[計算機視覺] 影象拼接 Image Stitching
作業要求:
1、將多張圖片合併拼接成一張全景圖(看下面效果圖)
2、儘量用C/C++(老師說用matlab會給很低的分_(:зゝ∠)_,所以下面的程式碼全部都用C++來寫)
效果圖:
實現大致步驟:
2、利用RANSAC演算法進行影象特徵匹配
3、利用匹配關鍵點進行影象拼接(Blending)
實現步驟詳解:
1、SIFT演算法進行影象特徵提取:
SIFT演算法在這裡就不詳細說了,上面的連結已經講的很詳細了(使用上面的程式碼要配置opencv環境,挺簡單的,網上很多教程)。我是將上面連結的程式碼改寫成C++,封裝了一些方法,使得能夠提取中間結果。
SIFT演算法的輸入是圖片,我們需要的輸出是各個關鍵點的位置、128維描述子(用於關鍵點匹配)。而程式碼把一個關鍵點的這些資訊都封裝在一個結構體Keypoint裡面。同時,程式碼將所有的關鍵點Keypoint儲存為一個連結串列List形式,即可以根據第一個節點訪問到所有的Keypoint節點。
因此我在改寫後的MySift.h檔案裡,添加了幾個方法,一個是SIFT的方法入口SiftMainProcess(),一個是獲取處理後得到的關鍵點的頭結點方法getFirstKeyDescriptors()。
MySift.h:
#ifdef _CH_ #pragma package <opencv> #endif #ifndef _EiC #include <stdio.h> #include "stdlib.h" #include "string.h" #include "malloc.h" #include "math.h" #include <assert.h> #include <ctype.h> #include <time.h> #include <cv.h> #include <cxcore.h> #include <highgui.h> #include <vector> #include <iostream> using namespace std; #endif #ifdef _EiC #define WIN32 #endif #define NUMSIZE 2 #define GAUSSKERN 3.5 #define PI 3.14159265358979323846 //Sigma of base image -- See D.L.'s paper. #define INITSIGMA 0.5 //Sigma of each octave -- See D.L.'s paper. #define SIGMA sqrt(3)//1.6// //Number of scales per octave. See D.L.'s paper. #define SCALESPEROCTAVE 2 #define MAXOCTAVES 4 #define CONTRAST_THRESHOLD 0.02 #define CURVATURE_THRESHOLD 10.0 #define DOUBLE_BASE_IMAGE_SIZE 1 #define peakRelThresh 0.8 #define LEN 128 #define min(a,b) (((a) < (b)) ? (a) : (b)) #define max(a,b) (((a) > (b)) ? (a) : (b)) //特徵描述點,網格 #define GridSpacing 4 //Data structure for a float image. typedef struct ImageSt { /*金字塔每一層*/ float levelsigma; int levelsigmalength; float absolute_sigma; CvMat *Level; //CvMat是OPENCV的矩陣類,其元素可以是影象的象素值 } ImageLevels; typedef struct ImageSt1 { /*金字塔每一階梯*/ int row, col; //Dimensions of image. float subsample; ImageLevels *Octave; } ImageOctaves; //keypoint資料結構,Lists of keypoints are linked by the "next" field. typedef struct KeypointSt { float row, col; /* 反饋回原影象大小,特徵點的位置 */ float sx, sy; /* 金字塔中特徵點的位置 */ int octave, level; /* 金字塔中,特徵點所在的階梯、層次 */ float scale, ori, mag; /* 所在層的尺度sigma,主方向orientation (range [-PI,PI]),以及幅值 */ float *descrip; /* 特徵描述字指標:128維或32維等 */ struct KeypointSt *next; /* Pointer to next keypoint in list. */ } *Keypoint; class MySift { public: MySift(); ~MySift(); MySift(char* _filename, int _isColor); CvMat * halfSizeImage(CvMat * im); //縮小影象:下采樣 CvMat * doubleSizeImage(CvMat * im); //擴大影象:最近臨方法 CvMat * doubleSizeImage2(CvMat * im); //擴大影象:線性插值 float getPixelBI(CvMat * im, float col, float row);//雙線性插值函式 void normalizeVec(float* vec, int dim);//向量歸一化 CvMat* GaussianKernel2D(float sigma); //得到2維高斯核 void normalizeMat(CvMat* mat); //矩陣歸一化 