pytorch手動實現梯度下降法,隨機梯度法--基於logistic Regression並探索Mini batch作用
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-12-28
簡述
基於這次凸優化的大專案作業。
下面會圍繞著通過logistic Regression來做MNIST集上的手寫數字識別~
以此來探索logistic Regression,梯度下降法,隨機梯度法,以及Mini batch的作用。
核心任務是實現梯度下降法和隨機梯度法。但是其他的準備工作也得做的較為好~
匯入的包
import os
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.utils.data as Data
import torchvision
讀取資料
EPOCH = 1 # train the training data n times, to save time, we just train 1 epoch sigmoid函式
sigmoid函式,將資料R對映到(0,1)區間上了。
softmax函式
softmax是將根據n個數值的大小來分配概率區間
- 一般來說,為了避免數值越界的話,會要求減去最大值。
- 但是這裡我們是用logistic regression,數值都會在0,1區間中,不會太大,因此不用擔心這個問題。
cross_Entropy函式
cross_Entropy 就是交叉熵。
這裡,一旦我們給出了標準的label之後,我們就知道實際的p值分佈為
只有一個元素為1,其他元素為0的概率分佈了。
也就說,我們這就是
也就是對應label的概率越大越好~
任務描述
- : softmax
- :sigmoid
- :cross_Entropy
- : 真實標籤
採用SDG,和DG演算法
本文采用了pytorch實現,主要是為了避免手動算梯度。pytorch有autograd的機制。
本文一直採用的是固定步長
SGD
-
batch = 1
-
(GD的alpha採用的是0.001)
-
最後的結果是:0.836
-
準確率的變化情況
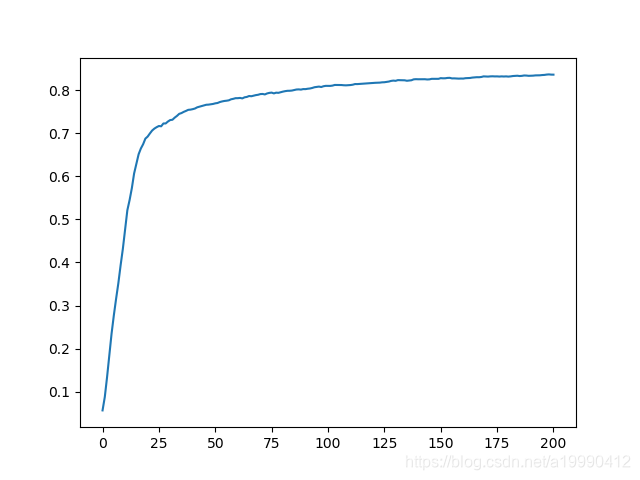
-
A和b和最優值的距離(這裡用的是矩陣二範數)
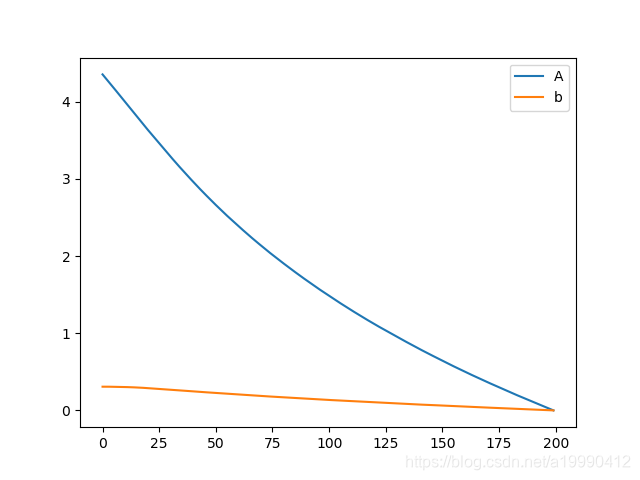
- 實現SDG的部分程式碼
從logistics regression模型中獲取了
A, b = [i for i in logits.parameters()]
A.cuda()
b.cuda()
通過檢視pytorch的原始碼實現中關於優化器部分的實現,手動設定了梯度歸零的操作,不然就會是累積梯度了。
if A.grad is not None:
A.grad.zero_()
b.grad.zero_()
- 梯度下降更新梯度
A.data = A.data - alpha * A.grad.data
b.data = b.data - alpha * b.grad.data
完整程式碼
import os
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.utils.data as Data
import torchvision
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
EPOCH = 5 # train the training data n times, to save time, we just train 1 epoch
BATCH_SIZE = 1
DOWNLOAD_MNIST = False
LR = 0.001
# Mnist digits dataset
if not (os.path.exists('./mnist/')) or not os.listdir('./mnist/'):
# not mnist dir or mnist is empyt dir
DOWNLOAD_MNIST = True
train_data = torchvision.datasets.MNIST(
root='./mnist/',
train=True, # this is training data
transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),
download=DOWNLOAD_MNIST,
)
# Data Loader for easy mini-batch return in training, the image batch shape will be (50, 1, 28, 28)
train_loader = Data.DataLoader(dataset=train_data, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=True)
class Logits(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Logits, self).__init__()
self.linear = nn.Linear(28 * 28, 10)
