非極大值抑制(Non-Maximum-Suppression)
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-01-03
注意看哦,有兩個版本的。
理論基礎
說實話,講理論基礎實在不是我的強項,但是還是得硬著頭皮來講,希望我的講解不至於晦澀難懂。
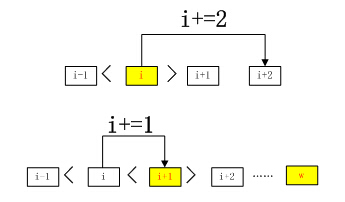
非極大值抑制,簡稱為NMS演算法。是一種獲取區域性最大值的有效方法。在3領域中,假設一個行向量的長度為w,從左向右,由第一個到第w個和其3領域中的數值進行比對。
如果某個i大於i+1並且小於i-1,則其為一個絕不最大值,同時也就意味著i+1不是一個區域性最大值,所以將i移動2個步長,從i+2開始繼續向後進行比較判斷。如果某個i不滿足上述條件,則將i+1,繼續對i+1進行比對。當比對到最後一個w時,直接將w設定為區域性最大值。演算法流程如下圖所示。
應用範圍
非極大值抑制NMS在目標檢測,定位等領域是一種被廣泛使用的方法。對於目標具體位置定位過程,不管是使用sw(sliding Window)還是ss(selective search)方法,都會產生好多的候選區域。實際看到的情形就是好多區域的交叉重疊,難以滿足實際的應用。如下圖所示。
針對該問題有3種傳統的解決思路。
第一種,選取好多矩形框的交集,即公共區域作為最後的目標區域。
第二種,選取好多矩形框的並集,即所有矩形框的最小外截矩作為目標區域。當然這裡也不是隻要相交就直接取並集,需要相交的框滿足交集佔最小框的面積達到一定比例(也就是閾值)才合併。
第三種,也就是本文的NMS,簡單的說,對於有相交的就選取其中置信度最高的一個作為最後結果,對於沒相交的就直接保留下來,作為最後結果。
總體來說,3種處理思路都各有千秋,不能一概評論哪種好壞。各種頂會論文也會選擇不同的處理方法。
#include <iostream>
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
// 新版本寫在下面檔案中:
#include <opencv2/nonfree/features2d.hpp>
//#include "opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp"
#include<opencv2/legacy/legacy.hpp>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
void nms(
const std::vector<cv::Rect>& srcRects,
std::vector<cv::Rect>& resRects,
float thresh
)
{
resRects.clear();
const size_t size = srcRects.size();
if (!size)
{
return;
}
// Sort the bounding boxes by the bottom - right y - coordinate of the bounding box
std::multimap<int, size_t> idxs;
for (size_t i = 0; i < size; ++i)
{
idxs.insert(std::pair<int, size_t>(srcRects[i].br().y, i));
}
// keep looping while some indexes still remain in the indexes list
while (idxs.size() > 0)
{
// grab the last rectangle
auto lastElem = --std::end(idxs);
const cv::Rect& rect1 = srcRects[lastElem->second];
resRects.push_back(rect1);
idxs.erase(lastElem);
for (auto pos = std::begin(idxs); pos != std::end(idxs); )
{
// grab the current rectangle
const cv::Rect& rect2 = srcRects[pos->second];
float intArea = (rect1 & rect2).area();
float unionArea = rect1.area() + rect2.area() - intArea;
float overlap = intArea / unionArea;
// if there is sufficient overlap, suppress the current bounding box
if (overlap > thresh)
{
pos = idxs.erase(pos);
}
else
{
++pos;
}
}
}
}
/**
*******************************************************************************
*
* main
*
*******************************************************************************
*/
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
std::vector<cv::Rect> srcRects;
/*
// Test 1
srcRects.push_back(cv::Rect(cv::Point(114, 60), cv::Point(178, 124)));
srcRects.push_back(cv::Rect(cv::Point(120, 60), cv::Point(184, 124)));
srcRects.push_back(cv::Rect(cv::Point(114, 66), cv::Point(178, 130)));*/
/*
// Test 2
srcRects.push_back(cv::Rect(cv::Point(12, 84), cv::Point(140, 212)));