float* GaussianKernel1D(float sigma, int dim); //得到1維高斯核 //在具體畫素處寬度方向進行高斯卷積 float ConvolveLocWidth(float* kernel, int dim, CvMat * src, int x, int y); //在整個影象寬度方向進行1D高斯卷積 void Convolve1DWidth(float* kern, int dim, CvMat * src, CvMat * dst); //在具體畫素處高度方向進行高斯卷積 float ConvolveLocHeight(float* kernel, int dim, CvMat * src, int x, int y); //在整個影象高度方向進行1D高斯卷積 void Convolve1DHeight(float* kern, int dim, CvMat * src, CvMat * dst); //用高斯函式模糊影象 int BlurImage(CvMat * src, CvMat * dst, float sigma); //SIFT演算法第一步:影象預處理 CvMat *ScaleInitImage(CvMat * im); //金字塔初始化 //SIFT演算法第二步:建立高斯金字塔函式 ImageOctaves* BuildGaussianOctaves(CvMat * image); //建立高斯金字塔 //SIFT演算法第三步:特徵點位置檢測,最後確定特徵點的位置 int DetectKeypoint(int numoctaves, ImageOctaves *GaussianPyr); void DisplayKeypointLocation(IplImage* image, ImageOctaves *GaussianPyr); //SIFT演算法第四步:計算高斯影象的梯度方向和幅值,計算各個特徵點的主方向 void ComputeGrad_DirecandMag(int numoctaves, ImageOctaves *GaussianPyr); int FindClosestRotationBin(int binCount, float angle); //進行方向直方圖統計 void AverageWeakBins(double* bins, int binCount); //對方向直方圖濾波 //確定真正的主方向 bool InterpolateOrientation(double left, double middle, double right, double *degreeCorrection, double *peakValue); //確定各個特徵點處的主方向函式 void AssignTheMainOrientation(int numoctaves, ImageOctaves *GaussianPyr, ImageOctaves *mag_pyr, ImageOctaves *grad_pyr); //顯示主方向 void DisplayOrientation(IplImage* image, ImageOctaves *GaussianPyr); //SIFT演算法第五步:抽取各個特徵點處的特徵描述字 void ExtractFeatureDescriptors(int numoctaves, ImageOctaves *GaussianPyr); //為了顯示圖象金字塔,而作的影象水平、垂直拼接 CvMat* MosaicHorizen(CvMat* im1, CvMat* im2); CvMat* MosaicVertical(CvMat* im1, CvMat* im2); /* 以下為在原始碼基礎上新增部分 */ void SiftMainProcess(); int getKeyPointsCount(); //獲取keypoint總數 Keypoint getFirstKeyDescriptors(); //獲取第一個keyDescriptor結點 void saveImgWithKeypoint(char* filename); private: char* filename; int isColor; int numoctaves; ImageOctaves *DOGoctaves; //DOG pyr,DOG運算元計算簡單,是尺度歸一化的LoG運算元的近似。 ImageOctaves *mag_thresh; ImageOctaves *mag_pyr; ImageOctaves *grad_pyr; int keypoint_count = 0; //定義特徵點具體變數 Keypoint keypoints = NULL; //用於臨時儲存特徵點的位置等 Keypoint keyDescriptors = NULL; //用於最後的確定特徵點以及特徵描述字 //聲明當前幀IplImage指標 IplImage* src = NULL; IplImage* image_kp = NULL; IplImage* image_featDir = NULL; IplImage* grey_im1 = NULL; IplImage* mosaic1 = NULL; IplImage* mosaic2 = NULL; CvMat* mosaicHorizen1 = NULL; CvMat* mosaicHorizen2 = NULL; CvMat* mosaicVertical1 = NULL; CvMat* image1Mat = NULL; CvMat* tempMat = NULL; ImageOctaves *Gaussianpyr; };
MySift.cpp:
由於.cpp程式碼有1000+行,由於篇幅問題,在這裡就不放出來了_(:зゝ∠)_。有需要的可以私聊下我哈_(:зゝ∠)_或者直接對著上面連結給的程式碼找一下就好了,函式名都一樣的。
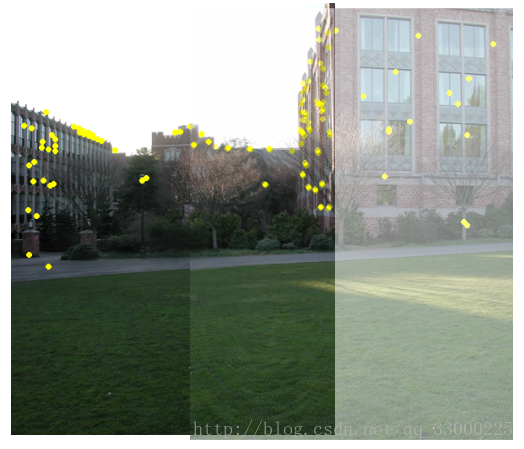
階段結果:
黃色圈圈的就是識別出來的關鍵點。

2、利用RANSAC演算法進行影象特徵匹配:
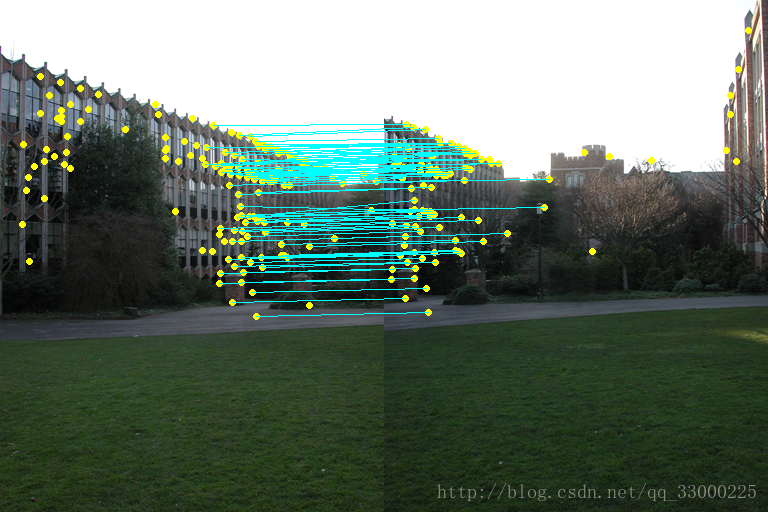
由於從上面步驟1得到的結果只是每張圖片自身的特徵點,即兩張圖片的特徵點之間還沒對應關係。因此我們需要先通過上面得到的128維描述子先進行大致的特徵點匹配(結果可能包括outliers)。匹配方法不難理解,只需計算兩個128維特徵描述子的距離差,小於某閾值即可視為相同的特徵點。
處理後得到下面的結果,黃色點為匹配的特徵點,另外再給每對特徵點連線:
可以看到連線特別雜亂,說明其中夾雜著很多outliers。因此需要用下面的RANSAC演算法去排除outliers。
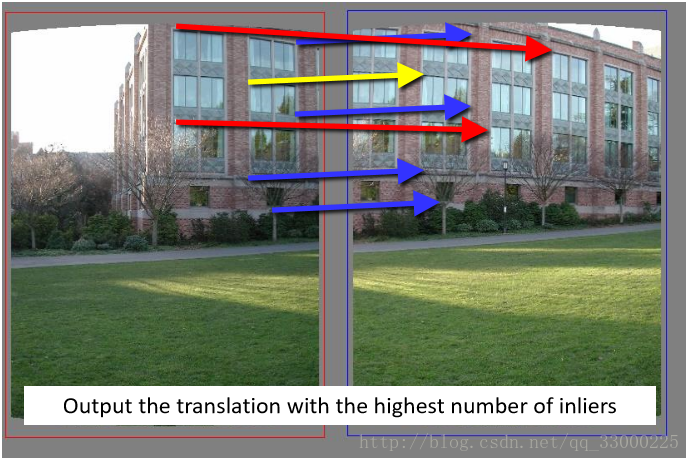
其實我用的可以說是偽RANSAC演算法_(:зゝ∠)_,簡單的說就是:
(1)對每一對關鍵點P,得到位置間的轉移向量v(位置相減)
(2)對其他的每一對關鍵點P' ,計算位置間的轉移向量v'。若v與v' 距離(計算尤拉距離即可)小於一定閾值,則認為P' 與P有相同的特徵點位置轉移,即為inlier(看下圖應該好理解一點)。
(3)計算擁有最多inliers的轉移向量v,即可視為兩張圖特徵點位置轉移向量V。
(4)再重新掃描所有的關鍵點對,屬於此特徵點位置轉移向量V的關鍵點對則視為兩張圖真正的特徵匹配點。
MyMatching.h:
#ifndef MYMATCHING_H
#define MYMATCHING_H
#include "MySift.h"
#include "CImg.h"
#include <vector>
using namespace cimg_library;
#define FeatureDescGap 1.0
#define InliersGap 500.0
struct Point {
int col; //x
int row; //y
Point() : col(-1), row(-1) {}
Point(int _col, int _row) : col(_col), row(_row) {}
};
struct MatchedPair {
Point keyPointA;
Point keyPointB;
float minDis;
MatchedPair(Point _pa, Point _pb, float _minDis) : keyPointA(_pa), keyPointB(_pb), minDis(_minDis) {}
};
class MyMatching
{
public:
MyMatching();
~MyMatching();
MyMatching(int _kp_count_A, Keypoint _firstKeyDesc_A, int _kp_count_B, Keypoint _firstKeyDesc_B);
/* 特徵匹配主函式,得到匹配點pair集 matchedPairSet */
void featureMatchMainProcess();
/* 在原圖上畫出當前得到的匹配點(不全是真正的匹配點) */
void drawOriKeypointOnImg(char* _filenameA, char* _filenameB, char* _saveAddrA, char* _saveAddrB);
/* 將兩張圖片拼在同一張圖片上,同時畫出匹配點之間連線 */
void mixImageAndDrawPairLine(char* mixImgAddr, char* mixImgWithLineAddr);
/* 使用RANSAC演算法找到真正的匹配點,並畫出來 */
void myRANSACtoFindKpTransAndDrawOut(char* _filename);
void drawRealKeypointOnImg(char* _filename, int maxIndex);
Point getMatchVec();
private:
int keypoint_count_A, keypoint_count_B;
Keypoint firstKeyDescriptor_A, firstKeyDescriptor_B;
vector<MatchedPair> matchedPairSet;
Point matchVec;
CImg<int> srcImgA, srcImgB;
CImg<int> srcImgWithKpA, srcImgWithKpB;
CImg<int> mixImg;
CImg<int> fixedMatchedImg;
};
#endif
MyMatching.cpp
#include "MyMatching.h"
MyMatching::MyMatching() {
}
MyMatching::~MyMatching() {
}
MyMatching::MyMatching(int _kp_count_A, Keypoint _firstKeyDesc_A, int _kp_count_B, Keypoint _firstKeyDesc_B) {
keypoint_count_A = _kp_count_A;
keypoint_count_B = _kp_count_B;
firstKeyDescriptor_A = _firstKeyDesc_A;
firstKeyDescriptor_B = _firstKeyDesc_B;
}
void MyMatching::featureMatchMainProcess() {
Keypoint tempDescA = firstKeyDescriptor_A;
while (tempDescA) {
float colA = tempDescA->col;
float rowA = tempDescA->row;
float* kp_desc_A = tempDescA->descrip;
Keypoint tempDescB = firstKeyDescriptor_B;
float minSSD = 100.0;
int minIndex = -1;
int colB = -1;
int rowB = -1;
while (tempDescB) { //對A圖每個點,找B圖各個點,計算距離
float ssd = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < LEN; i++) {
float descA = *(kp_desc_A + i);
float descB = *(tempDescB->descrip + i);
ssd += abs(descA - descB);
}
if (ssd < minSSD) {
minSSD = ssd;
colB = tempDescB->col;
rowB = tempDescB->row;
}
tempDescB = tempDescB->next;
}
if (minSSD < FeatureDescGap) { //當距離小於閾值,即當作一對匹配點
Point pa(tempDescA->col, tempDescA->row);
Point pb(colB, rowB);
MatchedPair mpair(pa, pb, minSSD);
matchedPairSet.push_back(mpair);
}
tempDescA = tempDescA->next;
}
for (int i = 0; i < matchedPairSet.size(); i++) {
cout << "A col: " << matchedPairSet[i].keyPointA.col << ", row: " << matchedPairSet[i].keyPointA.row << endl;
cout << " with B col: " << matchedPairSet[i].keyPointB.col << ", row: " << matchedPairSet[i].keyPointB.row << " , minSSD: " << matchedPairSet[i].minDis << endl;
}
cout << ">>> matchedPairSet.size: " << matchedPairSet.size() << endl;
}
void MyMatching::drawOriKeypointOnImg(char* _filenameA, char* _filenameB, char* _saveAddrA, char* _saveAddrB) {
srcImgA.load_bmp(_filenameA);
srcImgWithKpA = CImg<int>(srcImgA._width, srcImgA._height, 1, 3, 0);
cimg_forXY(srcImgWithKpA, x, y) {
srcImgWithKpA(x, y, 0, 0) = srcImgA(x, y, 0, 0);
srcImgWithKpA(x, y, 0, 1) = srcImgA(x, y, 0, 1);
srcImgWithKpA(x, y, 0, 2) = srcImgA(x, y, 0, 2);
}
srcImgB.load_bmp(_filenameB);
srcImgWithKpB = CImg<int>(srcImgB._width, srcImgB._height, 1, 3, 0);
cimg_forXY(srcImgWithKpB, x, y) {
srcImgWithKpB(x, y, 0, 0) = srcImgB(x, y, 0, 0);
srcImgWithKpB(x, y, 0, 1) = srcImgB(x, y, 0, 1);
srcImgWithKpB(x, y, 0, 2) = srcImgB(x, y, 0, 2);
}
const double yellow[] = { 255, 255, 0 };
for (int i = 0; i < matchedPairSet.size(); i++) {
cout << "A col: " << matchedPairSet[i].keyPointA.col << ", row: " << matchedPairSet[i].keyPointA.row << endl;
cout << " with B col: " << matchedPairSet[i].keyPointB.col << ", row: " << matchedPairSet[i].keyPointB.row << " , minSSD: " << matchedPairSet[i].minDis << endl;
srcImgWithKpA.draw_circle(matchedPairSet[i].keyPointA.col, matchedPairSet[i].keyPointA.row, 3, yellow, 1.0f);
srcImgWithKpB.draw_circle(matchedPairSet[i].keyPointB.col, matchedPairSet[i].keyPointB.row, 3, yellow, 1.0f);
}
srcImgWithKpA.display("srcImgWithKpA");
srcImgWithKpA.save(_saveAddrA);
srcImgWithKpB.display("srcImgWithKpB");
srcImgWithKpB.save(_saveAddrB);
}
void MyMatching::mixImageAndDrawPairLine(char* mixImgAddr, char* mixImgWithLineAddr) {
mixImg = CImg<int>(srcImgA._width + srcImgB._width, MAX(srcImgA._height, srcImgB._height), 1, 3, 0);
cimg_forXY(mixImg, x, y) {
if (x < srcImgA._width) {
if (y < srcImgA._height) {
mixImg(x, y, 0, 0) = srcImgWithKpA(x, y, 0, 0);
