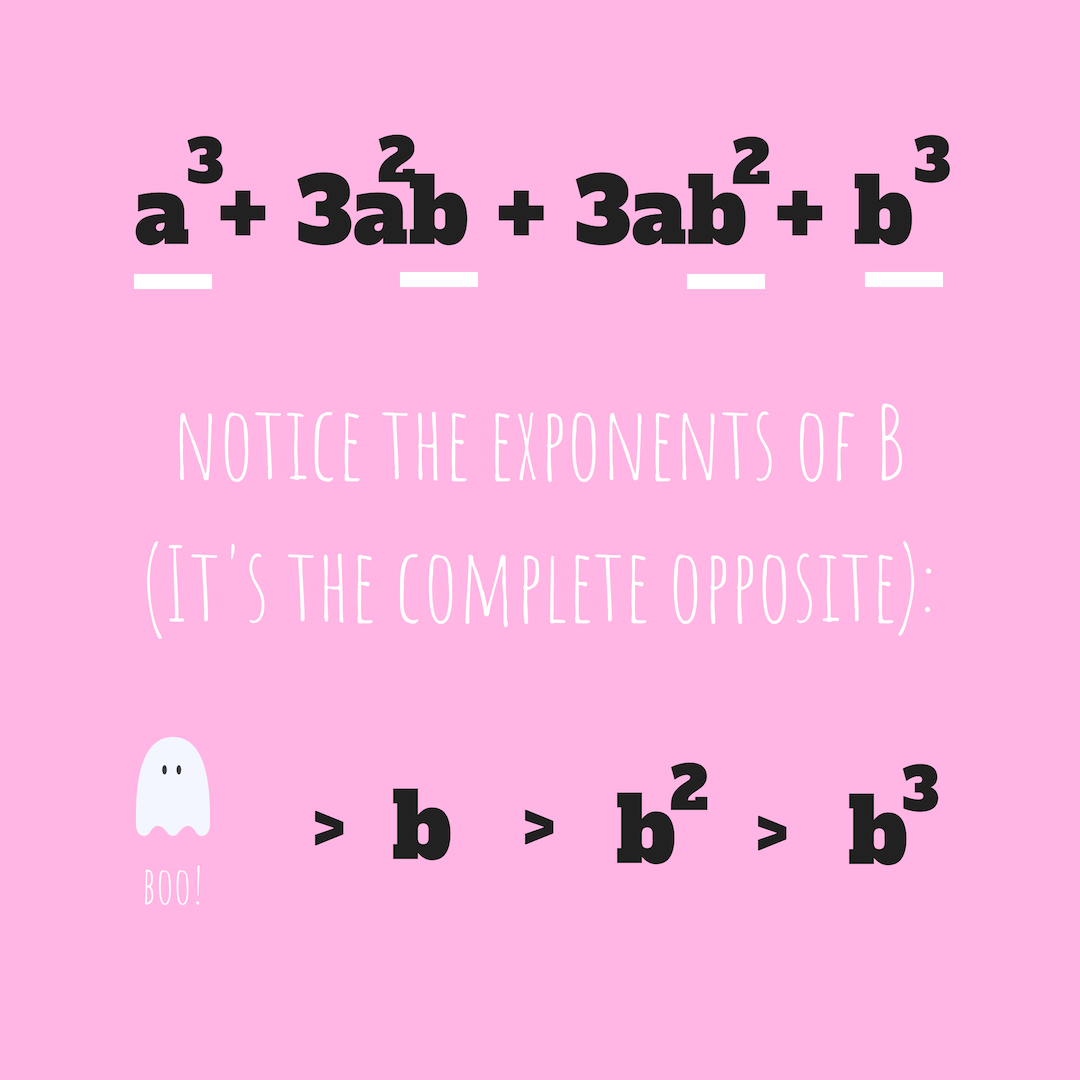
Now if we were to go back to the formula…
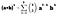
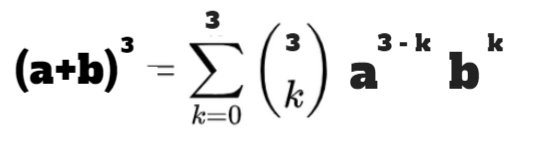
k will keep increasing (0 > 1 > 2 > 3) until it reaches 3.
a will keep decreasing as k increases (3–0 > 3–1 > 3–2 > 3–3).
b will keep increasing as k increases (0 > 1 > 2 > 3).
