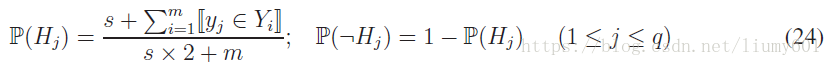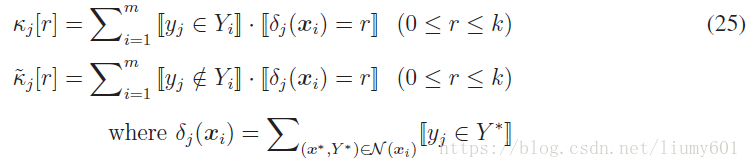基於ML-KNN的多標籤分類演算法
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-01-02
最近有一個專案需要用多標籤分類思想來建模,之前對這塊不是太瞭解,查了一些論文,發現目前主流的演算法包括ML-KNN、ML-DT、Rank-SVM、CML等,其中ML-KNN演算法思想最簡單,結合原始論文,本文大概介紹下演算法思想和程式碼實現。
ML-KNN借鑑了KNN的思想尋找K個近鄰樣本,並運用貝葉斯條件概率,來計算當前標籤為1和0的概率,概率大的標籤定為樣本最終的標籤,這就是ML-KNN的大致思想。
虛擬碼如下:
1、第1到3行計算樣本集中每個樣本的K個最近鄰。
2、第4到6行計算每個標籤出現的概率
其中Hj表示標籤j出現這一事件,m表示樣本總數,s是平滑項,通常取1。Kj[r]陣列表示當前標籤為1並且K相鄰樣本中標籤為1的個數為r的樣本總數。
3、第8行計算未知樣本的K近鄰
4、第9、10行計算未知樣本K近鄰中標籤j為1的個數
5、第12行計算未知樣本的每個標籤
其中P(Hj|Cj)表示未知樣本K近鄰中標籤j為1個數為Cj條件下,該樣本標籤j也為1的概率,P(Hj)表示樣本集中標籤j為1的概率,P(Cj|Hj)表示當前樣本標籤j為1條件下,K近鄰中標籤j為的個數為Cj的概率。
Python程式碼實現如下:
import numpy as np import pandas as pd def mlknn(train, test, id, label_columns, k): smooth = 1.0 #計算每個標籤出現的概率 phj = {} for label in label_columns: phj[label] = (smooth+train[train[label]==1].shape[0])/(smooth*2+train.shape[0]) train_ids = train[id].values tmp_train = train.drop(label_columns+[id], axis=1) test_ids = test[id].values test_labels = test[label_columns] tmp_test = test.drop(label_columns+[id], axis=1) data_columns = tmp_train.columns #計算訓練集每個樣本之間的相似度,並儲存跟每個樣本最相似的K個樣本 knn_records_train = {} cos_train = {} for i in range(tmp_train.shape[0]): record = tmp_train.iloc[i] norm = np.linalg.norm(record) cos_train[train_ids[i]] = {} for j in range(tmp_train.shape[0]): if cos_train.has_key(train_ids[j]) and cos_train[train_ids[j]].has_key(train_ids[i]): cos_train[train_ids[i]][train_ids[j]] = cos_train[train_ids[j]][train_ids[i]] else: cos = np.dot(record, tmp_train.iloc[j])/(norm*np.linalg.norm(tmp_train.iloc[j])) cos_train[train_ids[i]][train_ids[j]] = cos topk = sorted(cos_train[train_ids[i]].items(), key=lambda item:item[1], reverse=True)[0:k] knn_records_train[train_ids[i]] = [item[0] for item in topk] kjr = {} not_kjr = {} for label in label_columns: kjr[label] = {} not_kjr[label] = {} for m in range(train.shape[0]): record = train.iloc[m] if record[label]==1: #計算標籤為1並且相鄰K個樣本中標籤也為1的樣本個數 r = 0 for rec_id in knn_records_train[train_ids[m]]: if train[train[id]==rec_id][label].values[0]==1: r += 1 if not kjr[label].has_key(r): kjr[label][r] = 1 else: kjr[label][r] += 1 else: #計算標籤為0並且相鄰K個樣本中標籤也為1的樣本個數 r = 0 for rec_id in knn_records_train[train_ids[m]]: if train[train[id]==rec_id][label].values[0]==1: r += 1 if not not_kjr[label].has_key(r): not_kjr[label][r] = 1 else: not_kjr[label][r] += 1 #計算當前樣本標籤為1條件下,K個近鄰樣本中標籤為1個數為Cj的概率 pcjhj = {} for label in label_columns: pcjhj[label] = {} for L in range(k+1): if kjr[label].has_key(L): pcjhj[label][L] = (smooth+kjr[label][L])/(smooth*(k+1)+sum(kjr[label].values())) else: pcjhj[label][L] = (smooth+0)/(smooth*(k+1)+sum(kjr[label].values())) #計算當前樣本標籤為0條件下,K個近鄰樣本中標籤為1個數為Cj的概率 not_pcjhj = {} for label in label_columns: not_pcjhj[label] = {} for L in range(k+1): if not_kjr[label].has_key(L): not_pcjhj[label][L] = (smooth+not_kjr[label][L])/(smooth*(k+1)+sum(not_kjr[label].values())) else: not_pcjhj[label][L] = (smooth+0)/(smooth*(k+1)+sum(not_kjr[label].values())) #計算測試集中每個樣本與訓練集樣本之間的相似度,並儲存跟每個樣本最相似的K個樣本 knn_records_test = {} cos_test = {} for i in range(tmp_test.shape[0]): record = tmp_test.iloc[i] norm = np.linalg.norm(record) cos_test[test_ids[i]] = {} for j in range(tmp_train.shape[0]): cos = np.dot(record, tmp_train.iloc[j])/(norm*np.linalg.norm(tmp_train.iloc[j])) cos_test[test_ids[i]][train_ids[j]] = cos topk = sorted(cos_test[test_ids[i]].items(), key=lambda item:item[1], reverse=True)[0:k] knn_records_test[test_ids[i]] = [item[0] for item in topk] pred_test_labels = {} correct_rec = 0 for i in range(tmp_test.shape[0]): record = tmp_test.iloc[i] correct_col = 0 for label in label_columns: if not pred_test_labels.has_key(label): pred_test_labels[label] = [] #計算每個測試樣本K近鄰中標籤為1的個數 cj = 0 for rec_id in knn_records_test[test_ids[i]]: if train[train[id]==rec_id][label].values[0]==1: cj += 1 #計算包含Cj個標籤為1的K近鄰條件下,該測試樣本標籤為1的概率 phjcj = phj[label]*pcjhj[label][cj] #計算包含Cj個標籤為1的K近鄰條件下,該測試樣本標籤為0的概率 not_phjcj = (1-phj[label])*not_pcjhj[label][cj] if phjcj>not_phjcj: pred_test_labels[label].append(1) pred_label = 1 else: pred_test_labels[label].append(0) pred_label = 0 if pred_label==test_labels[label].values[i]: correct_col += 1 if correct_col==len(label_columns): correct_rec += 1 print '測試集標籤識別準確率', correct_rec*1.0/test.shape[0]