PyTorch學習:多項式迴歸的小例子
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-02-17
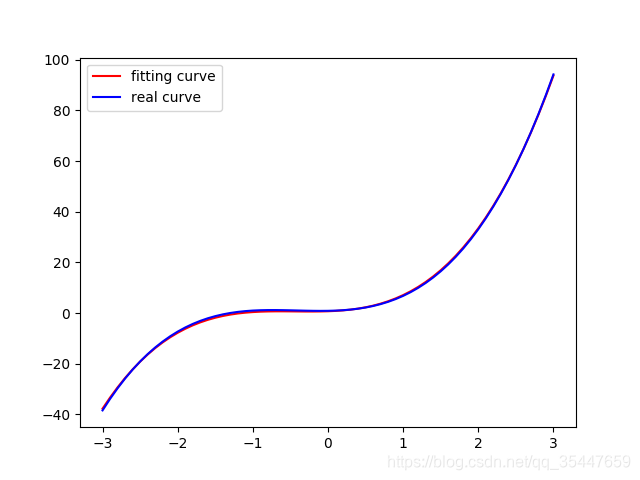
#多項式迴歸模型 import torch import numpy as np from torch.autograd import Variable import matplotlib.pyplot as plt torch.manual_seed(2018) # 定義一個多變數函式 w_target = np.array([0.5, 3, 2.4]) # 定義引數 b_target = np.array([0.9]) # 定義引數 f_des = 'y = {:.2f} + {:.2f} * x + {:.2f} * x^2 + {:.2f} * x^3'.format( b_target[0], w_target[0], w_target[1], w_target[2]) # 打印出函式的式子 print(f_des) # 畫出這個函式的曲線 x_sample = np.arange(-3, 3.1, 0.1) y_sample = b_target[0] + w_target[0] * x_sample + w_target[1] * x_sample ** 2 + w_target[2] * x_sample ** 3 x_train = np.stack([x_sample ** i for i in range(1, 4)], axis=1) x_train = torch.from_numpy(x_train).float() # 轉換成 float tensor y_train = torch.from_numpy(y_sample).float().unsqueeze(1) # 轉化成 float tensor # 定義引數和模型 w = Variable(torch.randn(3, 1), requires_grad=True) b = Variable(torch.zeros(1), requires_grad=True) # 將 x 和 y 轉換成 Variable x_train = Variable(x_train) y_train = Variable(y_train) def multi_linear(x): return torch.mm(x, w) + b # 計算誤差 def get_loss(y_, y): return torch.mean((y_ - y_train) ** 2) # 進行 100 次引數更新 for e in range(1000): y_pred = multi_linear(x_train) loss = get_loss(y_pred, y_train) if e!=0: w.grad.data.zero_() b.grad.data.zero_() loss.backward() # 更新引數 w.data = w.data - 0.001 * w.grad.data b.data = b.data - 0.001 * b.grad.data if (e + 1) % 20 == 0: print('epoch {}, Loss: {:.5f}'.format(e+1, loss.item())) # 畫出更新之後的結果 y_pred = multi_linear(x_train) plt.plot(x_train.data.numpy()[:, 0], y_pred.data.numpy(), label='fitting curve', color='r') plt.plot(x_train.data.numpy()[:, 0], y_sample, label='real curve', color='b') plt.legend() plt.show() plt.close()