bias & variance 以及 Mean squared error
標籤: machine_learning
bias & variance
Estimator(估計量): a function of the data that is used to infer the value of an unknown parameter in a statistical model,can be writed like
Estimand:The parameter being estimated,like
Estimate: a particular realization of this random variable
Bias: The bias of
Variance(方差)
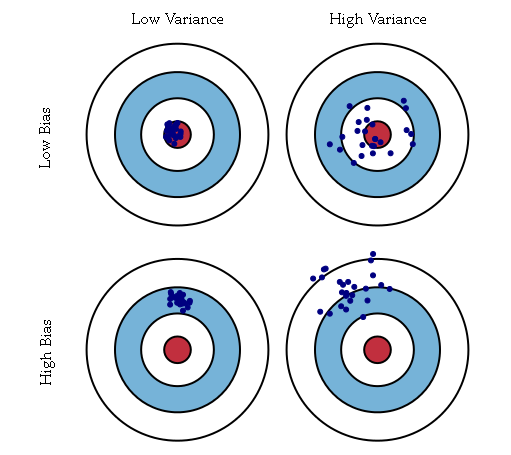
The relationship between bias and variance is analogous to the relationship between accuracy and precision.
從以上描述可以看出,bias表示預測值的均值與實際值的差值;而variance表示預測結果作為一個隨機變數時的方差,其描述中類比靶心的例子較為明瞭。http://blog.csdn.net/ywl22/article/details/8606166。
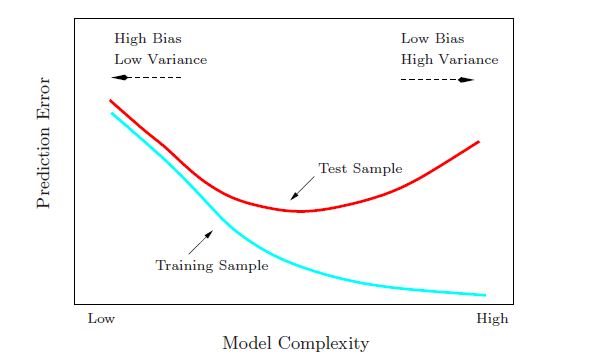
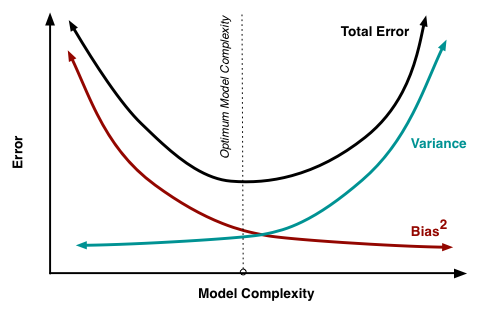
Bias、variance與複雜度的關係
note:the sample mean
樣本均值是總體均值的無偏估計,而樣本方差卻不是總體方差的無偏估計,其小於總體方差。
Mean squared error
In statistics, the mean squared error (MSE) of an estimator measures the average of the squares of the “errors”, that is, the difference between the estimator and what is estimated.MSE is a risk function, corresponding to the expected value of the squared error loss or quadratic loss.(損失函式or代價函式?)
proof
ps:
In statistics, the bias (or bias function) of an estimator is the difference between this estimator’s expected value and the true value of the parameter being estimated. An estimator or decision rule with zero bias is called unbiased. Otherwise the estimator is said to be biased.

