集合的檢索:點陣圖法
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-02-07
點陣圖法
點陣圖(bit-map)法是一種邏輯上很巧妙的描述集合的方法。
如集合S={2,4,1,5,12},它用點陣圖描述就是 0110 1100 0000 1000,兩個位元組即可描述S,左邊是低階位。用bitset<16>儲存的話就是{[15]、[14]、...[1]、[0]}={0001000000110110}。
用點陣圖對集合進行描述後,就很方便進行集合的運算,如交、並和差。
下面來演示具體操作
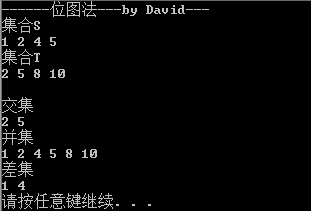
集合S={1,2,4,5},集合T={2,5,8,10}
集合S的點陣圖是 0110110000000000
集合T的點陣圖是 0010010010100000
求S與T的交集即是 S&T=0010010000000000={2,5}
求S與T的並集即是 S|T=0110110010100000={1,2,4,5,8,10}
求S與T的差集即是 S&~T=(0110110000000000)&(1101101101011111)=0100100000000000={1,4}
以上例子的完整程式碼如下
執行#include<iostream> #include<bitset> using namespace std; int main() { cout << "------點陣圖法---by David---" << endl; int S[] = { 1, 2, 4, 5 }; int T[] = { 2, 5, 8, 10 }; bitset<16> s, t; s.reset(); t.reset(); int size_s, size_t, i; size_s = sizeof(S) / sizeof(int); size_t = sizeof(T) / sizeof(int); cout << "集合S" << endl; for (i = 0; i < size_s; i++) { cout << S[i] << " "; s.set(S[i]); } cout << endl; cout << "集合T" << endl; for (i = 0; i < size_t; i++) { cout << T[i] << " " ; t.set(T[i]); } cout << endl << endl; //求交集 bitset<16> r1(s.to_ulong() & t.to_ulong()); //求並集 bitset<16> r2(s.to_ulong() | t.to_ulong()); //求差集 bitset<16> r3(s.to_ulong() & (~t.to_ulong())); cout << "交集" << endl; for (i = 0; i < 16; i++) if (r1[i]) cout << i << " "; cout << endl; cout << "並集" << endl; for (i = 0; i < 16; i++) if (r2[i]) cout << i << " "; cout << endl; cout << "差集" << endl; for (i = 0; i < 16; i++) if (r3[i]) cout << i << " "; cout << endl; system("pause"); return 0; }
專欄目錄