srcRects.push_back(cv::Rect(cv::Point(24, 84), cv::Point(152, 212)));
srcRects.push_back(cv::Rect(cv::Point(12, 96), cv::Point(140, 224)));
srcRects.push_back(cv::Rect(cv::Point(36, 84), cv::Point(164, 212)));
srcRects.push_back(cv::Rect(cv::Point(24, 96), cv::Point(152, 224)));
srcRects.push_back(cv::Rect(cv::Point(24, 108), cv::Point(152, 236)));*/
// Test 3
srcRects.push_back(cv::Rect(cv::Point(12, 30), cv::Point(76, 94)));
srcRects.push_back(cv::Rect(cv::Point(12, 36), cv::Point(76, 100)));
srcRects.push_back(cv::Rect(cv::Point(72, 36), cv::Point(200, 164)));
srcRects.push_back(cv::Rect(cv::Point(84, 48), cv::Point(212, 176)));
cv::Size size(0, 0);
for (const auto& r : srcRects)
{
size.width = std::max(size.width, r.x + r.width);
size.height = std::max(size.height, r.y + r.height);
}
cv::Mat img = cv::Mat(2 * size.height, 2 * size.width, CV_8UC3, cv::Scalar(0, 0, 0));
cv::Mat imgCopy = img.clone();
for (auto r : srcRects)
{
cv::rectangle(img, r, cv::Scalar(0, 0, 255), 2);
}
cv::namedWindow("before", cv::WINDOW_NORMAL);
cv::imshow("before", img);
cv::waitKey(1);
std::vector<cv::Rect> resRects;
nms(srcRects, resRects, 0.3f);
for (auto r : resRects)
{
cv::rectangle(imgCopy, r, cv::Scalar(0, 255, 0), 2);
}
cv::namedWindow("after", cv::WINDOW_NORMAL);
cv::imshow("after", imgCopy);
cv::waitKey(0);
return 0;
} 實驗結果:
#include <iostream>
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
// 新版本寫在下面檔案中:
#include <opencv2/nonfree/features2d.hpp>
//#include "opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp"
#include<opencv2/legacy/legacy.hpp>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
static void sort(int n, const vector<float> x, vector<int> indices)
{
// 排序函式,排序後進行交換的是indices中的資料
// n:排序總數// x:帶排序數// indices:初始為0~n-1數目
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
for (j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
{
if (x[indices[j]] > x[indices[i]])
{
//float x_tmp = x[i];
int index_tmp = indices[i];
//x[i] = x[j];
indices[i] = indices[j];
//x[j] = x_tmp;
indices[j] = index_tmp;
}
}
}
int nonMaximumSuppression(int numBoxes, const vector<CvPoint> points,const vector<CvPoint> oppositePoints,
const vector<float> score, float overlapThreshold,int& numBoxesOut, vector<CvPoint>& pointsOut,
vector<CvPoint>& oppositePointsOut, vector<float> scoreOut)
{
// 實現檢測出的矩形視窗的非極大值抑制nms
// numBoxes:視窗數目// points:視窗左上角座標點// oppositePoints:視窗右下角座標點// score:視窗得分
// overlapThreshold:重疊閾值控制// numBoxesOut:輸出視窗數目// pointsOut:輸出視窗左上角座標點
// oppositePoints:輸出視窗右下角座標點// scoreOut:輸出視窗得分
int i, j, index;
vector<float> box_area(numBoxes); // 定義視窗面積變數並分配空間
vector<int> indices(numBoxes); // 定義視窗索引並分配空間
vector<int> is_suppressed(numBoxes); // 定義是否抑制表標誌並分配空間
// 初始化indices、is_supperssed、box_area資訊