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=1)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.linear(x)
x = self.sigmoid(x)
x = self.softmax(x)
return x
test_data = torchvision.datasets.MNIST(root='./mnist/', train=False)
test_x = torch.unsqueeze(test_data.test_data, dim=1).type(
torch.FloatTensor).cuda() / 255. # shape from (2000, 28, 28) to (2000, 1, 28, 28), value in range(0,1)
test_y = test_data.test_labels
alpha = 0.001
logits = Logits().cuda()
# optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(logits.parameters(), lr=LR) # optimize all cnn parameters
# optimizer.zero_grad()
loss_func = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() # the target label is not one-hotted
Accurate = []
Astore = []
bstore = []
A, b = [i for i in logits.parameters()]
A.cuda()
b.cuda()
for e in range(EPOCH):
for step, (x, b_y) in enumerate(train_loader): # gives batch data
b_x = x.view(-1, 28 * 28).cuda() # reshape x to (batch, time_step, input_size)
b_y = b_y.cuda()
output = logits(b_x) # logits output
loss = loss_func(output, b_y) # cross entropy loss
if A.grad is not None:
A.grad.zero_()
b.grad.zero_()
loss.backward() # backpropagation, compute gradients
A.data = A.data - alpha * A.grad.data
b.data = b.data - alpha * b.grad.data
if step % 1500 == 0:
test_output = logits(test_x.view(-1, 28 * 28))
pred_y = torch.max(test_output, 1)[1].cuda().data.squeeze()
Accurate.append(sum(test_y.cpu().numpy() == pred_y.cpu().numpy()) / (1.0 * len(test_y.cpu().numpy())))
print(Accurate[-1])
Astore.append(A.detach())
bstore.append(b.detach())
test_output = logits(test_x.view(-1, 28 * 28))
pred_y = torch.max(test_output, 1)[1].cuda().data.squeeze()
print(pred_y, 'prediction number')
print(test_y, 'real number')
Accurate.append(sum(test_y.cpu().numpy() == pred_y.cpu().numpy()) / (1.0 * len(test_y.cpu().numpy())))
print(Accurate[-1])
for i in range(len(Astore)):
Astore[i] = (Astore[i] - Astore[-1]).norm()
bstore[i] = (bstore[i] - bstore[-1]).norm()
plt.plot(Astore, label='A')
plt.plot(bstore, label='b')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
plt.cla()
plt.plot(Accurate)
plt.show()
GD
將BATCHSIZE設定為6000(MNIST訓練集的數目)就是全梯度下降了。
- 但是這裡的步長不宜過小(GD的alpha採用的是0.05)
其他關鍵的地方都是一樣的,但是因為用到了GPU計算,而且資料集也只有一個,所以先將資料集也拿出來。避免反覆的呼叫MNIST loader讀取資料,再放到GPU上,浪費時間。
此外,將EPOCH次數,設定了為5000
- 在GPU環境下,很快就完成了運算
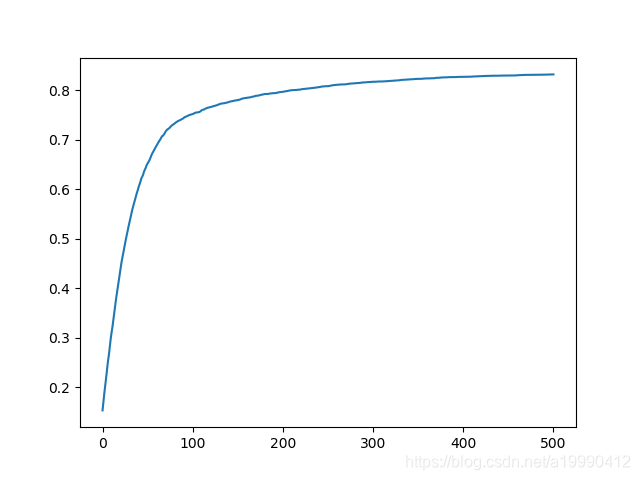
