目標定位和檢測系列(3):交併比(IOU)和非極大值抑制(NMS)的python實現
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-01-06
交併比(Intersection over Union)和非極大值抑制是(Non-Maximum Suppression)是目標檢測任務中非常重要的兩個概念。例如在用訓練好的模型進行測試時,網路會預測出一系列的候選框。這時候我們會用NMS來移除一些多餘的候選框。即移除一些IOU值大於某個閾值的框。然後在剩下的候選框中,分別計算與ground truth的IOU值,通常會規定當候選框和ground truth的IOU值大於0.5時,認為檢測正確。下面我們分別用python實現IOU和NMS。
交併比IOU
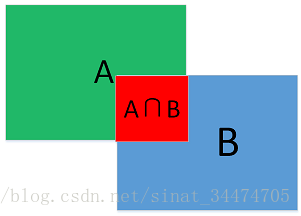
如上圖所示,IOU值定位為兩個矩形框面積的交集和並集的比值。即:
程式碼實現
import numpy as np
def compute_iou(box1, box2, wh=False):
"""
compute the iou of two boxes.
Args:
box1, box2: [xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax] (wh=False) or [xcenter, ycenter, w, h] (wh=True)
wh: the format of coordinate.
Return:
iou: iou of box1 and box2.
""" 非極大值抑制(NMS)
NMS的演算法步驟如下:
# INPUT:所有預測出的bounding box (bbx)資訊(座標和置信度confidence), IOU閾值(大於該閾值的bbx將被移除)
for object in all objects:
(1) 獲取當前目標類別下所有bbx的資訊
(2) 將bbx按照confidence從高到低排序,並記錄當前confidence最大的bbx
(3) 計算最大confidence對應的bbx與剩下所有的bbx的IOU,移除所有大於IOU閾值的bbx
(4) 對剩下的bbx,迴圈執行(2)和(3)直到所有的bbx均滿足要求(即不能再移除bbx)需要注意的是,NMS是對所有的類別分別執行的。舉個栗子,假設最後預測出的矩形框有2類(分別為cup, pen),在NMS之前,每個類別可能都會有不只一個bbx被預測出來,這個時候我們需要對這兩個類別分別執行一次NMS過程。
我們用python編寫NMS程式碼,假設對於一張圖片,所有的bbx資訊已經儲存在一個字典中,儲存形式如下:
predicts_dict: {"cup": [[x1_1, y1_1, x2_1, y2_1, scores1], [x1_2, y1_2, x2_2, y2_2, scores2], ...], "pen": [[x1_1, y1_1, x2_1, y2_1, scores1], [x1_2, y1_2, x2_2, y2_2, scores2], ...]}.即目標的位置和置信度用列表儲存,每個列表中的一個子列表代表一個bbx資訊。詳細的程式碼如下:
def non_max_suppress(predicts_dict, threshold=0.2):
"""
implement non-maximum supression on predict bounding boxes.
Args:
predicts_dict: {"stick": [[x1, y1, x2, y2, scores1], [...]]}.
