Java 常見的排序演算法
這篇文章主要介紹常見的排序演算法,圖片來源於網路,java程式碼實現為本人編寫,如若有不當之處還望指正。
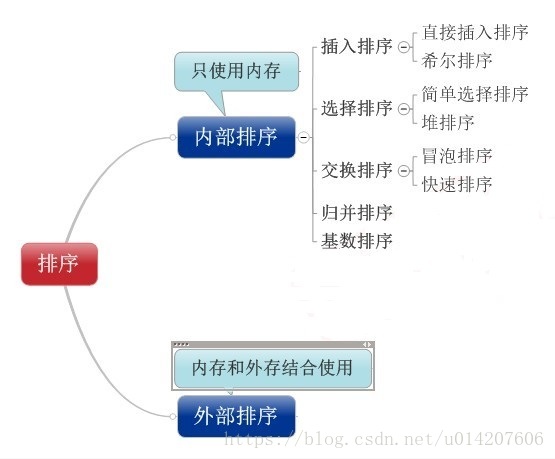
分類
1)插入排序(直接插入排序、希爾排序)
2)交換排序(氣泡排序、快速排序)
3)選擇排序(直接選擇排序、堆排序)
4)歸併排序
5)分配排序(基數排序)
所需輔助空間最多:歸併排序
所需輔助空間最少:堆排序
平均速度最快:快速排序
不穩定:快速排序,希爾排序,堆排序。
先來看看8種排序之間的關係:
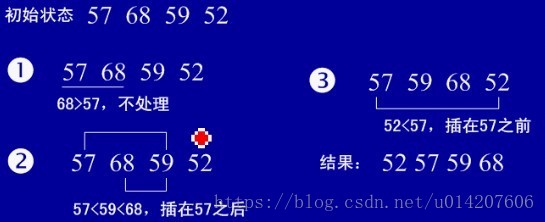
直接插入排序
(1)基本思想:在要排序的一組數中,假設前面(n-1)[n>=2] 個數已經是排
好順序的,現在要把第n個數插到前面的有序數中,使得這n個數
也是排好順序的。如此反覆迴圈,直到全部排好順序。
(2)例項
package test;
public class InsertSort {
private int[] a; public InsertSort() { a = new int[]{ 1, 54, 6, 3, 78, 34, 12, 45 }; } public void insertSort() { if ( a.length < 2 ) { return; } else { int curPosition = 1; for ( ; curPosition < a.length; curPosition++ ) { int prePosition = curPosition - 1; int temp = a[ curPosition ]; for ( ; prePosition >= 0 && temp < a[ prePosition ]; prePosition-- ) { a[ prePosition+1 ] = a[ prePosition ]; } a[ prePosition + 1 ] = temp; } } } public void printResult() { for ( int elem : a ) { System.out.println( elem ); } } public static void main( String[] args ) { InsertSort insetSort = new InsertSort(); insetSort.printResult(); insetSort.insertSort(); System.out.println( "\n" ); insetSort.printResult(); }
}
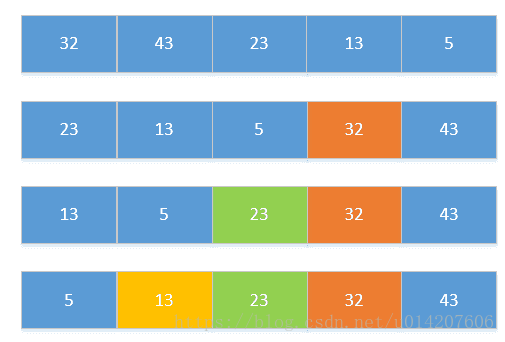
簡單選擇排序
(1)基本思想:在要排序的一組數中,選出最小的一個數與第一個位置的數交換;
然後在剩下的數當中再找最小的與第二個位置的數交換,如此迴圈到倒數第二個數和最後一個數比較為止。
(2)例項:
package test;
public class SelectSort {
private int[] a; public SelectSort() { a = new int[]{ 1, 54, 6, 3, 78, 34, 12, 45 }; } public void selectSort() { if ( a != null && a.length != 0 ) { for ( int i = 0; i < a.length - 1; i++ ) { int temp = a[ i ]; int min= temp ; int position = 0; for ( int j = i + 1; j < a.length; j++ ) { if ( a[ j ] < min ) { min = a[ j ]; position = j; } } if ( min < temp ) { a[ i ] = a[ position ]; a[ position ] = temp; } } } } public void printResult() { for ( int elem : a ) { System.out.println( elem ); } } public static void main( String[] args ) { SelectSort selectSort = new SelectSort(); selectSort.printResult(); selectSort.selectSort(); System.out.println( "\n" ); selectSort.printResult(); }
}
氣泡排序
(1)基本思想:在要排序的一組數中,對當前還未排好序的範圍內的全部數,自上而下對相鄰的兩個數依次進行比較和調整,讓較大的數往下沉,較小的往上冒。即:每當兩相鄰的數比較後發現它們的排序與排序要求相反時,就將它們互換。
(2)例項:
package test;
public class BubbleSort {
private int[] a;
public BubbleSort() {
a = new int[]{ 1, 54, 6, 3, 78, 34, 12, 45 };
}
public void bubbleSort() {
if ( a.length < 2 ) {
return;
}
for ( int i = 0; i < a.length - 1; i++ ) { // 每執行一次for語句的迴圈體,將最大的一個放在資料後面(length-1-i索引處)
for ( int j = 0; j < a.length - 1 - i; j++ ) { // 用於對兩兩相鄰元素進行比較,減i是因為已經有i個較大的元素放在資料的後面,不需要再比較
if ( a[ j ] > a[ j + 1 ] ) {
int temp = a[ j ];
a[ j ] = a[ j + 1 ];
a[ j + 1 ] = temp;
}
}
}
}
public void printResult() {
for ( int elem : a ) {
System.out.println( elem );
}
}
public static void main( String[] args ) {
BubbleSort bubbleSort = new BubbleSort();
bubbleSort.printResult();
bubbleSort.bubbleSort();
System.out.println( "\n" );
bubbleSort.printResult();
}
}
快速排序
