離散對數(Baby Step Giant Step)
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-02-11
現在我來介紹一種演算法叫做Baby Step Giant Step。它是用來解決如下方程最小正整數解的
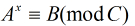
如果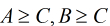
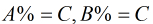
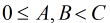
普通Baby Step Giant Step的步驟是這樣的:
(1)首先確定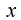
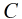
(2)把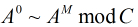
(3)把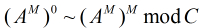
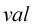
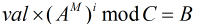
(4)最終答案就是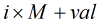
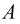
上面是普通Baby Step Giant Step的步驟,比較簡單,只適用 為素數的情況。如果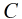
當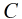
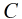
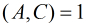
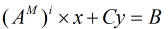
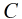
對於方程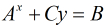
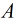
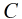
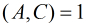
#include <iostream> #include <string.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <math.h> using namespace std; typedef long long LL; const int MOD = 99991; const int N = 100005; struct Hash { bool f; int id; int val; }; Hash hash[N]; void Init() { for(int i=0; i<N; i++) { hash[i].f = 0; hash[i].id = -1; hash[i].val = -1; } } void Insert(int id,LL val) { LL t = val % MOD; while(hash[t].f && hash[t].val != val) { t++; t %= MOD; } if(!hash[t].f) { hash[t].f = 1; hash[t].id = id; hash[t].val = val; } } int Find(LL val) { LL t = val % MOD; while(hash[t].f && hash[t].val != val) { t++; t %= MOD; } if(!hash[t].f) return -1; return hash[t].id; } LL gcd(LL a,LL b) { return b ? gcd(b,a%b):a; } void extend_Euclid(LL a,LL b,LL &x,LL &y) { if(b == 0) { x = 1; y = 0; return; } extend_Euclid(b,a%b,x,y); LL tmp = x; x = y; y = tmp - (a / b) * y; } LL Baby_Step(LL A,LL B,LL C) { LL ret = 1; for(int i=0; i<=50; i++) { if(ret == B) return i; ret = ret * A % C; } LL ans = 1; LL tmp,cnt = 0; while((tmp = gcd(A,C)) != 1) { if(B % tmp) return -1; B /= tmp; C /= tmp; ans = ans * (A / tmp) % C; cnt++; } LL M = ceil(sqrt(1.0*C)); LL t = 1; for(int i=0; i<M; i++) { Insert(i,t); t = t * A % C; } for(int i=0; i<M; i++) { LL x,y; extend_Euclid(ans,C,x,y); LL val = x * B % C; val = (val % C + C) % C; LL j = Find(val); if(j != -1) return i * M + j + cnt; ans = ans * t % C; } return -1; } int main() { LL A,B,C; while(cin>>A>>C>>B) { Init(); if(A + B + C == 0) break; A %= C; B %= C; LL ans = Baby_Step(A,B,C); if(ans == -1) { puts("No Solution"); continue; } cout<<ans<<endl; } return 0; }