spark 決策樹分類 DecisionTreeClassifier
決策樹分類是一個非概率模型,測試資料集用的是網上公開的泰坦尼克號乘客資料,用決策樹DecisionTreeClassifier的資料探勘演算法來通過三個引數,Pclass,Sex,Age,三個引數來預測乘客的獲救率。
pom.xml
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.penngo.spark.ml</groupId> <artifactId>sparkml</artifactId> <packaging>jar</packaging> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <name>sparkml</name> <url>http://maven.apache.org</url> <properties> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> <project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding> <java.version>1.8</java.version> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>3.8.1</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.spark</groupId> <artifactId>spark-core_2.11</artifactId> <version>2.2.3</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.spark</groupId> <artifactId>spark-sql_2.11</artifactId> <version>2.2.3</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.spark</groupId> <artifactId>spark-mllib_2.11</artifactId> <version>2.2.3</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.spark</groupId> <artifactId>spark-streaming_2.11</artifactId> <version>2.2.3</version> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId> <version>3.7.0</version> <configuration> <source>1.8</source> <target>1.8</target> <encoding>UTF-8</encoding> </configuration> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project>
DecisionTreeClassification.java
package com.penngo.spark.ml.main; import org.apache.log4j.Logger; import org.apache.spark.ml.Pipeline; import org.apache.spark.ml.PipelineModel; import org.apache.spark.ml.PipelineStage; import org.apache.spark.ml.classification.DecisionTreeClassificationModel; import org.apache.spark.ml.classification.DecisionTreeClassifier; import org.apache.spark.ml.evaluation.MulticlassClassificationEvaluator; import org.apache.spark.ml.feature.*; import org.apache.spark.sql.Dataset; import org.apache.spark.sql.Row; import org.apache.spark.sql.SparkSession; import java.io.File; import org.apache.spark.sql.functions; import static org.apache.spark.sql.types.DataTypes.DoubleType; /** * spark 決策樹分類 DecisionTreeClassifier * */ public class DecisionTreeClassification { private static Logger log = Logger.getLogger(DecisionTreeClassification.class); private static SparkSession spark = null; public static void initSpark(){ if (spark == null) { String os = System.getProperty("os.name").toLowerCase(); // linux上執行 if(os.indexOf("windows") == -1){ spark = SparkSession .builder() .appName("DecisionTreeClassification") .getOrCreate(); } // window上執行,本機除錯 else{ System.setProperty("hadoop.home.dir", "D:/hadoop/hadoop-2.7.6"); System.setProperty("HADOOP_USER_NAME", "hadoop"); spark = SparkSession .builder() .appName("DecisionTreeClassification" ).master("local[3]") .getOrCreate(); } } log.warn("spark.conf().getAll()=============" + spark.conf().getAll()); } public static void run(){ String dataPath = new File("").getAbsolutePath() + "/data/titanic.txt"; Dataset<Row> data = spark.read().option("header", "true").csv(dataPath); data.show(); //data.describe() //Dataset<Row> datana2 = data.na().fill(ImmutableMap.of("age", "30", "ticket", "1111")); Dataset<Row> meanDataset = data.select(functions.mean("age").as("mage")); Double mage = meanDataset.first().getAs("mage"); // 字串轉換為資料,處理空值 Dataset<Row> data1 = data.select( functions.col("user_id"), functions.col("survived").cast(DoubleType).as("label"), functions.when(functions.col("pclass").equalTo("1st"), 1) .when(functions.col("pclass").equalTo("2nd"), 2) .when(functions.col("pclass").equalTo("3rd"), 3) .cast(DoubleType).as("pclass1"), functions.when(functions.col("age").equalTo("NA"), mage.intValue()).otherwise(functions.col("age")).cast(DoubleType).as("age1"), functions.when(functions.col("sex").equalTo("female"), 0).otherwise(1).as("sex") ); VectorAssembler assembler = new VectorAssembler() .setInputCols(new String[]{"pclass1", "age1", "sex"}) .setOutputCol("features"); Dataset<Row> data2 = assembler.transform(data1); data2.show(); // 索引標籤,將元資料新增到標籤列中 StringIndexerModel labelIndexer = new StringIndexer() .setInputCol("label") .setOutputCol("indexedLabel") .fit(data2); // 自動識別分類的特徵,並對它們進行索引 // 具有大於5個不同的值的特徵被視為連續。 VectorIndexerModel featureIndexer = new VectorIndexer() .setInputCol("features") .setOutputCol("indexedFeatures") //.setMaxCategories(3) .fit(data2); // 將資料分為訓練和測試集(30%進行測試) Dataset<Row>[] splits = data2.randomSplit(new double[]{0.7, 0.3}); Dataset<Row> trainingData = splits[0]; Dataset<Row> testData = splits[1]; // 訓練決策樹模型 DecisionTreeClassifier dt = new DecisionTreeClassifier() .setLabelCol("indexedLabel") .setFeaturesCol("indexedFeatures"); //.setImpurity("entropy") // Gini不純度,entropy熵 //.setMaxBins(100) // 離散化"連續特徵"的最大劃分數 //.setMaxDepth(5) // 樹的最大深度 //.setMinInfoGain(0.01) //一個節點分裂的最小資訊增益,值為[0,1] //.setMinInstancesPerNode(10) //每個節點包含的最小樣本數 //.setSeed(123456) IndexToString labelConverter = new IndexToString() .setInputCol("prediction") .setOutputCol("predictedLabel") .setLabels(labelIndexer.labels()); // Chain indexers and tree in a Pipeline. Pipeline pipeline = new Pipeline() .setStages(new PipelineStage[]{labelIndexer, featureIndexer, dt, labelConverter}); // 訓練模型 PipelineModel model = pipeline.fit(trainingData); // 預測資料 Dataset<Row> predictions = model.transform(testData); predictions.select("user_id", "features", "label", "prediction").show(); //predictions.select("predictedLabel", "label", "features").show(5); // 計算錯誤率 MulticlassClassificationEvaluator evaluator = new MulticlassClassificationEvaluator() .setLabelCol("indexedLabel") .setPredictionCol("prediction") .setMetricName("accuracy"); double accuracy = evaluator.evaluate(predictions); System.out.println("Test Error = " + (1.0 - accuracy)); // 檢視決策樹 DecisionTreeClassificationModel treeModel = (DecisionTreeClassificationModel) (model.stages()[2]); System.out.println("Learned classification tree model:\n" + treeModel.toDebugString()); // $example off$ spark.stop(); } public static void main(String[] args){ initSpark(); run(); } }
基礎資料
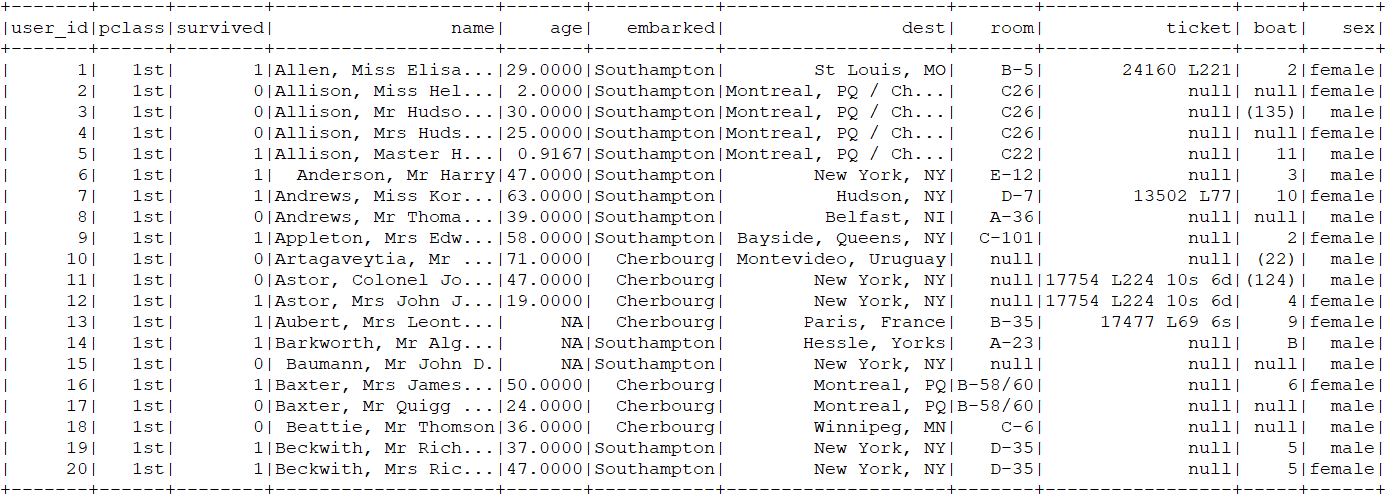
過濾、特徵化後的資料

預測結果
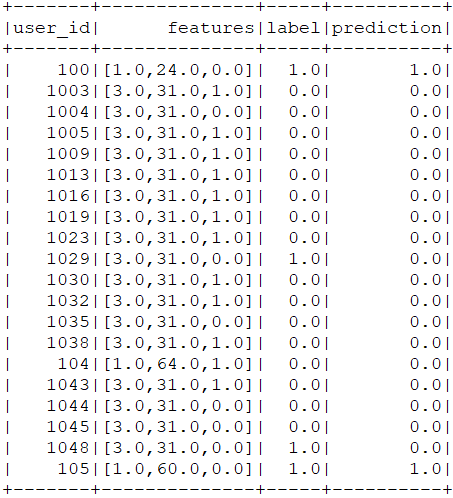
預測錯誤率和預測模型
相關推薦
spark 決策樹分類 DecisionTreeClassifier
浪費了“黃金五年”的Java程式設計師,還有救嗎? >>>
spark廈大---決策樹分類器 -- spark.ml
