【分散式鎖的演化】電商“超賣”場景實戰
阿新 • • 發佈:2020-12-29
### 前言
從本篇開始,老貓會通過電商中的業務場景和大家分享鎖在實際應用場景下的演化過程。從Java單體鎖到分散式環境下鎖的實踐。
### 超賣的第一種現象案例
其實在電商業務場景中,會有一個這樣讓人忌諱的現象,那就是“超賣”,那麼什麼是超賣呢?舉個例子,某商品的庫存數量只有10件,最終卻賣出了15件,簡而言之就是商品賣出的數量超過了商品本身的庫存數目。“超賣”會導致商家沒有商品發貨,發貨的時間延長,從引起交易雙方的糾紛。
我們來一起分析一下該現象產生的原因:假如商品只有最後一件,A使用者和B使用者同時看到了商品,並且同時加入了購物車提交了訂單,此時兩個使用者同時讀取庫存中的商品數量為一件,各自進行內存扣減之後,進行更新資料庫。因此產生超賣,我們具體看一下流程示意圖:
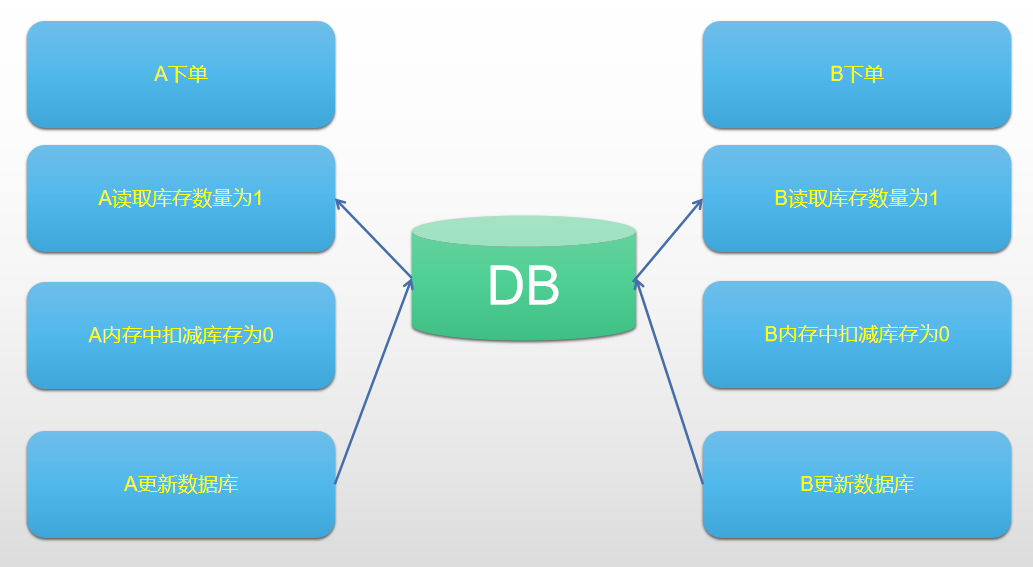
#### 解決方案
遇到上述問題,在單臺伺服器的時候我們如何解決呢?我們來看一下具體的方案。之前描述中提到,我們在扣減庫存的時候是在記憶體中進行。接下來我們將其進行下沉到資料庫中進行庫存的更新操作,我們可以向資料庫傳遞庫存增量,扣減一個庫存,增量為-1,在資料庫進行update語句計算庫存的時候,我們通過update行鎖解決併發問題。(資料庫行鎖:在資料庫進行更新的時候,當前行被鎖定,即為行鎖,此處老貓描述比較簡單,有興趣的小夥伴可以自發研究一下資料庫的鎖)。我們來看一下具體的程式碼例子。
業務邏輯程式碼如下:
```java
@Service
@Slf4j
public class OrderService {
@Resource
private KdOrderMapper orderMapper;
@Resource
private KdOrderItemMapper orderItemMapper;
@Resource
private KdProductMapper productMapper;
//購買商品id
private int purchaseProductId = 100100;
//購買商品數量
private int purchaseProductNum = 1;
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public Integer createOrder() throws Exception{
KdProduct product = productMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(purchaseProductId);
if (product==null){
throw new Exception("購買商品:"+purchaseProductId+"不存在");
}
//商品當前庫存
Integer currentCount = product.getCount();
//校驗庫存
if (purchaseProductNum > currentCount){
throw new Exception("商品"+purchaseProductId+"僅剩"+currentCount+"件,無法購買");
}
//計算剩餘庫存
Integer leftCount = currentCount -purchaseProductNum;
product.setCount(leftCount);
product.setTimeModified(new Date());
product.setUpdateUser("kdaddy");
productMapper.updateByPrimaryKeySelective(product);
//生成訂單
KdOrder order = new KdOrder();
order.setOrderAmount(product.getPrice().multiply(new BigDecimal(purchaseProductNum)));
order.setOrderStatus(1);//待處理
order.setReceiverName("kdaddy");
order.setReceiverMobile("13311112222");
order.setTimeCreated(new Date());
order.setTimeModified(new Date());
order.setCreateUser("kdaddy");
