自定義view(三) 貝塞爾曲線 水波紋效果實現
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-12-21
在上面的部落格中說了path的繪製,path繪製, 介紹了除了貝塞爾曲線的其他情況。 在這裡單獨介紹一下貝塞爾曲線。貝塞爾曲線是應用於二維圖形應用程式的數學曲線。一般的向量圖形軟體通過它來精確畫出曲線,貝塞爾曲線由線段與節點組成,節點是可拖動的支點,線段像可伸縮的皮筋,我們在繪圖工具上看到的鋼筆工具就是來做這種向量曲線的。貝塞爾曲線是計算機圖形學中相當重要的引數曲線。 我們再開發中很多都會用到貝塞爾曲線的情況,比如水波紋效果。貝塞爾曲線掃盲貼這一片部落格很形象的把它的原理解釋了一下。看完這個我們可以比較明白的看出。貝塞爾曲線就是兩個固定點確定的情況下,根據一個或者多個控制點通過計算得到的曲線。
-
api分析

這是貝塞爾曲線的數學解釋,我們再實現對path繪製的時候,的確不需要知道這個。只要知道大致的形式就行,但是對於後期瞭解屬性動畫之後,就有意義了。很多時候都是需要用到這個公式。比如經常出現的直播間花束心形點贊效果,那些心形的移動路線就是按照貝塞爾曲線繪製。
我們通過官方文件來看,關於二次,三次貝塞爾曲線的情況:
/** 從註釋中可以看出,x1,y1,就是控制點的座標,x2,y2就是最後固定點的座標。 * Add a quadratic bezier from the last point, approaching control point * (x1,y1), and ending at (x2,y2). If no moveTo() call has been made for * this contour, the first point is automatically set to (0,0). * * @param x1 The x-coordinate of the control point on a quadratic curve * @param y1 The y-coordinate of the control point on a quadratic curve * @param x2 The x-coordinate of the end point on a quadratic curve * @param y2 The y-coordinate of the end point on a quadratic curve */ public void quadTo(float x1, float y1, float x2, float y2) { isSimplePath = false; nQuadTo(mNativePath, x1, y1, x2, y2); } /** x1,y1,x2,y2就是控制點的座標,x3,y3就是末尾固定點的座標 * Add a cubic bezier from the last point, approaching control points * (x1,y1) and (x2,y2), and ending at (x3,y3). If no moveTo() call has been * made for this contour, the first point is automatically set to (0,0). * * @param x1 The x-coordinate of the 1st control point on a cubic curve * @param y1 The y-coordinate of the 1st control point on a cubic curve * @param x2 The x-coordinate of the 2nd control point on a cubic curve * @param y2 The y-coordinate of