Bobo老師機器學習筆記第九課-邏輯迴歸程式碼展示
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-12-28
在上一篇部落格中我們學習了邏輯迴歸(LogisticRegression)的理論。那麼在這篇部落格中,我們用程式碼展示一下,如何用梯度下降法獲取邏輯迴歸的引數
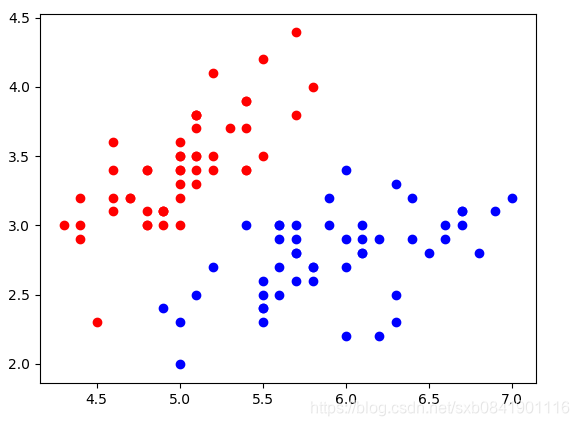
步驟1:我們載入sklearn中的鳶尾花資料進行測試,由於為了資料視覺化,我們選擇2種類型的鳶尾花,並且只選擇2個特徵。
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import datasets X, y = datasets.load_iris(return_X_y=True) X = X[y < 2, :2] y = y[y < 2] plt.scatter(X[y == 0, 0], X[y == 0, 1], color="red") plt.scatter(X[y == 1, 0], X[y == 1, 1], color="blue") plt.show()
視覺化一下:
步驟二: 我們編寫自己的迴歸演算法
# -*- encoding: utf-8 -*- import numpy as np from .metrics import accuracy_score class LogisticRegression: def __init__(self): """初始化Logistic Regression模型""" self.coef_ = None self.intercept_ = None self._theta = None def _sigmoid(self, t): return 1. / (1. + np.exp(-t)) def fit(self, X_train, y_train, eta=0.01, n_iters=1e4): """根據訓練資料集X_train, y_train, 使用梯度下降法訓練Logistic Regression模型""" assert X_train.shape[0] == y_train.shape[0], \ "the size of X_train must be equal to the size of y_train" def J(theta, X_b, y): y_hat = self._sigmoid(X_b.dot(theta)) try: return - np.sum(y*np.log(y_hat) + (1-y)*np.log(1-y_hat)) / len(y) except: return float('inf') def dJ(theta, X_b, y): return X_b.T.dot(self._sigmoid(X_b.dot(theta)) - y) / len(y) def gradient_descent(X_b, y, initial_theta, eta, n_iters=1e4, epsilon=1e-8): theta = initial_theta cur_iter = 0 while cur_iter < n_iters: gradient = dJ(theta, X_b, y) last_theta = theta theta = theta - eta * gradient if (abs(J(theta, X_b, y) - J(last_theta, X_b, y)) < epsilon): break cur_iter += 1 return theta X_b = np.hstack([np.ones((len(X_train), 1)), X_train]) initial_theta = np.zeros(X_b.shape[1]) self._theta = gradient_descent(X_b, y_train, initial_theta, eta, n_iters) self.intercept_ = self._theta[0] self.coef_ = self._theta[1:] return self def predict_proba(self, X_predict): """給定待預測資料集X_predict,返回表示X_predict的結果概率向量""" assert self.intercept_ is not None and self.coef_ is not None, \ "must fit before predict!" assert X_predict.shape[1] == len(self.coef_), \ "the feature number of X_predict must be equal to X_train" X_b = np.hstack([np.ones((len(X_predict), 1)), X_predict]) return self._sigmoid(X_b.dot(self._theta)) def predict(self, X_predict): """給定待預測資料集X_predict,返回表示X_predict的結果向量""" assert self.intercept_ is not None and self.coef_ is not None, \ "must fit before predict!" assert X_predict.shape[1] == len(self.coef_), \ "the feature number of X_predict must be equal to X_train" proba = self.predict_proba(X_predict) return np.array(proba >= 0.5, dtype='int') def score(self, X_test, y_test): """根據測試資料集 X_test 和 y_test 確定當前模型的準確度""" y_predict = self.predict(X_test) return accuracy_score(y_test, y_predict) def __repr__(self): return "LogisticRegression()"
步驟三、進行測試
from logisticregression import LogisticRegression iris = load_iris() X = iris.data y = iris.target X = X[y < 2, :2] y = y[y < 2] log_reg = LogisticRegression() X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, random_state=666) log_reg.fit(X_train, y_train) print log_reg.theta_ print log_reg.predict_probality(X_test) print log_reg.predict(X_test) print log_reg.scores(X_test, y_test)
執行結果:
引數: 第1個表示截距, 第2,3表示引數: [ 0. 2.93348784 -5.10537984]
預測出來的概率:
[0.92944114 0.98777304 0.15845401 0.18960373 0.03911344 0.02054764
0.05175747 0.99672293 0.9787036 0.7523886 0.04525759 0.003409
0.28048662 0.03911344 0.83661026 0.81299828 0.83506118 0.34328248
0.06419014 0.22523806 0.02384776 0.17983628 0.9787036 0.98804275
0.08845609]把概率進行映射出來的結果:
[1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0]準確率為:
1這個主要是由於資料比較少,並且我們只取了2個特徵,不復雜。所以評分高。
總結:
1、在程式碼實現過程中,梯度下降方法中初始化init_theta錯了,後來參考了一下老師的程式碼,重新改正過來了。
init_theta = np.zeros(X_b.shape[1]) 這裡面X_b已經增加了一列。 這個要注意。 要是你在西安,感興趣一起學習AIOPS,歡迎加入QQ群 860794445