mixImg(x, y, 0, 1) = srcImgWithKpA(x, y, 0, 1);
mixImg(x, y, 0, 2) = srcImgWithKpA(x, y, 0, 2);
}
else {
mixImg(x, y, 0, 0) = 0;
mixImg(x, y, 0, 1) = 0;
mixImg(x, y, 0, 2) = 0;
}
}
else {
if (y < srcImgB._height) {
mixImg(x, y, 0, 0) = srcImgWithKpB(x - srcImgA._width, y, 0, 0);
mixImg(x, y, 0, 1) = srcImgWithKpB(x - srcImgA._width, y, 0, 1);
mixImg(x, y, 0, 2) = srcImgWithKpB(x - srcImgA._width, y, 0, 2);
}
else {
mixImg(x, y, 0, 0) = 0;
mixImg(x, y, 0, 1) = 0;
mixImg(x, y, 0, 2) = 0;
}
}
}
mixImg.display("mixImg");
mixImg.save(mixImgAddr);
const double blue[] = { 0, 255, 255 };
for (int i = 0; i < matchedPairSet.size(); i++) {
int xa = matchedPairSet[i].keyPointA.col;
int ya = matchedPairSet[i].keyPointA.row;
int xb = matchedPairSet[i].keyPointB.col + srcImgA._width;
int yb = matchedPairSet[i].keyPointB.row;
mixImg.draw_line(xa, ya, xb, yb, blue);
}
mixImg.display("mixImgWithLine");
mixImg.save(mixImgWithLineAddr);
}
void MyMatching::myRANSACtoFindKpTransAndDrawOut(char* _filename) {
int maxInliers = 0;
int maxIndex = -1;
int inliersCount;
//對每一對匹配點,求匹配向量v
for (int i = 0; i < matchedPairSet.size(); i++) {
inliersCount = 0;
int xa = matchedPairSet[i].keyPointA.col;
int ya = matchedPairSet[i].keyPointA.row;
int xb = matchedPairSet[i].keyPointB.col + srcImgA._width;
int yb = matchedPairSet[i].keyPointB.row;
int deltaX = xb - xa;
int deltaY = yb - ya;
//對每一個v,找其他所有匹配向量與其距離。若小於閾值,則作為inlier
for (int j = 0; j < matchedPairSet.size(); j++) {
if (j != i) {
int txa = matchedPairSet[j].keyPointA.col;
int tya = matchedPairSet[j].keyPointA.row;
int txb = matchedPairSet[j].keyPointB.col + srcImgA._width;
int tyb = matchedPairSet[j].keyPointB.row;
int tdeltaX = txb - txa;
int tdeltaY = tyb - tya;
int vectorGap = (tdeltaX - deltaX) * (tdeltaX - deltaX) + (tdeltaY - deltaY) * (tdeltaY - deltaY);
//cout << "i: " << i << ", j: " << j << " vectorGap: " << vectorGap << endl;
if (vectorGap < InliersGap) {
inliersCount++;
}
}
}
//計算最多inliers的匹配向量v,此匹配向量即視為所有關鍵點的匹配向量
if (inliersCount > maxInliers) {
maxInliers = inliersCount;
maxIndex = i;
}
}
cout << "maxIndex: " << maxIndex << ", maxInliers: " << maxInliers << endl;
drawRealKeypointOnImg(_filename, maxIndex);
}
void MyMatching::drawRealKeypointOnImg(char* _filename, int maxIndex) {
//在新的合併圖上,畫出屬於該匹配關係的匹配點pair
fixedMatchedImg = CImg<int>(srcImgA._width + srcImgB._width, srcImgA._height, 1, 3, 0);
cimg_forXY(fixedMatchedImg, x, y) {
if (x < srcImgA._width) {
if (y < srcImgA._height) {
fixedMatchedImg(x, y, 0, 0) = srcImgWithKpA(x, y, 0, 0);
fixedMatchedImg(x, y, 0, 1) = srcImgWithKpA(x, y, 0, 1);
fixedMatchedImg(x, y, 0, 2) = srcImgWithKpA(x, y, 0, 2);
}
else {
fixedMatchedImg(x, y, 0, 0) = 0;
fixedMatchedImg(x, y, 0, 1) = 0;
fixedMatchedImg(x, y, 0, 2) = 0;
}
}
else {
if (y < srcImgB._height) {
fixedMatchedImg(x, y, 0, 0) = srcImgWithKpB(x - srcImgA._width, y, 0, 0);
fixedMatchedImg(x, y, 0, 1) = srcImgWithKpB(x - srcImgA._width, y, 0, 1);
fixedMatchedImg(x, y, 0, 2) = srcImgWithKpB(x - srcImgA._width, y, 0, 2);
}
else {
fixedMatchedImg(x, y, 0, 0) = 0;
fixedMatchedImg(x, y, 0, 1) = 0;
fixedMatchedImg(x, y, 0, 2) = 0;
}
}
}
int mxa = matchedPairSet[maxIndex].keyPointA.col;
int mya = matchedPairSet[maxIndex].keyPointA.row;
int mxb = matchedPairSet[maxIndex].keyPointB.col + srcImgA._width;
int myb = matchedPairSet[maxIndex].keyPointB.row;
int mdeltaX = mxb - mxa;
int mdeltaY = myb - mya; //得到真實匹配關係的匹配向量v
matchVec = Point(mdeltaX, mdeltaY);
cout << "Real match vector: (" << mdeltaX << ", " << mdeltaY << ")" << endl;
const double blue[] = { 0, 255, 255 };
for (int j = 0; j < matchedPairSet.size(); j++) { //計算所有匹配向量與v的距離d
int txa = matchedPairSet[j].keyPointA.col;
int tya = matchedPairSet[j].keyPointA.row;
int txb = matchedPairSet[j].keyPointB.col + srcImgA._width;
int tyb = matchedPairSet[j].keyPointB.row;
int tdeltaX = txb - txa;
int tdeltaY = tyb - tya;
int vectorGap = (tdeltaX - mdeltaX) * (tdeltaX - mdeltaX) + (tdeltaY - mdeltaY) * (tdeltaY - mdeltaY);
if (vectorGap < InliersGap) { //距離d小於閾值,則視為正確的匹配點
fixedMatchedImg.draw_line(txa, tya, txb, tyb, blue);
}
}
fixedMatchedImg.display("mixImgWithLine_fixed");
fixedMatchedImg.save(_filename);
}
Point MyMatching::getMatchVec() {
return matchVec;
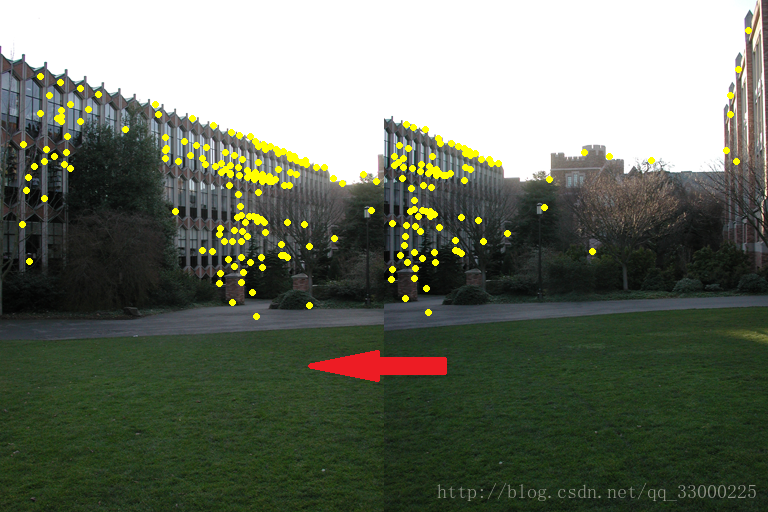
}階段結果:
(可以看到轉移向量V基本一致了)
3、利用匹配關鍵點進行影象拼接(Blending)
我使用的影象拼接方法其實只是最簡單的平移+畫素RGB值插值的方法(好在這次的資料集影象不存在太大的放縮,不然就不能用這種方法了_(:зゝ∠)_ 涉及到放縮的圖片暫時還想不到怎麼做_(:зゝ∠)_)。
可以直觀的從下面的圖(用ppt拼湊的哈哈)看到,由於輸入影象始終保持左圖在右圖的左側,即兩圖並排的時候,右圖需要向左移動:
變成:
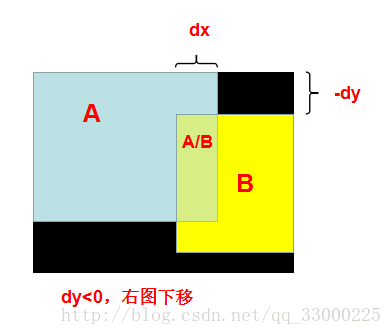
從上面可以看到,右圖不僅需要向左平移,還需要向下/上平移。回想我們第2步得到的轉移向量V(dx, dy),就不難理解轉移向量V的作用了:dy<0,右圖向下平移;dy>=0,右圖向上平移。
如果右圖是向下平移時,可以得到如下的模型圖,而區域的劃分我們可以通過簡單的數學關係計算出來。明顯,A和B單獨的區域可以直接取原影象素RGB值;由於兩張圖長寬可能不一致,以及平移的原因,可能產生黑邊(黑色部分)。
最後剩下兩圖混合部分A/B。如果只是簡單的,對混合區域,兩張圖上對應點畫素RGB值各取50%,則容易造成上面那張圖那樣,在分界處有明顯的邊緣,以及邊緣兩邊匹配不上。因此我使用了插值的方法,即:根據混合區域內點P的與兩邊邊緣的水平距離,按不同比例取兩張圖上對應點畫素RGB值組合成點P的RGB值(即越靠近左邊邊緣的點,取左圖對應點RGB值的佔比越大)。這樣就可以實現較好的過渡。
MyBlending.h:
#ifndef MYBLENDING_H
#define MYBLENDING_H
#include "CImg.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace cimg_library;
using namespace std;
struct TransVector {
int dx;
int dy;
TransVector() : dx(-1), dy(-1) {}
TransVector(int _dx, int _dy) : dx(_dx), dy(_dy) {}
};
class MyBlending
{
public:
MyBlending();
~MyBlending();
MyBlending(int sx, int sy);
void blendingMainProcess(char* _filenameA, char* _filenameB);
void saveBlendedImg(char* blendedImgAddr);
private:
TransVector matchVec; //x為合併圖上的水平距離,y
CImg<int> srcImgA, srcImgB;
CImg<int> blendedImg;
};
#endif
MyBlending.cpp:
#include "MyBlending.h"
MyBlending::MyBlending() {
}
MyBlending::~MyBlending() {
}
MyBlending::MyBlending(int sx, int sy) {
matchVec.dx = sx;
matchVec.dy = sy;
}
void MyBlending::blendingMainProcess(char* _filenameA, char* _filenameB) {
srcImgA.load_bmp(_filenameA);
srcImgB.load_bmp(_filenameB);
blendedImg = CImg<int>(srcImgA._width + srcImgB._width - matchVec.dx,
srcImgA._height + abs(matchVec.dy), 1, 3, 0);
cimg_forXY(blendedImg, x, y) {
if (matchVec.dy <= 0) { //右側圖片需要往下左移動
if (x < srcImgA._width && y < srcImgA._height) {
if (x >= (srcImgA._width - matchVec.dx) && y >= (0 - matchVec.dy)) { //混合
blendedImg(x, y, 0, 0) = (float)srcImgA(x, y, 0, 0)
* (float)(srcImgA._width - x) / (float)abs(matchVec.dx)
+ (float)srcImgB(x - (srcImgA._width - matchVec.dx), y - (0 - matchVec.dy), 0, 0)
* (float)(x - (srcImgA._width - matchVec.dx)) / (float)abs(matchVec.dx);
blendedImg(x, y, 0, 1) = (float)srcImgA(x, y, 0, 1)
* (float)(srcImgA._width - x) / (float)abs(matchVec.dx)
+ (float)srcImgB(x - (srcImgA._width - matchVec.dx), y - (0 - matchVec.dy), 0, 1)
* (float)(x - (srcImgA._width - matchVec.dx)) / (float)abs(matchVec.dx);
blendedImg(x, y, 0, 2) = (float)srcImgA(x, y, 0, 2)
* (float)(srcImgA._width - x) / (float)abs(matchVec.dx)
+ (float)srcImgB(x - (srcImgA._width - matchVec.dx), y - (0 - matchVec.dy), 0, 2)
* (float)(x - (srcImgA._width - matchVec.dx)) / (float)abs(matchVec.dx);
}
else { //A獨在部分
blendedImg(x, y, 0, 0) = srcImgA(x, y, 0, 0);
blendedImg(x, y, 0, 1) = srcImgA(x, y, 0, 1);
blendedImg(x, y, 0, 2) = srcImgA(x, y, 0, 2);
}
}
else if (x >= (srcImgA._width - matchVec.dx)
&& y >= (0 - matchVec.dy) && y < (0 - matchVec.dy) + srcImgB._height) { //B獨在部分
blendedImg(x, y, 0, 0) = srcImgB(x - (srcImgA._width - matchVec.dx), y - (0 - matchVec.dy), 0, 0);
blendedImg(x, y, 0, 1) = srcImgB(x - (srcImgA._width - matchVec.dx), y - (0 - matchVec.dy), 0, 1);
blendedImg(x, y, 0, 2) = srcImgB(x - (srcImgA._width - matchVec.dx), y - (0 - matchVec.dy), 0, 2);
}
else { //黑色部分
blendedImg(x, y, 0, 0) = 0;
blendedImg(x, y, 0, 1) = 0;
blendedImg(x, y, 0, 2) = 0;
}
}
else { //matchVec.dy > 0; 右側圖片需要往上左移動
if (x < srcImgA._width && y >= matchVec.dy) {
if (x >= (srcImgA._width - matchVec.dx) && y < srcImgB._height) { //混合
blendedImg(x, y, 0, 0) = (float)srcImgA(x, y - matchVec.dy, 0, 0)
* (float)(srcImgA._width - x) / (float)abs(matchVec.dx)
+ (float)srcImgB(x - (srcImgA._width - matchVec.dx), y, 0, 0)
* (float)(x - (srcImgA._width - matchVec.dx)) / (float)abs(matchVec.dx);
