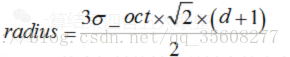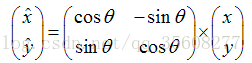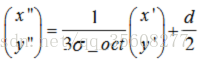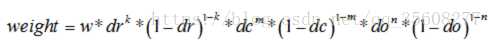SIFT演算法特徵描述子構建---特徵描述子構建原理及程式碼
0.引言
sift針對區域性特徵進行特徵提取,在尺度空間尋找極值點,提取位置,尺度,旋轉不變數,生成特徵描述子。
總共分四個步驟:
-
4 特徵描述子構建
每個關鍵點的方向、位置、尺度資訊都具備後,可以對區域性特徵進行描述,即特徵描述子。
4.1 確定描述子區域
將關鍵點劃分為d*d(Lowe建議4)個子區域,每個子區域為一個種子點,
每個種子點有8個方向,即128維特徵。為每個子區域分配邊長為3*sigma_oct的矩形取樣,考慮實際計算用雙線性插值,以及旋轉,放大sqrt(2)*(d+1),
最終所選影象視窗半徑
4.2 座標軸旋轉為關鍵點的方向
旋轉保持旋轉不變性
4.3 將子區域內的梯度值插值加權分配到8 個方向上
//對每個種子點每個方向插值
//weight=w*dr^k*(1-dr)^(1-k)*dc^m*(1-dc)^(1-m)*do^n*(1-do)^(1-n)
//m,n,k為0,1
void InterpHistEntry(double*** hist, double xbin, double ybin, double obin, double mag, int bins, int d)
{
//對鄰近兩行的貢獻因子為dr和1 - dr,對鄰近兩列的貢獻因子為dc和1 - dc,對鄰近兩個方向的貢獻因子為do和1 - do
double double*** CalculateDescrHist(const Mat&gauss, int x, int y, double octave_scale, double ori, int bins, int width)
{
//二維陣列指標,width 為子區域尺寸d=4*4
double *hist = new double [width];
for (int i = 0; i < width; i++)
{
//長度為width的一維陣列指標
hist[i] = new double *[width];
for (int j = 0; j < width; j++)
{
//每個hist處是一個36維陣列
hist[i][j] = new double[bins];
}
}
//初始化
for (int r = 0; r < width; r++)
for (int c = 0; c < width; c++)
for (int o = 0; o < bins; o++)
hist[r][c][o] = 0.0;
//高斯權值,Lowe建議子區域的畫素的梯度大小按sigma=0.5*d的高斯加權計算,即2
double sigma = 0.5*width;
double conste = -1.0 / (2 * sigma*sigma);
double sub_hist_width = DESCR_SCALE_ADJUST*octave_scale;//每個子區域尺寸為mσ個像元 尺度特徵點的尺度值3*sig_oct
//子區域半徑
int radius = cvRound((sqrt(2)*sub_hist_width*(width + 1)) / 2.0);
double grad_ori;
double grad_mag;
/*計算取樣區域點座標旋轉
|x`| |cos -sin| |x|
| | =| |*| |
|y`| |sin cos| |y|
子區域下標
| x``| 1 |x|
| |=--------------* | | +1/d
| y``| sub_hist_width |y|
*/
double cos_ori = cos(ori);
double sin_ori = sin(ori);
for (int i = -radius; i < radius; i++)
{
for (int j = -radius; j < radius; j++)
{
double rot_x = (cos_ori*j - sin_ori + i);
double rot_y = (sin_ori*j + cos_ori + i);
double xbin = rot_x / sub_hist_width + width / 2 - 0.5; //xbin, ybin為落在4 * 4視窗中的下標值
double ybin = rot_y / sub_hist_width + width / 2 - 0.5;
if (xbin>-1.0&&xbin<width&&ybin>-1 && ybin<width)
{
//計算關鍵點的梯度
if (CalcGradMagOri(gauss, x + j, y + i, grad_mag, grad_ori))
{
//梯度方向夾角
grad_ori = (CV_PI - grad_ori) - ori;
while (grad_ori<0)
{
grad_ori += CV_PI * 2;
}
while (grad_ori >= CV_PI * 2)
{
grad_ori -= 2 * CV_PI;
}
double obin = grad_ori*(bins / (2 * CV_PI));//種子點所在子視窗的方向
//公式子區域畫素梯度進行高斯加權:exp(-((x`2)+(y`2))/(2*(0.5d)^2))
double weight = exp(conste*(rot_x*rot_x + rot_y*rot_y));
//插值計算每個種子點處的梯度
InterpHistEntry(hist, xbin, ybin, obin, grad_mag*weight, bins, width);
}
}
}
}
return hist;
}
4.4 歸一化及門限
如上統計的4*4*8=128個梯度資訊即為該關鍵點的特徵向量。特徵向量形成後,為了去除光照變化的影響,需要對它們進行歸一化處理,對於影象灰度值整體漂移,影象各點的梯度是鄰域畫素相減得到,所以也能去除。
void NormalizeDescr(Keypoint& feat)
{
double len_sq = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < feat.descr_length; i++)
{
len_sq += feat.descriptor[i] * feat.descriptor[i];
}
len_sq = sqrt(len_sq);
for (int i = 0; i < feat.descr_length; i++)
{
feat.descriptor[i] = feat.descriptor[i] / len_sq;
}
}
設定門限
非線性光照,相機飽和度變化對造成某些方向的梯度值過大,而對方向的影響微弱。因此設定門限值(向量歸一化後,一般取0.2)截斷較大的梯度值。然後,再進行一次歸一化處理,提高特徵的鑑別性。
//直方圖存入特徵描述子
void HistToDescriptor(double***hist, int width, int bins, Keypoint& feature)
{
int k = 0;
for (int r = 0; r < width; r++)
{
for (int c = 0; c < width; c++)
{
for (int o = 0; o < bins; o++)
{
feature.descriptor[k++] = hist[r][c][o];//放進128維特徵描述子內
}
}
}
feature.descr_length = k;
//描述子歸一化
NormalizeDescr(feature);
//描述子門限
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
if (feature.descriptor[i]>DESCR_MAG_THR)
{
feature.descriptor[i] = DESCR_MAG_THR;
}
}
//第二次歸一化
NormalizeDescr(feature);
int int_val;//整形值 將double型轉為整形描述子
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
int_val = INT_DESCR_FCTR*feature.descriptor[i];
feature.descriptor[i] = min(255, int_val);
}
}
4.5 生成描述子
void DescriptorRepresentation(vector<Keypoint>&features, const vector<Mat>& guass_pyr, int bins, int width)
{
double ***hist;
for (int i = 0; i < features.size(); i++)
{
hist = CalculateDescrHist(guass_pyr[features[i].octave*(INTERVALS + 3) + features[i].interval], features[i].x, features[i].y, features[i].octave_scale, features[i].ori, bins, width);
HistToDescriptor(hist, width, bins, features[i]);
//釋放空間
for (int j = 0; j < width; j++)
{
for (int k = 0; k < width; k++)
{
delete[] hist[j][k];
}
delete[] hist[j];
}
delete[] hist;
}
}