order.setUpdateUser("kdaddy");
orderMapper.insertSelective(order);
KdOrderItem orderItem = new KdOrderItem();
orderItem.setOrderId(order.getId());
orderItem.setProductId(product.getId());
orderItem.setPurchasePrice(product.getPrice());
orderItem.setPurchaseNum(purchaseProductNum);
orderItem.setCreateUser("kdaddy");
orderItem.setTimeCreated(new Date());
orderItem.setTimeModified(new Date());
orderItem.setUpdateUser("kdaddy");
orderItemMapper.insertSelective(orderItem);
return order.getId();
}
}
```
通過以上程式碼我們可以看到的是庫存的扣減在記憶體中完成。那麼我們再看一下具體的單元測試程式碼:
```java
@SpringBootTest
class DistributeApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private OrderService orderService;
@Test
public void concurrentOrder() throws InterruptedException {
//簡單來說表示計數器
CountDownLatch cdl = new CountDownLatch(5);
//用來進行等待五個執行緒同時併發的場景
CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrier = new CyclicBarrier(5);
ExecutorService es = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
for (int i =0;i<5;i++){
es.execute(()->{
try {
//等待五個執行緒同時併發的場景
cyclicBarrier.await();
Integer orderId = orderService.createOrder();
System.out.println("訂單id:"+orderId);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
cdl.countDown();
}
});
}
//避擴音前關閉資料庫連線池
cdl.await();
es.shutdown();
}
}
```
程式碼執完畢之後我們看一下結果:
```tex
訂單id:1
訂單id:2
訂單id:3
訂單id:4
訂單id:5
```
很顯然,資料庫中雖然只有一個庫存,但是產生了五個下單記錄,如下圖:
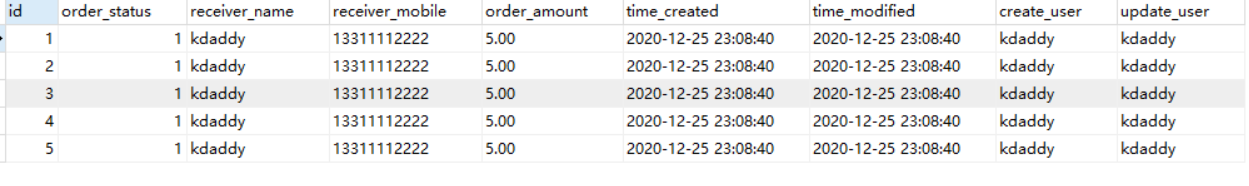

這也就產生了超賣的現象,那麼如何才能解決這個問題呢?
#### 單體架構中,利用資料庫行鎖解決電商超賣問題。
那麼如果是這種解決方案的話,我們就要將我們扣減庫存的動作下沉到我們的資料庫中,利用資料庫的行鎖解決併發情況下同時操作的問題,我們來看一下程式碼的改造點。
```java
@Service
@Slf4j
public class OrderServiceOptimizeOne {
.....篇幅限制,此處省略,具體可參考github原始碼
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public Integer createOrder() throws Exception{
KdProduct product = productMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(purchaseProductId);
if (product==null){
throw new Exception("購買商品:"+purchaseProductId+"不存在");
}
//商品當前庫存
Integer currentCount = product.getCount();