the 2nd control point on a cubic curve * @param x3 The x-coordinate of the end point on a cubic curve * @param y3 The y-coordinate of the end point on a cubic curve */ public void cubicTo(float x1, float y1, float x2, float y2, float x3, float y3) { isSimplePath = false; nCubicTo(mNativePath, x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3); }
我們可以可以做一個例子,通過控制控制點的座標,來看看貝塞爾曲線的情況 。
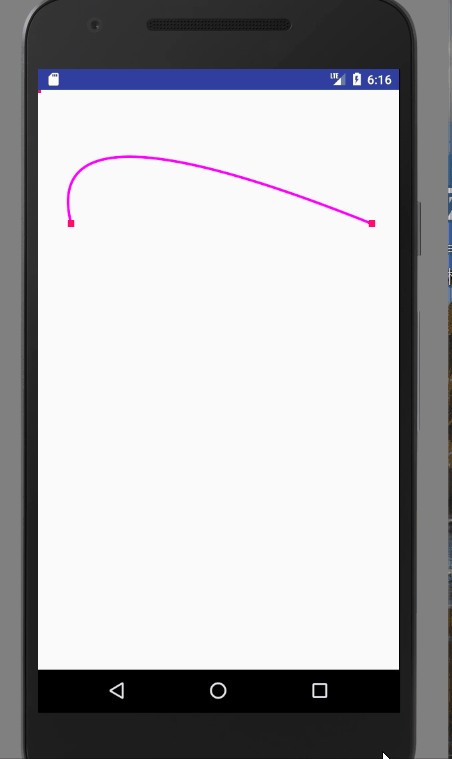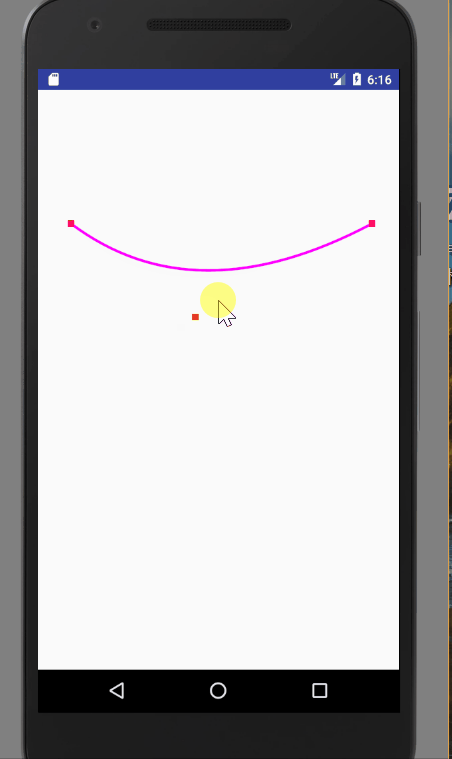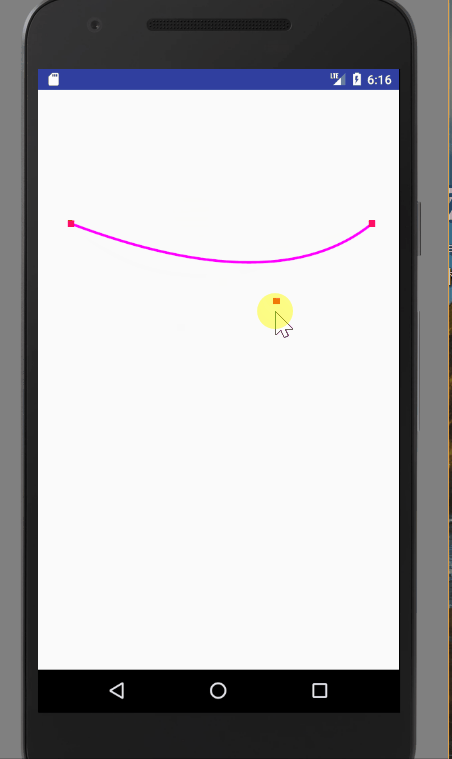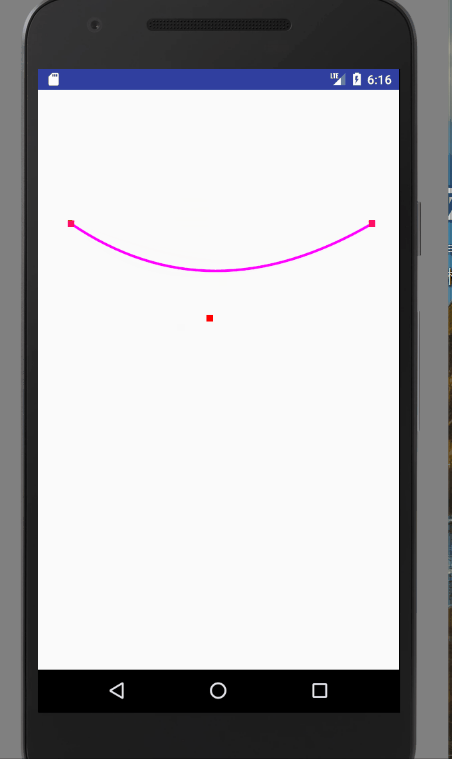
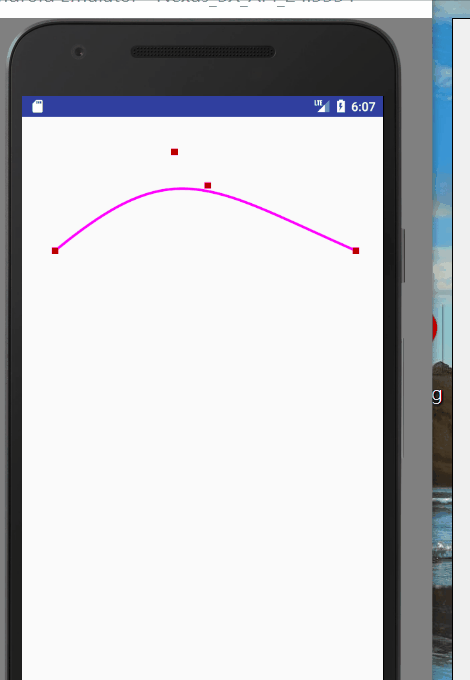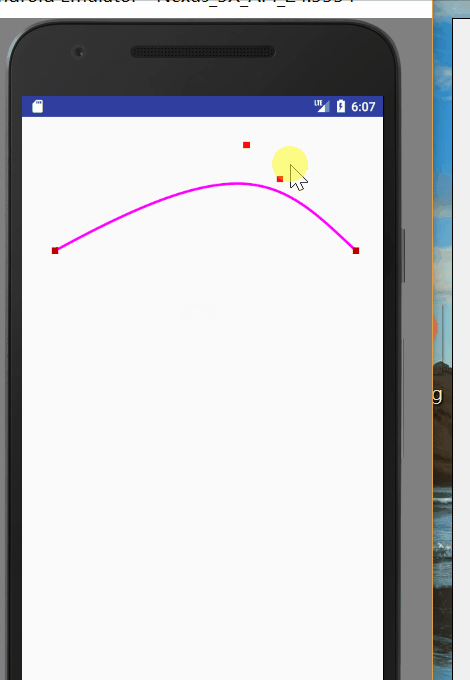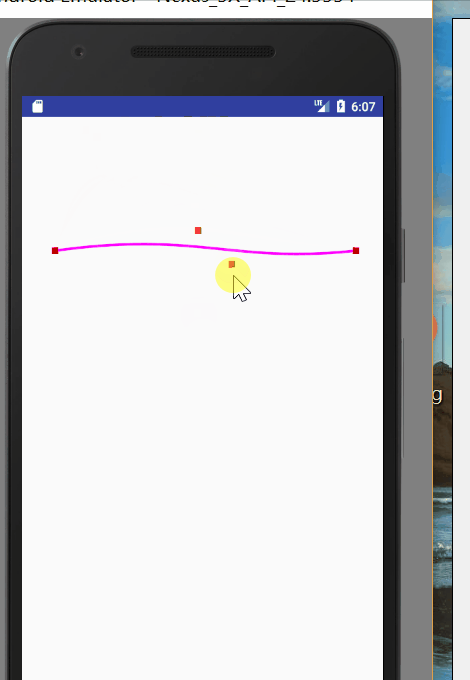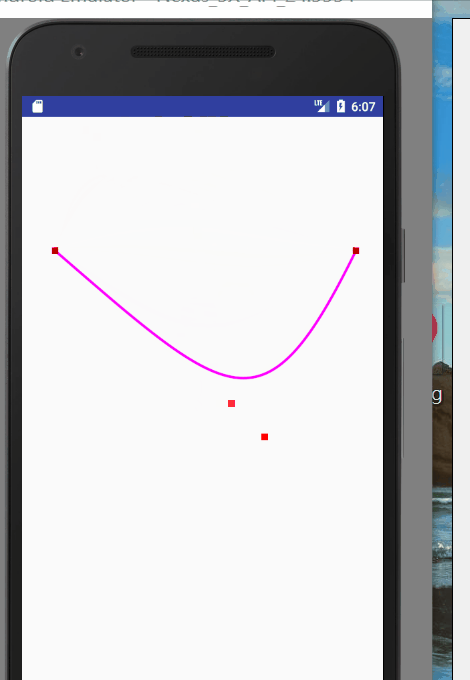
圖一就是quadTo的應用,圖二就是cubicTo的應用。我們可以通過改變控制點的座標,來改變曲線的樣式。程式碼如下:
@Override public void onDraw(Canvas canvas) { super.onDraw(canvas); mPath.reset(); mPaint.setStrokeWidth(8); mPaint.setColor(Color.parseColor("#ff00ff")); mPath.moveTo(100,400); mPath.quadTo(mControlPoint.x,mControlPoint.y,1000,400); canvas.drawPath(mPath,mPaint); mPaint.setColor(Color.RED); mPaint.setStrokeWidth(20); canvas.drawPoint(100,400,mPaint); canvas.drawPoint(1000,400,mPaint); canvas.drawPoint(mControlPoint.x,mControlPoint.y,mPaint); } @Override public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) { //通過移動改變控制點的座標,然後重繪,改變貝塞爾曲線的狀態 mControlPoint.set((int) event.getX(), (int) event.getY()); invalidate(); return true; }
-
水波紋效果
我們可以想象水波紋其實就可以看做是兩個曲線相互交叉的效果,比如下圖所示:

其實這就相當於一個向左移動和一個向右移動的兩個曲線,然後和一個圓形相交的部分。 其實繪製所需要的特殊view。就是想它一步步分解的過程,分解成最基本的可以直接通過api繪畫的模組。
public class BezierView extends View {
private static final String TAG = ViewPath.class.getSimpleName();
private ValueAnimator mAnimator;
private int currentValue;
