P3272 [SCOI2011]地板
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-01-08
\(\color{#0066ff}{ 題目描述 }\)
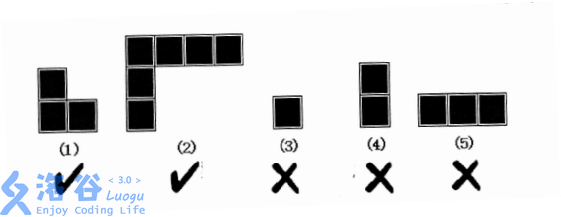
lxhgww的小名叫”小L“,這是因為他總是很喜歡L型的東西。小L家的客廳是一個R*C的矩形,現在他想用L型的地板來鋪滿整個客廳,客廳裡有些位置有柱子,不能鋪地板。現在小L想知道,用L型的地板鋪滿整個客廳有多少種不同的方案?需要注意的是,如下圖所示,L型地板的兩端長度可以任意變化,但不能長度為0。
鋪設完成後,客廳裡面所有沒有柱子的地方都必須鋪上地板,但同一個地方不能被鋪多次。
\(\color{#0066ff}{輸入格式}\)
輸入的第一行包含兩個整數,R和C,表示客廳的大小。接著是R行,每行C個字元。'_'表示對應的位置是空的,必須鋪地板;'*'表示對應的位置有柱子,不能鋪地板。
\(\color{#0066ff}{輸出格式}\)
輸出包含q行,第i行為m[i]個整數,該行的第j(j=1,2...,,m[i])個數表示第i年被授權的聚居地h[j]的臨時議事處管理的種族個數。
\(\color{#0066ff}{輸入樣例}\)
3 3
___
_*_
___\(\color{#0066ff}{輸出樣例}\)
8\(\color{#0066ff}{資料範圍與提示}\)
測試點編號 資料範圍 1,2 R*C<=25 3-5 R*C<=100並且(R=2或者C=2) 6-10 R*C<=100
\(\color{#0066ff}{ 題解 }\)
一道不錯的插頭DP
情況要考慮全面
考慮插頭,0:無,1:未拐彎插頭,2:已拐彎插頭(題中要求必須是拐彎的磚)
套板子就行啦
再次宣告,我TM就不寫hash表,暴力卡常開\(O2\),980ms卡過去!!!
// luogu-judger-enable-o2 #include<bits/stdc++.h> #define LL long long LL in() { char ch; LL x = 0, f = 1; while(!isdigit(ch = getchar()))(ch == '-') && (f = -f); for(x = ch ^ 48; isdigit(ch = getchar()); x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (ch ^ 48)); return x * f; } std::unordered_map<int, int> f[2]; int n, m, s, t; bool mp[120][120]; char getch() { char ch = getchar(); while(ch != '*' && ch != '_') ch = getchar(); return ch; } void init() { n = in(), m = in(); static bool cp[120][120]; for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++) cp[i][j] = getch() == '_'; if(m > n) { std::swap(n, m); for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++) { mp[i][j] = cp[j][i]; if(mp[i][j]) s = i, t = j; } } else { for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++) { mp[i][j] = cp[i][j]; if(mp[i][j]) s = i, t = j; } } } const int mod = 20110520; int pos(int v, int x) { return (v << (x << 1LL)); } void ins(int &x, int y) { x %= mod, (x += y) %= mod; } int work() { int now = 0, nxt = 1; int ans = 0; f[now][0] = 1; int U = (1 << ((m + 1) << 1)) - 1; for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++) { f[nxt].clear(); for(auto &k:f[now]) { int S = k.first, val = k.second; int L = (S >> ((j - 1) << 1)) & 3, R = (S >> (j << 1)) & 3; if(!mp[i][j]) { if(!L && !R) ins(f[nxt][S], val); continue; } if(!L && !R) { //right 1 if(mp[i][j + 1]) ins(f[nxt][S ^ pos(1, j)], val); //down 1 if(mp[i + 1][j]) ins(f[nxt][S ^ pos(1, j - 1)], val); //middle double 2 if(mp[i][j + 1] && mp[i + 1][j]) ins(f[nxt][S ^ pos(2, j - 1) ^ pos(2, j)], val); } //要麼直走還是1,要麼拐彎變成2 else if(L == 0 && R == 1) { if(mp[i + 1][j]) ins(f[nxt][S ^ pos(1, j - 1) ^ pos(1, j)], val); if(mp[i][j + 1]) ins(f[nxt][S ^ pos(1, j) ^ pos(2, j)], val); } //要麼直走還是2,要麼停下變成0 else if(L == 0 && R == 2) { if(mp[i + 1][j]) ins(f[nxt][S ^ pos(2, j - 1) ^ pos(2, j)], val); ins(f[nxt][S ^ pos(2, j)], val); } //跟上面差不多 else if(L == 1 && R == 0) { if(mp[i][j + 1]) ins(f[nxt][S ^ pos(1, j - 1) ^ pos(1, j)], val); if(mp[i + 1][j]) ins(f[nxt][S ^ pos(1, j - 1) ^ pos(2, j - 1)], val); } else if(L == 2 && R == 0) { if(mp[i][j + 1]) ins(f[nxt][S ^ pos(2, j - 1) ^ pos(2, j)], val); ins(f[nxt][S ^ pos(2, j - 1)], val); } //必須拼上,沒有其他情況 else if(L == 1 && R == 1) { ins(f[nxt][S ^ pos(1, j - 1) ^ pos(1, j)], val); } //這些情況都是不成立的 else if(L == 1 && R == 2) {} else if(L == 2 && R == 1) {} else if(L == 2 && R == 2) {} if(i == s && j == t) { //1 1 // 0 2 // 2 0 第一個是接上,後兩個是直接停下,都可以收集ans if(L + R == 2) ins(ans, val); } } std::swap(now, nxt); } f[nxt].clear(); for(auto &k:f[now]) ins(f[nxt][(k.first << 2) & U], k.second); std::swap(nxt, now); } return ans; } int main() { init(); printf("%d\n", work() % mod); return 0; }