(1)基本思想:選擇一個基準元素,通常選擇第一個元素或者最後一個元素,通過一趟掃描,將待排序列分成兩部分,一部分比基準元素小,一部分大於等於基準元素,此時基準元素在其排好序後的正確位置,然後再用同樣的方法遞迴地排序劃分的兩部分。
(2)例項:
package test;
public class QuickSort {
private int[] a;
public QuickSort() {
a = new int[]{ 49, 38, 65, 97, 76, 13, 27, 49, 78, 34, 12, 64, 5, 4, 62, 99, 98, 54, 56, 17, 18, 23, 34, 15, 35,
25, 53, 51 };
}
public int[] getDatas() {
return a;
}
public void quickSort( int[] datas ) {
quickSort( datas, 0, datas.length - 1 );
}
private void quickSort( int[] datas, int startIndex, int endIndex ) {
if ( datas == null || datas.length == 0 || datas.length < 2 ) {
return;
}
if ( startIndex >= endIndex ) {
return;
}
int baseNum = datas[ startIndex ];// 基準值
int i = startIndex;
int j = endIndex;
while ( i < j ) { // 執行一次迴圈體,將一個大於基準值的數和一個小於基準值的數交換位置
while ( i < j && datas[ j ] > baseNum ) {
j-- ;
}
if ( i < j ) {
datas[ i++ ] = datas[ j ];
}
while ( i < j && datas[ i ] < baseNum ) {
i++ ;
}
if ( i < j ) {
a[ j-- ] = a[ i ];
}
}
a[ i ] = baseNum;
quickSort( datas, startIndex, i - 1 );
quickSort( datas, i + 1, endIndex );
}
public void printResult() {
for ( int elem : a ) {
System.out.println( elem );
}
}
public static void main( String[] args ) {
QuickSort quickSort = new QuickSort();
quickSort.printResult();
quickSort.quickSort( quickSort.getDatas() );
System.out.println( "\n" );
quickSort.printResult();
}
}
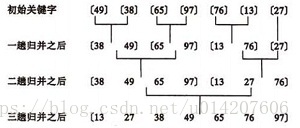
歸併排序
基本思想:
歸併(Merge)排序法是將兩個(或兩個以上)有序表合併成一個新的有序表,即把待排序序列分為若干個子序列,每個子序列是有序的。然後再把有序子序列合併為整體有序序列。
歸併排序示例:
public class MergeSortTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] data = new int[] { 5, 3, 6, 2, 1, 9, 4, 8, 7 };
print(data);
mergeSort(data);
System.out.println("排序後的陣列:");
print(data);
}
public static void mergeSort(int[] data) {
sort(data, 0, data.length - 1);
}
public static void sort(int[] data, int left, int right) {
if (left >= right)
return;
// 找出中間索引
int center = (left + right) / 2;
// 對左邊陣列進行遞迴
sort(data, left, center);
// 對右邊陣列進行遞迴
sort(data, center + 1, right);
// 合併
merge(data, left, center, right);
print(data);
}
/**
* 將兩個陣列進行歸併,歸併前面2個數組已有序,歸併後依然有序
*
* @param data
* 陣列物件
* @param left
* 左陣列的第一個元素的索引
* @param center
* 左陣列的最後一個元素的索引,center+1是右陣列第一個元素的索引
* @param right
* 右陣列最後一個元素的索引
*/
public static void merge(int[] data, int left, int center, int right) {
// 臨時陣列
int[] tmpArr = new int[data.length];
// 右陣列第一個元素索引
int mid = center + 1;
// third 記錄臨時陣列的索引
int third = left;
// 快取左陣列第一個元素的索引
int tmp = left;
while (left <= center && mid <= right) {
// 從兩個陣列中取出最小的放入臨時陣列
if (data[left] <= data[mid]) {
tmpArr[third++] = data[left++];
} else {
tmpArr[third++] = data[mid++];
}
}
// 剩餘部分依次放入臨時陣列(`**實際上兩個while只會執行其中一個**`)
while (mid <= right) {
tmpArr[third++] = data[mid++];
}
while (left <= center) {
tmpArr[third++] = data[left++];
}
// 將臨時陣列中的內容拷貝回原陣列中
// (原left-right範圍的內容被複制回原陣列)
while (tmp <= right) {
data[tmp] = tmpArr[tmp++];
}
}
public static void print(int[] data) {
for (int i = 0; i < data.length; i++) {
System.out.print(data[i] + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}