AlexNet對MNIST分類
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-01-14
一.AlexNet介紹
https://blog.csdn.net/MESSI_JAMES/article/details/81384534#t8
二.過程介紹
一次完整的訓練模型和評估模型的過程一般分為 3 個步驟:
1.載入資料,
2.定義網路模型,
3. 訓練模型和評估模型。
三.程式碼實現
import tensorflow as tf # 1.載入資料 # 輸入資料 from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("MNIST_data", one_hot=True) # 定義網路的一引數 learning_rate = 0.001 training_iters = 20000 batch_size = 128 display_step = 10 # 定義網路的引數 n_input = 784 # 輸入的維度(img shape: 28×28) n_classes = 10 # 標記的維度 (0-9 digits) dropout = 0.75 # Dropout 的概率,輸出的可能性 # 輸入佔位符 x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, n_input]) y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, n_classes]) keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32) #dropout # 2.構建網路模型 # 定義卷積操作 def conv2d(name, x, W, b, strides=1): x = tf.nn.conv2d(x, W, strides=[1, strides, strides, 1], padding='SAME') x = tf.nn.bias_add(x, b) return tf.nn.relu(x, name=name) # 使用 relu 啟用函式 # 定義池化層操作 def maxpool2d(name, x, k=2): return tf.nn.max_pool(x, ksize=[1, k, k, 1], strides=[1, k, k, 1], padding='SAME', name=name) # 規範化操作 def norm(name, l_input, lsize=4): return tf.nn.lrn(l_input, lsize, bias=1.0, alpha=0.001 / 9.0, beta=0.75, name=name) # 定義所有的網路引數 weights = { 'wc1': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([11, 11, 1, 96])), 'wc2': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([5, 5, 96, 256])), 'wc3': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3, 3, 256, 384])), 'wc4': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3, 3, 384, 384])), 'wc5': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([3, 3, 384, 256])), 'wd1': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([4*4*256, 4096])), 'wd2': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([4096, 4096])), 'out': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([4096, 10])) } biases = { 'bc1': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([96])), 'bc2': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([256])), 'bc3': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([384])), 'bc4': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([384])), 'bc5': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([256])), 'bd1': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([4096])), 'bd2': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([4096])), 'out': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_classes])) } # 定義整個網路 def alex_net(x, weights, biases, dropout): # Reshape input picture x = tf.reshape(x, shape=[-1, 28, 28, 1]) # 第一層卷積 # 卷積 conv1 = conv2d('conv1', x, weights['wc1'], biases['bc1']) # 下采樣 pool1 = maxpool2d('pool1', conv1, k=2) # 規範化 norm1 = norm('norm1', pool1, lsize=4) # 第二層卷積 # 卷積 conv2 = conv2d('conv2', conv1, weights['wc2'], biases['bc2']) # 最大池化(向下取樣) pool2 = maxpool2d('pool2', conv2, k=2) # 規範化 norm2 = norm('norm2', pool2, lsize=4) # 第三層卷積 # 卷積 conv3 = conv2d('conv3', norm2, weights['wc3'], biases['bc3']) # 下采樣 pool3 = maxpool2d('pool3', conv3, k=2) # 規範化 norm3 = norm('norm3', pool3, lsize=4) # 第四層卷積 conv4 = conv2d('conv4', norm3, weights['wc4'], biases['bc4']) # 第五層卷積 conv5 = conv2d('conv5', norm3, weights['wc5'], biases['bc5']) # 下采樣 pool5 = maxpool2d('pool5', conv5, k=2) # 規範化 norm5 = norm('norm5', pool5, lsize=4) # 全連線層 1 fc1 = tf.reshape(norm5, [-1, weights['wd1'].get_shape().as_list()[0]]) fc1 = tf.add(tf.matmul(fc1, weights['wd1']), biases['bd1']) fc1 = tf.nn.relu(fc1) # dropout fc1 = tf.nn.dropout(fc1, dropout) # 全連線層 2 fc2 = tf.reshape(fc1, [-1, weights['wd1'].get_shape().as_list()[0]]) fc2 = tf.add(tf.matmul(fc2, weights['wd1']), biases['bd1']) fc2 = tf.nn.relu(fc2) # dropout fc2 = tf.nn.dropout(fc2, dropout) # 輸出層 out = tf.add(tf.matmul(fc2, weights['out']), biases['out']) return out # 構建模型 pred = alex_net(x, weights, biases, keep_prob) # 定義損失函式和優化器 cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=pred, labels=y)) optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=learning_rate).minimize(cost) # 評估函式 correct_pred = tf.equal(tf.argmax(pred, 1), tf.argmax(y, 1)) accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_pred, tf.float32)) # 3.訓練模型和評估模型 # 初始化變數 init = tf.global_variables_initializer() with tf.Session() as sess: sess.run(init) step = 1 # 開始訓練,直到達到 training_iters,即 20000 while step * batch_size < training_iters: batch_x, batch_y = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size) sess.run(optimizer, feed_dict={x: batch_x, y: batch_y, keep_prob: dropout}) if step % display_step == 0: # 計算損失值和準確度,輸出 loss, acc = sess.run([cost, accuracy], feed_dict={x: batch_x, y: batch_y, keep_prob: 1.}) print("Iter " + str(step * batch_size) + ", Minibatch Loss= " + \ "{:.6f}".format(loss) + ", Training Accuracy= " + \ "{:.5f}".format(acc)) step+=1 print("訓練完成!") # 計算測試集的準確度 print("測試集的準確度:", \ sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x: mnist.test.images[:256], y: mnist.test.labels[:256], keep_prob: 1.}))
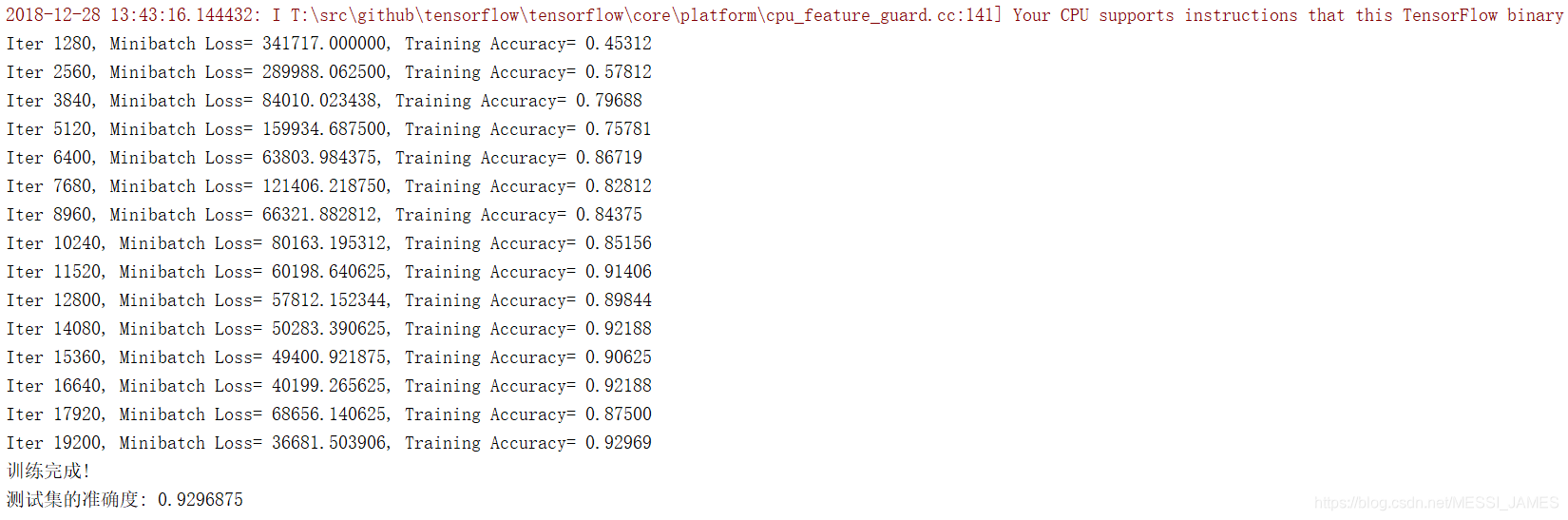
四.結果展示
五.總結
我們也可以像實現AlexNet的模型這樣,用TensorFlow 實現其他網路(如VGGNet、GoogLeNet、
ResNet),具體實現的步驟我們總結如下:
(1)仔細研讀該網路的論文,理解每一層的輸入/輸出值以及網路結構;
(2)按照載入資料,定義網路模型,訓練模型和評估模型這樣的步驟實現網路。