“3 choose k” is the coefficient that will change according to the value “k”.

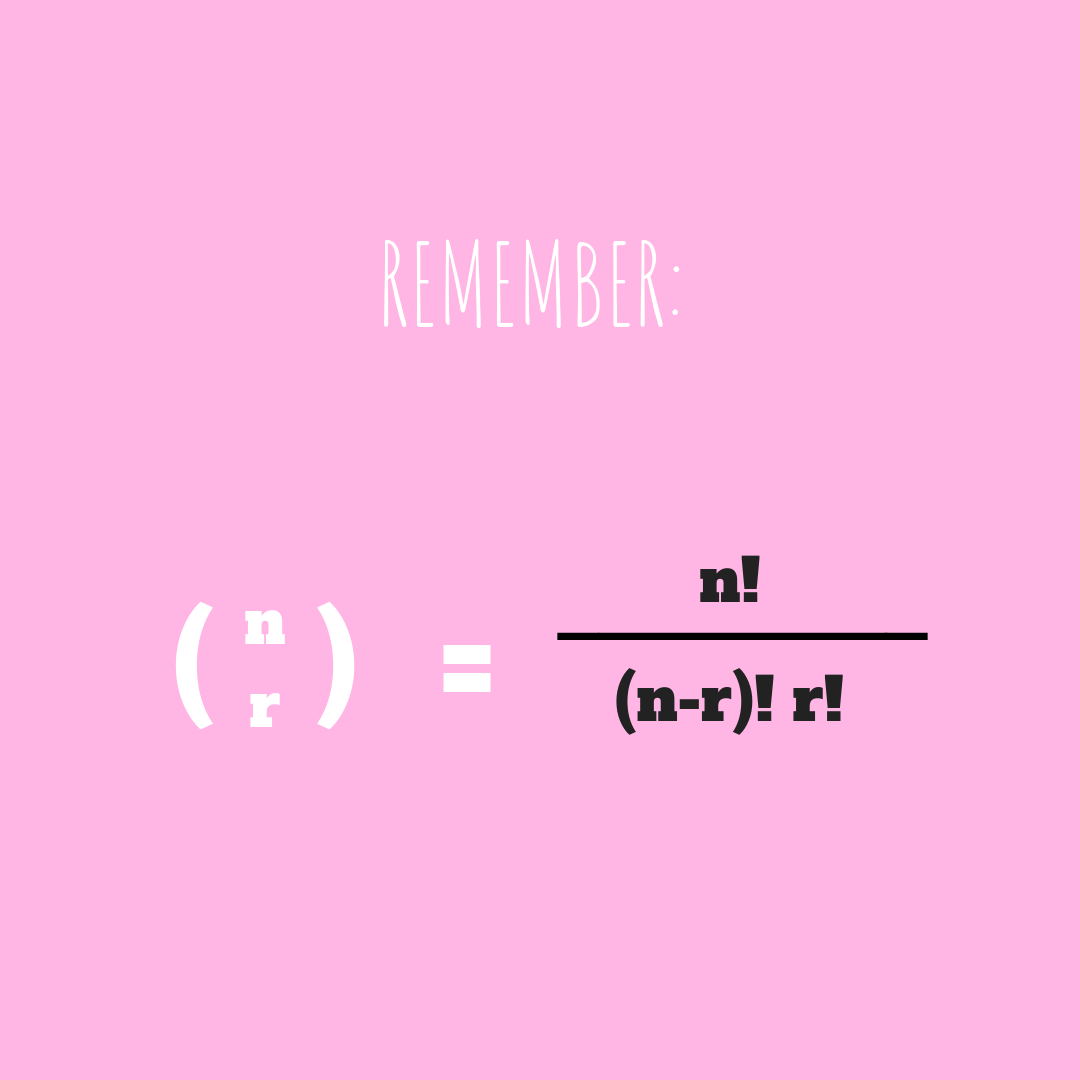
Now all you have to do is get the sum of all the outcomes for when k=0, k=1, k=2, k=3.