for (i = 0; i < numBoxes; i++)
{
indices[i] = i;
is_suppressed[i] = 0;
box_area[i] = (float)( (oppositePoints[i].x - points[i].x + 1) *(oppositePoints[i].y - points[i].y + 1));
}
// 對輸入視窗按照分數比值進行排序,排序後的編號放在indices中
sort(numBoxes, score, indices);
for (i = 0; i < numBoxes; i++) // 迴圈所有視窗
{
if (!is_suppressed[indices[i]]) // 判斷視窗是否被抑制
{
for (j = i + 1; j < numBoxes; j++) // 迴圈當前視窗之後的視窗
{
if (!is_suppressed[indices[j]]) // 判斷視窗是否被抑制
{
int x1max = max(points[indices[i]].x, points[indices[j]].x); // 求兩個視窗左上角x座標最大值
int x2min = min(oppositePoints[indices[i]].x, oppositePoints[indices[j]].x); // 求兩個視窗右下角x座標最小值
int y1max = max(points[indices[i]].y, points[indices[j]].y); // 求兩個視窗左上角y座標最大值
int y2min = min(oppositePoints[indices[i]].y, oppositePoints[indices[j]].y); // 求兩個視窗右下角y座標最小值
int overlapWidth = x2min - x1max + 1; // 計算兩矩形重疊的寬度
int overlapHeight = y2min - y1max + 1; // 計算兩矩形重疊的高度
if (overlapWidth > 0 && overlapHeight > 0)
{
float overlapPart = (overlapWidth * overlapHeight) / box_area[indices[j]]; // 計算重疊的比率
if (overlapPart > overlapThreshold) // 判斷重疊比率是否超過重疊閾值
{
is_suppressed[indices[j]] = 1; // 將視窗j標記為抑制
}
}
}
}
}
}
numBoxesOut = 0; // 初始化輸出視窗數目0
for (i = 0; i < numBoxes; i++)
{
if (!is_suppressed[i]) numBoxesOut++; // 統計輸出視窗數目
}
index = 0;
for (i = 0; i < numBoxes; i++) // 遍歷所有輸入視窗
{
if (!is_suppressed[indices[i]]) // 將未發生抑制的視窗資訊儲存到輸出資訊中
{
pointsOut.push_back(Point(points[indices[i]].x,points[indices[i]].y));
oppositePointsOut.push_back(Point(oppositePoints[indices[i]].x,oppositePoints[indices[i]].y));
scoreOut.push_back(score[indices[i]]);
index++;
}
}
return true;
}
int main()
{
Mat image=Mat::zeros(600,600,CV_8UC3);
int numBoxes=4;
vector<CvPoint> points(numBoxes);
vector<CvPoint> oppositePoints(numBoxes);
vector<float> score(numBoxes);
points[0]=Point(200,200);oppositePoints[0]=Point(400,400);score[0]=0.99;
points[1]=Point(220,220);oppositePoints[1]=Point(420,420);score[1]=0.9;
points[2]=Point(100,100);oppositePoints[2]=Point(150,150);score[2]=0.82;
points[3]=Point(200,240);oppositePoints[3]=Point(400,440);score[3]=0.5;
float overlapThreshold=0.8;
int numBoxesOut;
vector<CvPoint> pointsOut;
vector<CvPoint> oppositePointsOut;
vector<float> scoreOut;
nonMaximumSuppression( numBoxes,points,oppositePoints,score,overlapThreshold,numBoxesOut,pointsOut,oppositePointsOut,scoreOut);
for (int i=0;i<numBoxes;i++)
{
rectangle(image,points[i],oppositePoints[i],Scalar(0,255,255),6);
char text[20];
sprintf(text,"%f",score[i]);
putText(image,text,points[i],CV_FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX, 1,Scalar(0,255,255));
}
for (int i=0;i<numBoxesOut;i++)
{
rectangle(image,pointsOut[i],oppositePointsOut[i],Scalar(0,0,255),2);
}
imshow("result",image);
waitKey();
return 0;
}

如果幫到你了,請讚賞支援: