Trie 資料結構原始碼分析(原始碼來源 rt.jar)
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-02-04
先上圖:
如下是 Trie 數的資料結構:
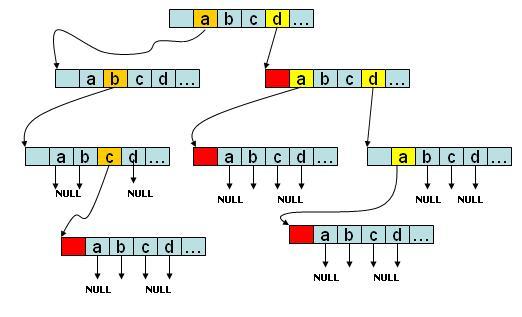
Trie 樹的作用:統計,排序和儲存字串
快速查詢某個單詞key 所對應的 value 值(類似 Map 的功能)
(擴充套件的時候,可以判斷某個 key 是否存在, 統計某個字首被多少個單詞佔用(文章後面提到))
優點:
做查詢的時候, 效能不會隨著總的資料量增加而導致查詢效率下降(空間換時間的思想)
(其他樹形查詢演算法, 如二叉樹查詢, 效能會隨著總的資料量增長而下降,而 Trie 樹查詢時的比較次數只跟 key 的長度有關係)
node 節點資料結構:
/**
* The node representation for the trie.
* @xsl put()方法:
/**
* Put an object into the trie for lookup.
*
* @param get()方法:
public Object get(final String key)
{
final int len = key.length();
/* If the name is too long, we won't find it, this also keeps us
* from overflowing m_charBuffer
*/
if (m_charBuffer.length < len)
return null;
Node node = m_Root;
switch (len)
{
// case 0 looks silly, but the generated bytecode runs
// faster for lookup of elements of length 2 with this in
// and a fair bit faster. Don't know why.
case 0 :
{
return null;
}
//直接查詢跟節點 Node
case 1 :
{
final char ch = key.charAt(0);
if (ch < ALPHA_SIZE)
{
node = node.m_nextChar[ch];
if (node != null)
return node.m_Value;
}
return null;
}
default :
{
key.getChars(0, len, m_charBuffer, 0);
// copy string into array
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
final char ch = m_charBuffer[i];
//非 ASCII碼不處理
if (ALPHA_SIZE <= ch)
{
return null;
}
node = node.m_nextChar[ch];
if (node == null)
return null;
}
return node.m_Value;
}
}
}原始碼的資料結構是沒法統計多少個單詞佔用了相同的字首的.
要實現該功能, 則需要在 Node 節點中加入一個屬性(如:sum), 每 put一個單詞 到 Trie 樹時, 所經過的字元都+1 ; 當需要統計某個字首被多少個單詞共用時, 直接讀取該字首的最後一個字元的sum 欄位即可.
要使用 Trie 樹判斷某個 key 是否在樹上, 可以在 Node 節點中加入一個boolean 標誌位, 在插入每個單詞的時候, 最後一個字元所在的 node 把標誌位設定為 true 即可.(就實現了 set 的功能)
如果要實現 Trie 樹排序的功能, 只需要先將所有 key 存入 Trie 樹, 然後通過深度遍歷的方式讀取即可實現排序.
從原始碼看, Node根節點是儲存資料的 , Trie物件有個屬性m_Root指向最上層的 node 節點(根節點).
測試程式碼:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Trie trie = new Trie();
trie.put("adef", "yangyang");
trie.put("abg", "xiaochen");
Object tem = trie.get("ABG");
System.out.println(trie);
} 