threshhold: iou threshold
Return:
predicts_dict processed by non-maximum suppression
"""
for object_name, bbox in predicts_dict.items(): #對每一個類別的目標分別進行NMS
bbox_array = np.array(bbox, dtype=np.float)
## 獲取當前目標類別下所有矩形框(bounding box,下面簡稱bbx)的座標和confidence,並計算所有bbx的面積
x1, y1, x2, y2, scores = bbox_array[:,0], bbox_array[:,1], bbox_array[:,2], bbox_array[:,3], bbox_array[:,4]
areas = (x2-x1+1) * (y2-y1+1)
#print "areas shape = ", areas.shape
## 對當前類別下所有的bbx的confidence進行從高到低排序(order儲存索引資訊)
order = scores.argsort()[::-1]
print "order = ", order
keep = [] #用來存放最終保留的bbx的索引資訊
## 依次從按confidence從高到低遍歷bbx,移除所有與該矩形框的IOU值大於threshold的矩形框
while order.size > 0:
i = order[0]
keep.append(i) #保留當前最大confidence對應的bbx索引
## 獲取所有與當前bbx的交集對應的左上角和右下角座標,並計算IOU(注意這裡是同時計算一個bbx與其他所有bbx的IOU)
xx1 = np.maximum(x1[i], x1[order[1:]]) #當order.size=1時,下面的計算結果都為np.array([]),不影響最終結果
yy1 = np.maximum(y1[i], y1[order[1:]])
xx2 = np.minimum(x2[i], x2[order[1:]])
yy2 = np.minimum(y2[i], y2[order[1:]])
inter = np.maximum(0.0, xx2-xx1+1) * np.maximum(0.0, yy2-yy1+1)
iou = inter/(areas[i]+areas[order[1:]]-inter)
print "iou =", iou
print np.where(iou<=threshold) #輸出沒有被移除的bbx索引(相對於iou向量的索引)
indexs = np.where(iou<=threshold)[0] + 1 #獲取保留下來的索引(因為沒有計算與自身的IOU,所以索引相差1,需要加上)
print "indexs = ", type(indexs)
order = order[indexs] #更新保留下來的索引
print "order = ", order
bbox = bbox_array[keep]
predicts_dict[object_name] = bbox.tolist()
predicts_dict = predicts_dict
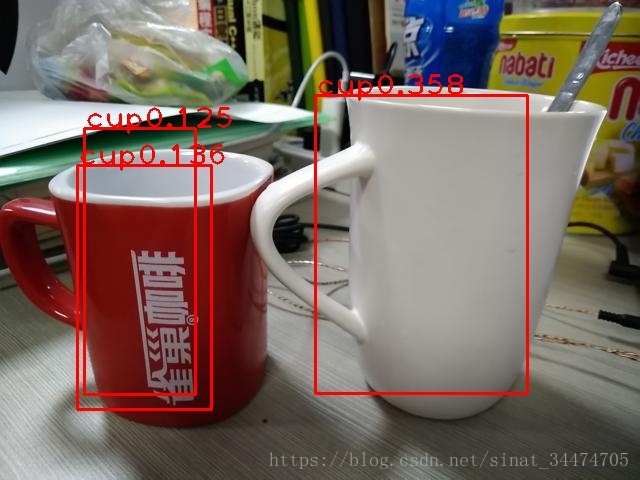
return predicts_dict假設我們現在已經計算得到了網路輸出的bbx資訊如下:
predict dict = {'cup': [[59, 120, 137, 368, 0.124648176], [221, 89, 369, 367, 0.35818103], [54, 154, 148, 382, 0.13638769]]}即模型已經預測出了三個bbx,我們看一下在原圖上的結果:

我們呼叫上面的non_max_suppress函式,並使用預設閾值,再看處理後的結果:
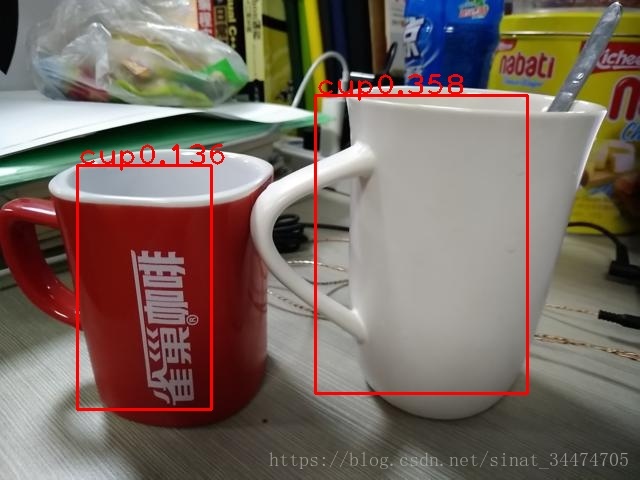

可以發現,多餘的bbx已經被抑制了。