//校驗庫存
if (purchaseProductNum > currentCount){
throw new Exception("商品"+purchaseProductId+"僅剩"+currentCount+"件,無法購買");
}
//在資料庫中完成減量操作
productMapper.updateProductCount(purchaseProductNum,"kd",new Date(),product.getId());
//生成訂單
.....篇幅限制,此處省略,具體可參考github原始碼
return order.getId();
}
}
```
我們再來看一下執行的結果


從上述結果中,我們發現我們的訂單數量依舊是5個訂單,但是庫存數量此時不再是0,而是由1變成了-4,這樣的結果顯然依舊不是我們想要的,那麼此時其實又是超賣的另外一種現象。我們來看一下超賣現象二所產生的原因。
### 超賣的第二種現象案例
上述其實是第二種現象,那麼產生的原因是什麼呢?其實是在校驗庫存的時候出現了問題,在校驗庫存的時候是併發進行對庫存的校驗,五個執行緒同時拿到了庫存,並且發現庫存數量都為1,造成了庫存充足的假象。此時由於寫操作的時候具有update的行鎖,所以會依次扣減執行,扣減操作的時候並無校驗邏輯。因此就產生了這種超賣顯現。簡單的如下圖所示:
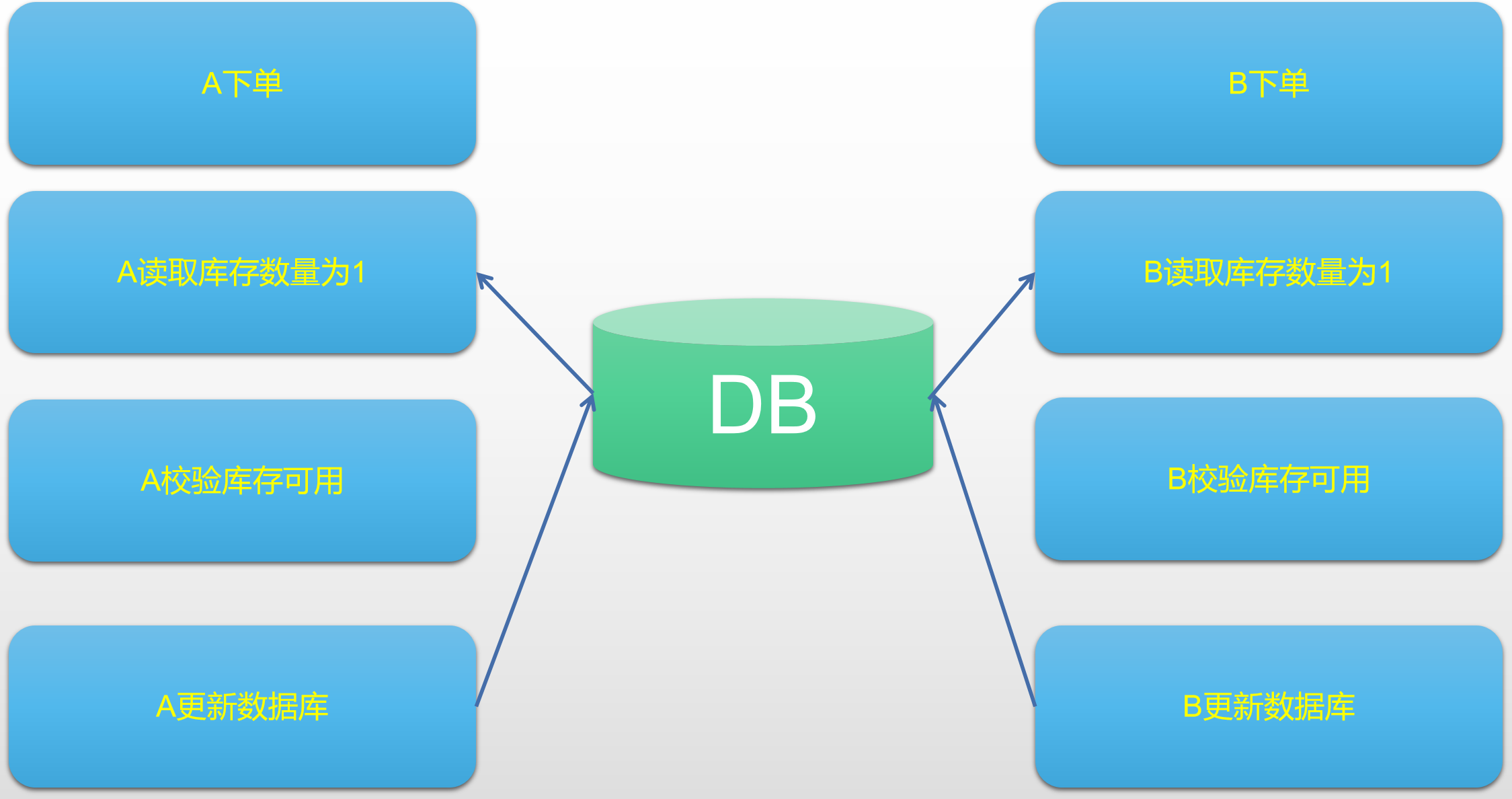
#### 解決方案一:
單體架構中,利用資料庫行鎖解決電商超賣問題。就針對當前該案例,其實我們的解決方式也比較簡單,就是更新完畢之後,我們立即查詢一下庫存的數量是否大於等於0即可。如果為負數的時候,我們直接丟擲異常即可。(當然由於此種操作並未涉及到鎖的知識,所以此方案僅做提出,不做實際程式碼實踐)
#### 解決方案二:
校驗庫存和扣減庫存的時候統一加鎖,讓其成為原子性的操作,併發的時候只有獲取鎖的時候才會去讀庫庫存並且扣減庫存操作。當扣減結束之後,釋放鎖,確保庫存不會扣成負數。那此時我們就需要用到前面博文提到的java中的兩個鎖的關鍵字`synchronized`關鍵字 和 `ReentrantLock`。
關於`synchronized`關鍵字的用法在之前的博文中也提到過,有方法鎖和程式碼塊鎖兩種方式,我們一次來通過實踐看一下程式碼,首先是通過方法鎖的方式,具體的程式碼如下:
```java
//`synchronized`方法塊鎖
@Service
@Slf4j
public class OrderServiceSync01 {
.....篇幅限制,此處省略,具體可參考github原始碼
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public synchronized Integer createOrder() throws Exception{
KdProduct product = productMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(purchaseProductId);
if (product==null){
throw new Exception("購買商品:"+purchaseProductId+"不存在");
}
//商品當前庫存
Integer currentCount = product.getCount();
//校驗庫存
if (purchaseProductNum > currentCount){
throw new Exception("商品"+purchaseProductId+"僅剩"+currentCount+"件,無法購買");
}
//在資料庫中完成減量操作
productMapper.updateProductCount(purchaseProductNum,"kd",new Date(),product.getId());
//生成訂單
.....篇幅限制,此處省略,具體可參考github原始碼
return order.getId();
}
}
```
此時我們看一下執行的結果。
```tex
[pool-1-thread-2] c.k.d.service.OrderServiceSync01 : pool-1-thread-2庫存數1
[pool-1-thread-1] c.k.d.service.OrderServiceSync01 : pool-1-thread-1庫存數1
訂單id:12
[pool-1-thread-5] c.k.d.service.OrderServiceSync01 : pool-1-thread-5庫存數-1
訂單id:13
[pool-1-thread-3] c.k.d.service.OrderServiceSync01 : pool-1-thread-3庫存數-1
```


此時我們很明顯地發現數據還是存在問題,那麼這個是什麼原因呢?
其實聰明的小夥伴其實已經發現了,我們第二個執行緒讀取到的資料依舊是1,那麼為什麼呢?其實很簡單,第二個執行緒在讀取商品庫存的時候是1的原因是因為上一個執行緒的事務並沒有提交,我們也能比較清晰地看到目前我們方法上的事務是在鎖的外面的。所以就產生了該問題,那麼針對這個問題,我們其實可以將事務的提交進行手動提交,然後放到鎖的程式碼塊中。具體改造如下。
```java
public synchronized Integer createOrder() throws Exception{
//手動獲取當前事務
TransactionStatus transaction = platformTransactionManager.getTransaction(transactionDefinition);
KdProduct product = productMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(purchaseProductId);
if (product==null){
platformTransactionManager.rollback(transaction);
throw new Exception("購買商品:"+purchaseProductId+"不存在");
}
//商品當前庫存
Integer currentCount = product.getCount();
log.info(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"庫存數"+currentCount);
//校驗庫存
if (purchaseProductNum > currentCount){
platformTransactionManager.rollback(transaction);
throw new Exception("商品"+purchaseProductId+"僅剩"+currentCount+"件,無法購買");
}
//在資料庫中完成減量操作
productMapper.updateProductCount(purchaseProductNum,"kd",new Date(),product.getId());
//生成訂單並完成訂單的儲存操作
.....篇幅限制,此處省略,具體可參考github原始碼
platformTransactionManager.commit(transaction);
return order.getId();
}
```
此時我們再看一下執行的結果:
```
[pool-1-thread-3] c.k.d.service.OrderServiceSync01 : pool-1-thread-3庫存數1
[pool-1-thread-5] c.k.d.service.OrderServiceSync01 : pool-1-thread-5庫存數0
訂單id:16
[pool-1-thread-4] c.k.d.service.OrderServiceSync01 : pool-1-thread-4庫存數0
[pool-1-thread-1] c.k.d.service.OrderServiceSync01 : pool-1-thread-1庫存數0
```
根據上面的結果我們可以很清楚的看到只有第一個執行緒讀取到了庫存是1,後面所有的執行緒獲取到的都是0庫存。我們再來看一下具體的資料庫。


很明顯,我們到此資料庫的庫存和訂單數量也都正確了。
後面`synchronized`程式碼塊鎖以及`ReentrantLock`交給小夥伴們自己去嘗試著完成,當然老貓也已經把相關的程式碼寫好了。具體的原始碼地址為:https://github.com/maoba/kd-distribute
### 寫在最後
本文通過電商中兩種超賣現象和小夥伴們分享了一下單體鎖解決問題過程。當然這種鎖的使用是無法跨越jvm的,當遇到多個jvm的時候就失效了,所以後面的文章中會和大家分享分散式鎖的實現。當然也是通過電商中超賣的例子和大家分享。敬請期待。
### 當然更多幹貨也歡迎大家搜尋關注公眾號“程式設計師老貓”。老貓,一個專注原創乾貨的男人
