VUEX及VUE專案結構粗解
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-01-25
VUEX核心
store 一般使用方法 export default{ const store = new Vuex.Store({ state: { }, actions: { }, mutations: { }, getters: { }, modules: { } }) }
1.state 定義了應用狀態的資料結構,同樣可以在這裡設定預設的初始狀態。
定義: state: { projects: [], userProfile: {} } 使用: computed: { projects () { return this.$store.state.projects } } 可以通過mapState函式簡化程式碼
2.actions 即是定義提交觸發更改資訊的描述,常見的例子有從服務端獲取資料,在資料獲取完成後會呼叫store.commit()來呼叫更改 Store 中的狀態。
可以在元件中使用dispatch來發出 Actions。 定義: 如 actions: { LOAD_PROJECT_LIST: function ({ commit }) { axios.get('/secured/projects').then((response) => { commit('SET_PROJECT_LIST', { list: response.data }) }, (err) => { console.log(err) }) } } 使用: 如 this.$store.dispatch('LOAD_PROJECT_LIST', {})
3.mutations 呼叫 mutations 是唯一允許更新應用狀態的地方。
定義:
mutations: {
SET_PROJECT_LIST: (state, { list }) => {
state.projects = list
}
}
使用:一般在action中使用commit('SET_PROJECT_LIST', { list: response.data })
4.getters Getters 允許元件從 Store 中獲取資料
定義:
getters: {
completedProjects: state => {
return state.projects.filter(project => project.completed).length
}
}
可以使用mapGetters簡化程式碼
注: 在專案中一般很少在store中定義getters,而是在使用store的地方定義getters,並且可以通過mapGetters。
5.modules 物件允許將單一的 Store 拆分為多個 Store 的同時儲存在單一的狀態樹中。
隨著應用複雜度的增加,這種拆分能夠更好地組織程式碼
VUE專案結構
assets 靜態資源目錄
components 公共元件
router 路由
service 對api請求的統一管理
store 狀態統一管理
view 元件
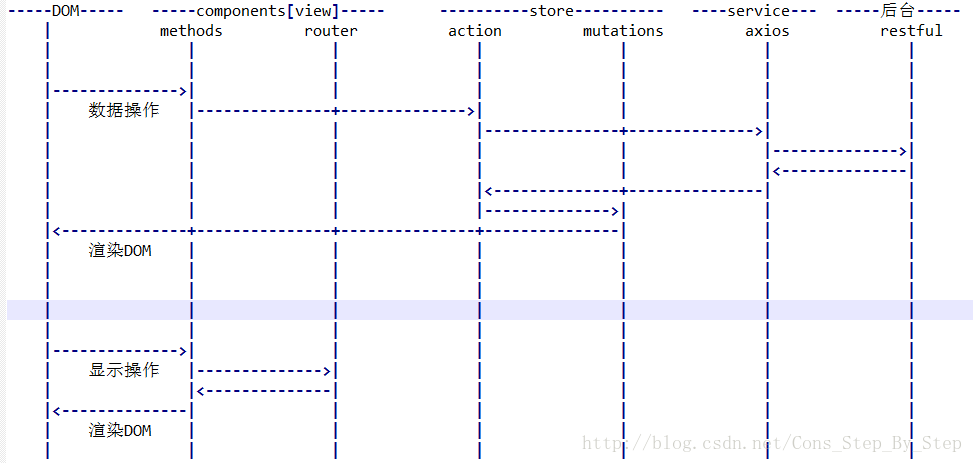
資料流