private int xOffset;
Paint mPaint;
Point mCenterPoint;
Path mPath;
private int windowWidth;
Path mRightPath;
Path mDesPath;
public BezierView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
init();
}
private void init() {
mPaint = new Paint();
//抗鋸齒
mPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
mPaint.setStrokeWidth(8);
// mPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
mCenterPoint = new Point();
mCenterPoint.set(500, 100);
mPath = new Path();
mRightPath = new Path();
mDesPath = new Path();
}
@Override
public void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
//獲取螢幕寬度
windowWidth = getWidth();
drawRightWave(canvas);
drawLeftWave(canvas);
}
//從右向左移動的曲線
private void drawRightWave(Canvas canvas) {
mRightPath.reset();
mDesPath.reset();
mPaint.setStrokeWidth(5);
mPaint.setColor(Color.parseColor("#7700CDCD"));
mPaint.setAlpha(200);
mPaint.setStrokeWidth(5);
mPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
//計算真個向左移動的貝塞爾曲線中需要點的個數,
//因為每個貝塞爾曲線中的兩個固定點之間的間距是300畫素,所以要除以300
//移動的距離這裡取的是螢幕寬度的7倍,以當前可見螢幕為標準,向左,右各擴充套件到3個螢幕寬度
//這個具體的一定距離,可以按需設定,我這裡就直接用了一個比較大的值
int pointNumbers = windowWidth*7/300;
mRightPath.moveTo(windowWidth*4 - xOffset, 400);
//從右向左依次把曲線新增到path中,用rQuadTo是因為他總是以path的最後一個點為原點
for (int i = 0; i < pointNumbers+1; i++) {
if (i % 2 == 0) {
mRightPath.rQuadTo(-150, -50, -300, 0);
} else {
mRightPath.rQuadTo(-150, 50, -300, 0);
}
}
//因為有一個圓形在裡面所以首先要將path形成一個閉環,因為我們在這裡寫死圓的位置
//它是一個以400,400為圓心,300為半徑的圓,所以我們的mRightPath形成的閉環Y軸座標應該是
//700, 以保證和圓的底部相切
mRightPath.lineTo(-(windowWidth*3)-xOffset - 300*(pointNumbers+1),700);
mRightPath.lineTo(windowWidth*4 - xOffset,700);
mRightPath.close();
mDesPath.addCircle(400,400,300, Path.Direction.CW);
//將圓形和曲線取交集