blendedImg(x, y, 0, 1) = (float)srcImgA(x, y - matchVec.dy, 0, 1)
* (float)(srcImgA._width - x) / (float)abs(matchVec.dx)
+ (float)srcImgB(x - (srcImgA._width - matchVec.dx), y, 0, 1)
* (float)(x - (srcImgA._width - matchVec.dx)) / (float)abs(matchVec.dx);
blendedImg(x, y, 0, 2) = (float)srcImgA(x, y - matchVec.dy, 0, 2)
* (float)(srcImgA._width - x) / (float)abs(matchVec.dx)
+ (float)srcImgB(x - (srcImgA._width - matchVec.dx), y, 0, 2)
* (float)(x - (srcImgA._width - matchVec.dx)) / (float)abs(matchVec.dx);
}
else { //A獨在部分
blendedImg(x, y, 0, 0) = srcImgA(x, y - matchVec.dy, 0, 0);
blendedImg(x, y, 0, 1) = srcImgA(x, y - matchVec.dy, 0, 1);
blendedImg(x, y, 0, 2) = srcImgA(x, y - matchVec.dy, 0, 2);
}
}
else if (x >= (srcImgA._width - matchVec.dx) && y < srcImgB._height) { //B獨在部分
blendedImg(x, y, 0, 0) = srcImgB(x - (srcImgA._width - matchVec.dx), y, 0, 0);
blendedImg(x, y, 0, 1) = srcImgB(x - (srcImgA._width - matchVec.dx), y, 0, 1);
blendedImg(x, y, 0, 2) = srcImgB(x - (srcImgA._width - matchVec.dx), y, 0, 2);
}
else { //黑色部分
blendedImg(x, y, 0, 0) = 0;
blendedImg(x, y, 0, 1) = 0;
blendedImg(x, y, 0, 2) = 0;
}
}
}
blendedImg.display("blendedImg");
}
void MyBlending::saveBlendedImg(char* blendedImgAddr) {
blendedImg.save(blendedImgAddr);
}
階段結果:
4、最後再放上使用上面3個類的主函式的程式碼吧:
Main.cpp:
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "MyMatching.h"
#include "MyBlending.h"
int main() {
char* inputAddr1 = "Input/1.bmp";
char* inputAddr2 = "Input/2.bmp";
MySift mySift1(inputAddr1, 1);
mySift1.SiftMainProcess();
mySift1.saveImgWithKeypoint("Output/1-2/1_kp.bmp");
MySift mySift2(inputAddr2, 1);
mySift2.SiftMainProcess();
mySift2.saveImgWithKeypoint("Output/1-2/2_kp.bmp");
MyMatching myMatching(mySift1.getKeyPointsCount(), mySift1.getFirstKeyDescriptors(),
mySift2.getKeyPointsCount(), mySift2.getFirstKeyDescriptors());
myMatching.featureMatchMainProcess();
myMatching.drawOriKeypointOnImg(inputAddr1, inputAddr2, "Output/1-2/1_kp_real.bmp", "Output/1-2/2_kp_real.bmp");
myMatching.mixImageAndDrawPairLine("Output/1-2/mixImg.bmp", "Output/1-2/mixImgWithLine.bmp");
myMatching.myRANSACtoFindKpTransAndDrawOut("Output/1-2/mixImgWithLine_fixed.bmp");
MyBlending myBlending(myMatching.getMatchVec().col, myMatching.getMatchVec().row);
myBlending.blendingMainProcess(inputAddr1, inputAddr2);
myBlending.saveBlendedImg("Output/1-2/blendedImg.bmp");
int i;
cin >> i;
return 0;
}
好了,這就差不多了。(其實差很多_(:зゝ∠)_)
其實這份程式碼普適性不高_(:зゝ∠)_,比如圖片是需要先人工排序再扔進去跑的,這個問題想了下應該可以根據轉移向量V來進行一定的判別。另外上面也提到了,如果圖片之間存在物體放縮,那就不能用上面的方法了(放縮的暫時還想不到解決方案……)。還有就是如果圖片的橫著的,比如資料集2,就也不能解決了。(想想就很難_(:зゝ∠)_)
如果有大佬能解決上面問題的可以跟我說說,也想了解一下_(:зゝ∠)_