來源:http://mocom.xmu.edu.cn/article/show/58667ae3aa2c3f280956e7b0/0/1 一、方法簡介 決策樹(decision tree)是一種基本的分類與迴歸方法,這裡主要介紹用於分類的決策樹。決策樹模式呈樹形結
統計學習方法五 決策樹分類
回歸 element row tps 樣本 pan 類別 表示 splay 決策樹分類 1,概念 2,決策樹算法 2.1,特征選擇: 熵:值越大,不確定性因素越大;條件熵:條件對結果的影響不確定性;信息增益;信息增益比
Spark 決策樹--回歸模型
pipe sele nal evaluate 回歸 textfile style mode ssi package Spark_MLlib import org.apache.spark.ml.Pipeline import org.apache.spark.ml.ev
機器學習之路: python 決策樹分類 預測泰坦尼克號乘客是否幸存
現象 info n) 指標 ssi 直觀 learn 保持 afr 使用python3 學習了決策樹分類器的api 涉及到 特征的提取,數據類型保留,分類類型抽取出來新的類型 需要網上下載數據集,我把他們下載到了本地, 可以到我的git下載代碼和數據集: https
R語言學習(三)——決策樹分類
分類 分類(Classification)任務就是通過學習獲得一個目標函式(Target Function)f, 將每個屬性集x對映到一個預先定義好的類標號y。 分類任務的輸入資料是記錄的集合,每條記錄也稱為例項或者樣例。用元組(X,y)表示,其中,X 是屬性集合,y是一個特殊的
sklearn的快速使用之六(決策樹分類)
print(__doc__) import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn.datasets import load_iris from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClas
決策樹分類鳶尾花資料集
import numpy as np import pandas as pd import matplotlib as mpl import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier iris_
sklearn學習筆記之決策樹分類和線性迴歸
decisoin tree: # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import sklearn from sklearn import tree import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn.model_selection impor
Python sklearn庫中決策樹tree.DecisionTreeClassifier()函式引數介紹
max_leaf_nodes:int,None 可選(預設為None) 在最優方法中使用max_leaf_nodes構建一個樹。最好的節點是在雜質相對減少。如果是None則對葉節點的數目沒有限制。如果不是None則不考慮max_depth.class_weight:dict,list of dicts,
決策樹分類器演算法實現
# -*- coding: cp936 -*- #決策樹分類器 my_data=[['slashdot','USA','yes',18,'None'],['google','France','yes',23,'Premium'], ['digg','USA
機器學習演算法(二)——決策樹分類演算法及R語言實現方法
決策樹演算法是分類演算法中最常用的演算法之一。決策樹是一種類似流程圖的樹形結構,可以處理高維資料,直觀易理解,且準確率較高,因此應用廣泛。本篇小博就決策樹的若干演算法:ID3演算法、C4.5演算法以及分類迴歸樹(CART)、C5.0進行對比介紹,並對比C4.5與C5.0處理
決策樹分類鳶尾花資料demo
code:import numpy as np import pandas as pd import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import matplotlib as mpl from sklearn import tree from sklearn
使用R完成決策樹分類
關於決策樹理論方面的介紹,李航的《統計機器學習》第五章有很好的講解。 傳統的ID3和C4.5一般用於分類問題,其中ID3使用資訊增益進行特徵選擇,即遞迴的選擇分類能力最強的特徵對資料進行分割,C4.5唯一不同的是使用資訊增益比進行特徵選擇。 特徵A對訓練資料D的資訊增益g(
決策樹分類——matlab程式
%% 使用ID3決策樹演算法預測銷量高低 clc; clear ; %% 資料預處理 disp('正在進行資料預處理...'); [matrix,attributes_label,attributes] = id3_preprocess(); %% 構造ID3決策樹,其
影像資訊提取之——基於專家知識的決策樹分類
可以將多源資料用於影像分類當中,這就是專家知識的決策樹分類器,本專題以ENVI中Decision Tree為例來敘述這一分類器。 本專題包括以下內容: 專家知識分類器概述 知識(規則)定義 ENVI中Decision Tree的使用 概述 基於知識的決策樹分
決策樹分類器(ID3、C4.5 Java實現)
分類 什麼是分類?舉個例子,銀行貸款員需要分析資料,以便搞清楚哪些是貸款申請者是值得信賴的。通訊公司也希望能分清楚哪些客戶容易接受某一套餐,從而定向營銷。資料分類一般又包括學習階段(構建分類器)和分類階段(使用模型預測給定資料的類標號)。 決策樹分類器
[Java][機器學習]用決策樹分類演算法對Iris花資料集進行處理
Iris Data Set是很經典的一個數據集,在很多地方都能看到,一般用於教學分類演算法。這個資料集在UCI Machine Learning Repository裡可以找到(還是下載量排第一的資料喲)。這個資料集裡面,每個資料都包含4個值(sepal len
python實現決策樹分類(三)
在上一篇文章中,我們已經構建了決策樹,接下來可以使用它用於實際的資料分類。在執行資料分類時,需要決策時以及標籤向量。程式比較測試資料和決策樹上的數值,遞迴執行直到進入葉子節點。 這篇文章主要使用決策樹分類器就行分類,資料集採用UCI資料庫中的紅酒,白酒資料,主要特徵包括12
Spark2 機器學習之決策樹分類Decision tree classifier
show(10,truncate=false) +-------+------+----+------------+--------+-------------+---------+----------+------+ |affairs|gender|age |yearsmarried|children|re