mDesPath.op(mRightPath, Path.Op.INTERSECT);
canvas.drawPath(mDesPath, mPaint);
mPaint.setColor(Color.GREEN);
mPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
canvas.drawCircle(400,400,300,mPaint);
}
//從左向右移動的曲線,這個與從右向左類似
private void drawLeftWave(Canvas canvas) {
mPath.reset();
mPaint.setStrokeWidth(5);
mPaint.setColor(Color.parseColor("#7700F5FF"));
mPaint.setAlpha(200);
mPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
mPath.moveTo(-(windowWidth*3) + xOffset, 400);
int pointNumbers = windowWidth*7/300;
for (int i = 0; i < pointNumbers+1; i++) {
if (i % 2 == 0) {
mPath.rQuadTo(100, -50, 200, 0);
} else {
mPath.rQuadTo(100, 50, 200, 0);
}
}
mPath.lineTo(windowWidth*4 + xOffset,700);
mPath.lineTo(-(windowWidth*3) + xOffset,400);
mDesPath.addCircle(400,400,300, Path.Direction.CW);
mDesPath.op(mPath, Path.Op.INTERSECT);
canvas.drawPath(mDesPath, mPaint);
mPaint.setColor(Color.GREEN);
mPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
canvas.drawCircle(400,400,300,mPaint);
}
//設定移動的動畫,通過valueanimator進行對連個曲線的移動
private void startAnimator(int start, int end, long animTime) {
mAnimator = ValueAnimator.ofInt(start, end);
mAnimator.setDuration(animTime);
mAnimator.setRepeatCount(ValueAnimator.INFINITE);
mAnimator.setRepeatMode(ValueAnimator.RESTART);
mAnimator.setInterpolator(new LinearInterpolator());
mAnimator.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator animation) {
int value = (int) animation.getAnimatedValue();
xOffset = value;
currentValue = (int) (value * 0.6);
invalidate();
}
});
mAnimator.start();
}
public void setCurrentValue(int value, int offset) {
startAnimator(0, offset, 1000*2);
}
}很多進度條需要這樣實現 ,如果是進度條的話,那麼他的變數就是圓的y軸的位置變化,通過移動兩個曲線y軸的座標來實現這個功能。