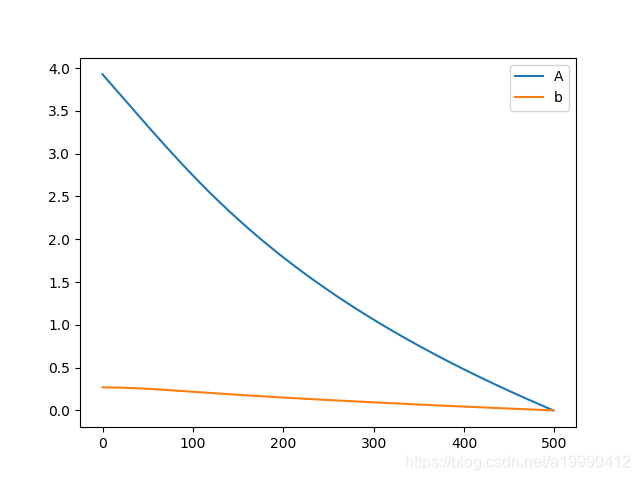
import os
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.utils.data as Data
import torchvision
EPOCH = 5000 # train the training data n times, to save time, we just train 1 epoch
BATCH_SIZE = 60000
DOWNLOAD_MNIST = False
# Mnist digits dataset
if not (os.path.exists('./mnist/')) or not os.listdir('./mnist/'):
# not mnist dir or mnist is empyt dir
DOWNLOAD_MNIST = True
train_data = torchvision.datasets.MNIST(
root='./mnist/',
train=True, # this is training data
transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),
download=DOWNLOAD_MNIST,
)
# Data Loader for easy mini-batch return in training, the image batch shape will be (50, 1, 28, 28)
train_loader = Data.DataLoader(dataset=train_data, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=True)
class Logits(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Logits, self).__init__()
self.linear = nn.Linear(28 * 28, 10)
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=1)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.linear(x)
x = self.sigmoid(x)
x = self.softmax(x)
return x
test_data = torchvision.datasets.MNIST(root='./mnist/', train=False)
test_x = torch.unsqueeze(test_data.test_data, dim=1).type(
torch.FloatTensor).cuda() / 255. # shape from (2000, 28, 28) to (2000, 1, 28, 28), value in range(0,1)
test_y = test_data.test_labels
alpha = 0.05
logits = Logits().cuda()
# optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(logits.parameters(), lr=LR) # optimize all cnn parameters
# optimizer.zero_grad()
loss_func = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() # the target label is not one-hotted
Accurate = []
Astore = []
bstore = []
A, b = [i for i in logits.parameters()]
A.cuda()
b.cuda()
x, b_y = [(i, j) for i, j in train_loader][0]
b_x = x.view(-1, 28 * 28).cuda() # reshape x to (batch, time_step, input_size)
b_y = b_y.cuda()
for e in range(EPOCH):
output = logits(b_x) # logits output
loss = loss_func(output, b_y) # cross entropy loss
if A.grad is not None:
A.grad.zero_()
b.grad.zero_()
loss.backward() # backpropagation, compute gradients
A.data = A.data - alpha * A.grad.data
b.data = b.data - alpha * b.grad.data
test_output = logits(test_x.view(-1, 28 * 28))
# print(e)
if e % 10 == 0:
pred_y = torch.max(test_output, 1)[1].cuda().data.squeeze()
Accurate.
